版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,欢迎大家转载,但是要注明我的文章地址。 https://blog.csdn.net/program_developer/article/details/82925265
题目链接:
题目描述:
解题思路:
(1)方法一:
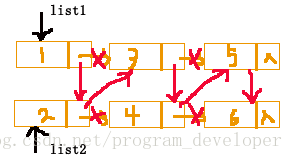
修改两个待合并链表的引用域,使它们称为一个有序的链表list3。具体思路如下图所示:
已经AC的代码:
public class MergeLinkedList {
// 定义结点
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
// 创建链表
public ListNode currentNode = null;
ListNode head_cre = null;
public ListNode createList(int val) {
if (head_cre == null) {
head_cre = new ListNode(val);
currentNode = head_cre;
} else {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
currentNode.next = temp;
currentNode = temp;
}
return head_cre;
}
// 合并两个有序链表
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode pc = null; // 用于记录当前链表的结点
ListNode list3 = null; // 需要返回的链表头引用
if (list1 == null)
return list2;
if (list2 == null)
return list1;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
if (pc == null) {
pc = list1;
list3 = pc;
} else {
pc.next = list1;
pc = list1;
}
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
if (pc == null) {
pc = list2;
list3 = pc;
} else {
pc.next = list2;
pc = list2;
}
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if (list1 == null) {
pc.next = list2;
} else {
pc.next = list1;
}
return list3;
}
// 方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历
ListNode current = null;
public void print(ListNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
current = node;
while (current != null) {
System.out.println(current.val);
current = current.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
MergeLinkedList mg = new MergeLinkedList();
ListNode list1 = null;
ListNode list2 = null;
ListNode list3 = null;
// 测试用例
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i += 2) {
list1 = mg.createList(i);
}
mg.head_cre = null;
mg.currentNode = null;
for (int i = 2; i <= 6; i += 2) {
list2 = mg.createList(i);
}
// 合并两个有序链表
list3 = mg.Merge(list1, list2);
// 打印出合并后的新链表
mg.print(list3);
}
}(2)方法二:递归法
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
ListNode pc = null;
if(list1 == null) {
return list2;
}else if(list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
if(list1.val <= list2.val) {
pc = list1;
pc.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
}else {
pc = list2;
pc.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
}
return pc;
}