版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/github_39611196/article/details/82844473
Gan的全称是Generative Adveratial Nets,生成对抗网络。
Generator采用随机数生成有意义的数据,Discriminator学习判定哪些是真实数据哪些是生成数据,并反向传递到Generator。
生成对抗网络接收一些信息,生成有意义的物体。
下面是示例代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.autograd import Variable
# 超参数
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR_G = 0.0001 # learning rate for generator
LR_D = 0.0001 # learning rate for discriminator
N_IDEAS = 5 # think of this as number of ideas for generating an art work(Generator)
ART_COMPONETS = 15 # it could be total point G can draw in the canvas
PAINT_POINTS = np.vstack([np.linspace(-1, 1, ART_COMPONETS) for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE)])
# show paiting range
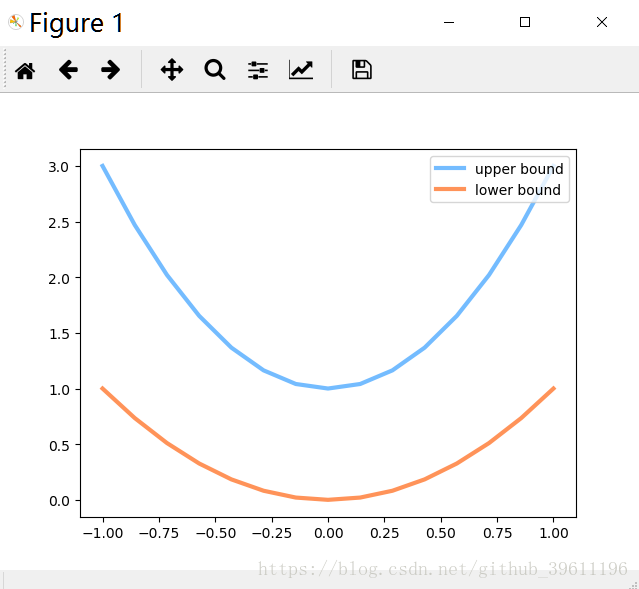
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
# plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
# plt.legend(loc='upper right')
# plt.show()
def artist_works():
a = np.random.uniform(1, 2, size=BATCH_SIZE)[:, np.newaxis]
painting = a * np.power(PAINT_POINTS, 2) + (a - 1)
painting = torch.from_numpy(painting).float()
return Variable(painting)
G = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(N_IDEAS, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, ART_COMPONETS)
)
D = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(ART_COMPONETS, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
opt_D = torch.optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=LR_D)
opt_G = torch.optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=LR_G)
plt.ion()
for step in range(10000):
artist_paintings = artist_works()
G_ideas = Variable(torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, N_IDEAS))
G_paintings = G(G_ideas)
prob_artist0 = D(artist_paintings)
prob_artist1 = D(G_paintings)
D_loss = - torch.mean(torch.log(prob_artist0) + torch.log(1 - prob_artist1))
G_Loss = torch.mean(torch.log(1-prob_artist1))
opt_D.zero_grad()
D_loss.backward(retain_variables=True)
opt_D.step()
opt_G.zero_grad()
G_Loss.backward()
opt_G.step()
if step % 50 == 0: # plotting
plt.cla()
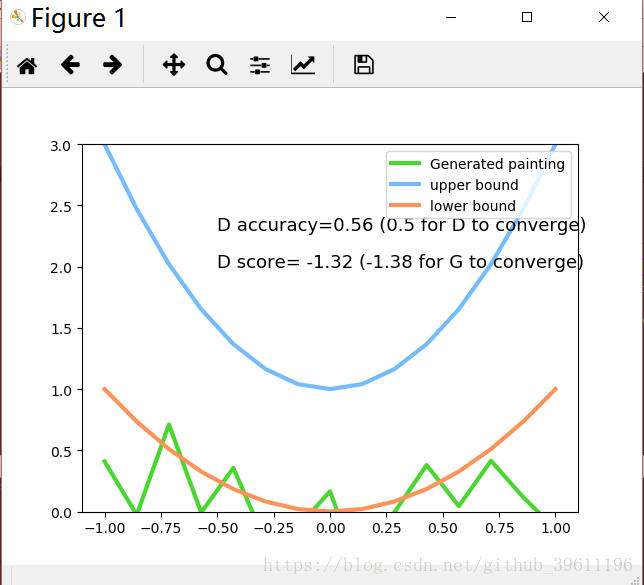
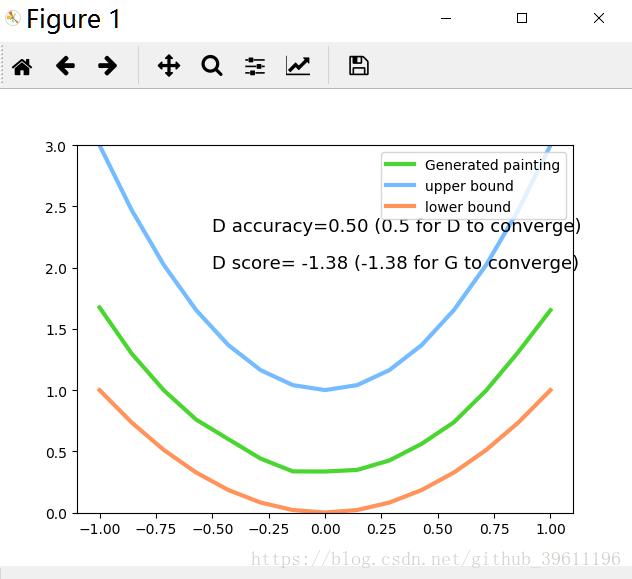
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], G_paintings.data.numpy()[0], c='#4AD631', lw=3, label='Generated painting', )
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 1, c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='upper bound')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0], 1 * np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0], 2) + 0, c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='lower bound')
plt.text(-.5, 2.3, 'D accuracy=%.2f (0.5 for D to converge)' % prob_artist0.data.numpy().mean(),
fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.text(-.5, 2, 'D score= %.2f (-1.38 for G to converge)' % -D_loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 13})
plt.ylim((0, 3));
plt.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10);
plt.draw();
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
数据:
结果: