转载注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/dmk877/article/details/49632959
话说一个乞丐在看一个程序员写程序,程序员遇到一个问题怎么都解决不了,这时乞丐说这少个分号,程序员照做结果问题解决了,就问:你怎么知道?乞丐笑笑说:我之前就是干这个的。通过这个笑话我们学到了不会唱歌的主播不是好司机,那么问题来了今天我们要学习什么呢?
通过本篇博客你将学到
①自定义控件中onLayout的源码分析
②getLeft,getRight,getWidth,getHeight表示的意义
③一个例子来理解自定义控件的onLayout的过程
④getMeasureWidth和getWidth的区别
如有谬误欢迎批评指正,如有疑问欢迎留言,谢谢
1.简单回顾
在上一篇我们详细讲解了onMeasure方法,我们首先来回顾一下上一篇的内容如果你还没有阅读请先阅读(Android开发之自定义控件(一)---onMeasure详解),上一篇我们说到onMeasure的过程,在onMeasure方法中最终调用setMeasuredDimension方法来确定控件的大小,假如是自定义一个View的话,测量一下其大小就行了,如果是ViewGroup呢,则需要遍历其所有的子View来,并为每个子View测量它的大小。在测量子View时需要两个参数,measureWidth和measureHeight这两个值是根布局传过来的,也就是说是父View和子View本身共同决定子View的大小。
2.源码分析
今天呢,就和大家一起来探讨自定义控件的第二步onLayout即确定控件的位置,上篇文章我们说到performTraversals方法中会调用host.measure方法,在调用完host.measure方法后,就会调用host.layout对View进行定位,这也是今天我们要讨论的内容。
首先我们来看看layout的源码
public final void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
boolean changed = setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) {
ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.ON_LAYOUT);
}
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~FORCE_LAYOUT;
}在其中调用了setFrame方法的源码如下
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
。。。省略部分代码。。。
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
。。。省略部分代码。。。
}
return changed;
}在setFrame方法中将left,top,right,bottom这四个值保存下来。也就是说在layout中的setFrame方法中会将子View相对于父View的左,上,右,下这四个值保存下来,这四个值就会确定子View在父View中的位置。仔细的看layout方法的源码你会发现和measure方法一样在layout中调用了onLayout方法,赶紧先去看看View的onLayout的逻辑
View——onLayout
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}啊?啥都没有,你这是弄啥嘞?其实仔细想想你就会理解,因为onLayout的目的是确定子View在父View中的位置,那么这个步骤肯定是由父View来决定的,因此在View中onLayout是一个空的实现,既然如此我们就去看看ViewGroup的onLayout的源码呗。
ViewGroup——onLayout
@Override
protected abstract void onLayout(boolean changed,
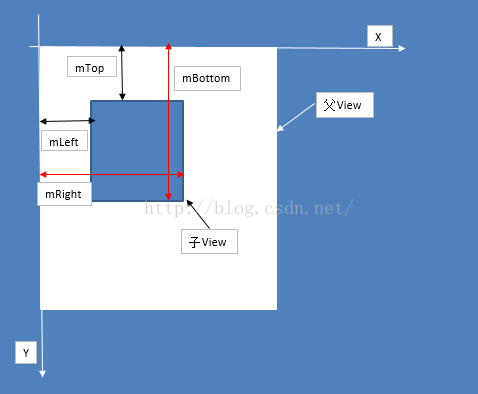
int l, int t, int r, int b);我们看到它是一个抽象的方法,我们都知道当继承一个类时必须实现其中的抽象方法,这也就是说在自定义ViewGroup时我们必须实现onLayout方法。在上一篇我们就说过onLayout的作用就是确定子View的位置,那么它是怎样确定子View的位置的呢?其实它是通过四个参数 l,t,r,b即代表距离父View的左上右下的距离,看张图你就会明白它的含义
mLeft,mTop,mRight,mBottom的讲解
mLeft——View.getLeft():子View的左边界到父View的左边界的距离
// 获取子View的左边界到父View的左边界的距离
public final int getLeft() {
return mLeft;
}mTop——View.getTop():子View的顶部到父View顶部的距离
mRight——View.getRight():子View的右边界到父View的左边界的距离
mBottom——View.getBottom():子View的底部到父View的顶部的距离
它们在源码中的表现如下
/**
* Top position of this view relative to its parent.
*
* @return The top of this view, in pixels.
*/
// 获取子View的顶部到父View顶部的距离
public final int getTop() {
return mTop;
}
// 获取子View的底部到父View的顶部的距离
public final int getBottom() {
return mBottom;
}
// 获取子View的左边界到父View的左边界的距离
public final int getLeft() {
return mLeft;
}
// 获取子View的右边界到父View的左边界的距离
public final int getRight() {
return mRight;
}
public final int getWidth() {
return mRight - mLeft;
}
/**
* Return the height of your view.
*
* @return The height of your view, in pixels.
*/
public final int getHeight() {
return mBottom - mTop;
}
/**
* The height of this view as measured in the most recent call to measure().
* This should be used during measurement and layout calculations only. Use
* {@link #getHeight()} to see how tall a view is after layout.
*
* @return The measured height of this view.
*/
// 获取测量的宽度
public final int getMeasuredWidth() {
return mMeasuredWidth;
}
/**
* The width of this view as measured in the most recent call to measure().
* This should be used during measurement and layout calculations only. Use
* {@link #getWidth()} to see how wide a view is after layout.
*
* @return The measured width of this view.
*/
// 获取测量的高度
public final int getMeasuredHeight() {
return mMeasuredHeight;
}①getMeasureWidth()方法在measure()过程结束后就可以获得到它的值,而getWidth()方法要在layout()过程结束后才能获取到。这么说有什么依据?首先看看getMeasureWidth()方法的返回值,它是mMeasureWidth,对于它你熟悉吗?这就是在上篇博客中通过setMeasureDimension()方法设置的值,而getWidth()的返回值是mRight-mLeft,这两个值是在layout()过程中的setFrame方法中才设置的值,也就是说在layout结束后才确定的。
②getMeasureWidth()方法中的值是通过setMeasuredDimension()方法来进行设置的,而getWidth()方法中的值则是通过视图右边的坐标减去左边的坐标计算出来的。关于这两个方法的区别,现在有网上的很多说法是不正确的,我将通过一篇博客来给大家详细的说说这两个值的区别。
3.小例子
接下来通过一个简单的例子来了解下latyout的过程,这个例子是这样的,自定义一个ViewGroup让其子View在屏幕中间位置横向排列,首先我们来谈谈它的思想,我觉得当你在做一件事情的时候一定认真的去分析它的实现过程,按照自己的思想去设计自己的东西,不管可不可行,去尝试即使错了对自己也是一个很好的历练,这样时间长了你会发现你的技术提升了很多
我的思路是这样的
让自定义的ViewGroup的子View在屏幕中间横向排列思路:
①获得屏幕的高度
②获得子View的宽度和高度,通过屏幕的高度和子View的高度来计算layout时子View到父View顶端的距离
③因为子View是横向排列的,所以需要设定一个变量表示子View到父View左边界的距离,每次循环加上子View的宽度来设定下一个子View到父View左侧的距离
先上效果图
就是这么一个效果,接下来看看其代码吧,按照上面我们分析的思路,跟着代码看看吧
package com.example.customviewpractice;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class MyViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
private Context mContext;
private int sreenH;
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mContext = context;
// 获取屏幕的高度
sreenH = getScreenSize(((Activity) mContext))[1];
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, widthMeasureSpec);
// 测量子View
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 获得子View个数
int childCount = getChildCount();
// 设置一个变量保存到父View左侧的距离
int mLeft = 0;
// 遍历子View
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
// 获得子View的高度
int childViewHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
// 获得子View的宽度
int childViewWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
// 让子View在竖直方向上显示在屏幕的中间位置
int height = sreenH / 2 - childViewHeight / 2;
// 调用layout给每一个子View设定位置mLeft,mTop,mRight,mBottom.左上右下
childView.layout(mLeft, height, mLeft + childViewWidth, height
+ childViewHeight);
// 改变下一个子View到父View左侧的距离
mLeft += childViewWidth;
}
}
/**
* 获取屏幕尺寸
*/
public static int[] getScreenSize(Activity activity) {
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
return new int[] { metrics.widthPixels, metrics.heightPixels };
}
}
<com.example.customviewpractice.MyViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试一" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试二" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试三" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="测试四" />
</com.example.customviewpractice.MyViewGroup>运行后就会看到上面的效果图,这里需要注意的是,在这个小例子中我们并没有进行换行处理,这里只是学习下layout的用法,如果需要你掌握了自定义控件的过程,完全可以去自定义一个FlowLayout。
4.总结
到这里关于自定义控件的基础知识onMeasure和onLayout就讲完了,其实刚开始的时候很惧怕这部分的内容,感觉很难,但是沉下心来认真的去学习,认真去屡清思路,你会发现其实并不是特别难,有了上两篇的基础我们就可以去实现一些小的自定义控件了,在进行自定义控件时思路很重要,只有把基础掌握好了,才能按照我们的设计去实现所要实现的效果,学习编程就是这样它需要我们有思想这个思想是靠平时我们不断的积累而产生的。
如果你觉得本篇博客对你有用就顶一下,留个言赞个呗,我绝对不介意,哈哈哈。。。