一个类里面包含另外一个类,构造函数调用的先后关系。
1)A类的对象是B类的私有成员:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int mInt;
A()
{
cout<< "in A Default Constructor:mInt = " << mInt<< endl;
mInt = 0;
}
void setIntVal(int mSet)
{
cout<< "in setIntVal:mInt = " << mInt<<"mSet="<< mSet<< endl;
if (mInt< mSet)
{
mInt= mSet;
}
}
};
class B{
private:
int b;
A aObj; //A类的对象
public:
B()
{
cout<< "in B Default Constructor"<< endl;
b = 10;
aObj.setIntVal(20);
}
};
int main()
{
B * pB = new B();
delete pB;
return 0;
}
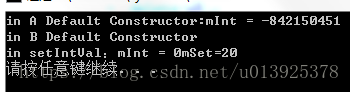
执行结果:
在主函数中new B的时候,先调用A的构造函数,再调用B的构造函数。
2)指向A类对象的指针是B类的私有成员:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int mInt;
A()
{
cout<< "in A Default Constructor:mInt = " << mInt<< endl;
mInt = 0;
}
void setIntVal(int mSet)
{
cout<< "in setIntVal:mInt = " << mInt<<"mSet="<< mSet<< endl;
if (mInt< mSet)
{
mInt= mSet;
}
}
};
class B{
private:
int b;
A *pA; //指向A类对象的指针
public:
B()
{
cout<< "in B Default Constructor"<< endl;
b = 10;
pA = new A();
pA->setIntVal(15);
}
};
int main()
{
B * pB = new B();
delete pB;
return 0;
}
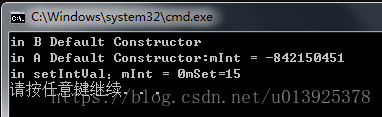
执行结果:
在主函数中new B的时候,先调用B的构造函数,B的构造函数中有new A的操作,则调用A的构造函数。