版权声明:有问题欢迎留言,转载请声明出处 https://blog.csdn.net/larger5/article/details/82826047
一、前言
之前动手写一个功能类似 JPA 的框架:
[自己造轮子] 动手设计实现数据库访问层框架 JPA
功能类似,相当有成就感。
参考了网上很多文章,试着写个 SpringMVC,遇到很多瓶颈,主要问题是 @Autowired 注解,笔者使用了反射赋值,但总是赋值失败(null),就写到这里就结束了。
二、小框架
重点在于 DispatcherServlet ,贴一下代码,其他的,看GitHub。
代码放到了 GitHub 上:https://github.com/larger5/MySpringMVC.git
package servlet;
import annotation.CunAutowired;
import annotation.CunController;
import annotation.CunRequestMapping;
import annotation.CunService;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
/*
覆盖反射常规操作
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/",loadOnStartup = 0)
public class CunDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
// properties 配置
private Properties contextConfig = new Properties();
// 存储全类名,备反射加载到 ioc 中
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>();
// ioc 容器
private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// 保存所有 url 和方法的映射关系
private Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String, Method>();
// method.invoke 时用到
private Map<String, Object> controllerMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//处理请求
doDispatcher(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>500!! Server Exception</h1>");
}
}
// 对 RequestMapping 做出响应
private void doDispatcher(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// ①request.getRequestURL() 返回全路径、②request.getRequestURI() 返回除去host(域名或者ip)部分的路径
String url = req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
// 去掉多个 /
url = url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/");
if (!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)) {
try {
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>url:" + url + " --> 404" + "</h1>");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
try {
Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(url);
resp.getWriter().write("<h1>" + url + "</h1");
Object o = this.controllerMap.get(url);
System.out.println(o.getClass().getName());
try {
// 反射调用方法格式:方法名.invoke(类名,参数)
method.invoke(this.controllerMap.get(url));
System.out.println(ioc);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
// 1、加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
// 2、扫描配置文件
doSCanner((String) contextConfig.get("scanPackage"));
// 3、实例化
doInstance();
// 4、自动赋值
doAutowired();
// 5、初始化 initHandlerMapping,SpringMVC
initHandlerMapping();
}
// 5、把 @RequestMapping 产生的 url 保存
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CunController.class)) {
continue;
}
String baseUrl = null;
// 先获取类上的 @RequestMapping
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CunRequestMapping.class)) {
CunRequestMapping cunRequestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(CunRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = cunRequestMapping.value();
}
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(CunRequestMapping.class)) {
return;
}
CunRequestMapping cunRequestMapping = method.getAnnotation(CunRequestMapping.class);
String url = cunRequestMapping.value();
// 防止用户设置 url 多个 /
url = (baseUrl + "/" + url).replaceAll("/+", "/");
this.handlerMapping.put(url, method);
try {
this.controllerMap.put(url, clazz.newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 4、对@Autowired 的对象,赋予 IOC 容器中的对象
private void doAutowired() {
System.out.println(ioc);
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
/*
getFields()只能获取public的字段,包括父类中的字段
getDeclaredFields()只能获取自己声明的各种字段,包括public,protected,private,但是不包括父类的申明字段
返回的都是Field对象:获取名称直接field.getName()、属性值则是field.get(Object)、field.set(obj,value)
field.getModifiers() 获取字段的修饰符
*/
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
// 加了 @Autowired 的
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(CunAutowired.class)) {
continue;
}
CunAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(CunAutowired.class);
String beanName = autowired.value().trim();
// 是否 @Autowired 里边 value 有自定义值,即 bean 名
if (beanName.equals("")) {
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
// 授权访问,就是当字段修饰符为private时,我们需要加上
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
System.out.println("field.getName():" + field.getName());
System.out.println("ioc:" + ioc);
System.out.println("beanName:" + beanName);
System.out.println("entry.getValue():" + entry.getValue());
System.out.println("ioc.get(beanName):" + ioc.get(beanName));
// 属性.set(类,值)
field.set(entry.getValue(), ioc.get(beanName));
System.out.println("success");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 3.1、只对 @Controller、@Service 类进行实例化对象,放到 IOC 容器中
private void doInstance() {
if (classNames.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// @Controller
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CunController.class)) {
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
// key 在 Spring 中默认是首字母小写的类名
String beanName = instance.getClass().getSimpleName();
// String beanName = LowerFirstCase(instance.getClass().getSimpleName());
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
}
// @Service
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CunService.class)) {
CunService cunService = clazz.getAnnotation(CunService.class);
String beanName = cunService.value();
// 该注解的默认值是 空
if ("".equals(beanName.trim())) {
beanName = clazz.getSimpleName();
// beanName = LowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
// 这里选择同名覆盖,而 Spring 则是报错
Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> i : interfaces) {
// key 为接口名,而 value 为实现类对象
ioc.put(i.getName(), instance);
}
}
continue;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 3.2、首字母小写
private String LowerFirstCase(String simpleName) {
// return simpleName.toLowerCase().substring(0, 1) + simpleName.substring(1);
char[] chars = simpleName.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
// 2、扫描包下的所有类,并将全类名保存
private void doSCanner(String scanPackage) {
// 递归、替换包名中的".",将包结构转换为目录结构
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File classDir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : classDir.listFiles()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
doSCanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
continue;
}
// 注意去掉后缀 .class
String className = scanPackage + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", "");
classNames.add(className);
}
}
// 1、加载配置文件
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭输入流
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
三、测试小框架的 demo
代码已经放到 GitHub 上了:https://github.com/larger5/TestMySpringMVC.git
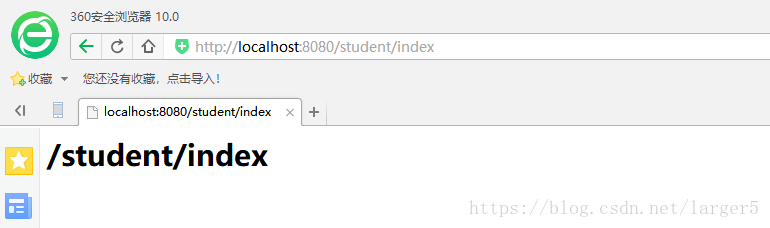
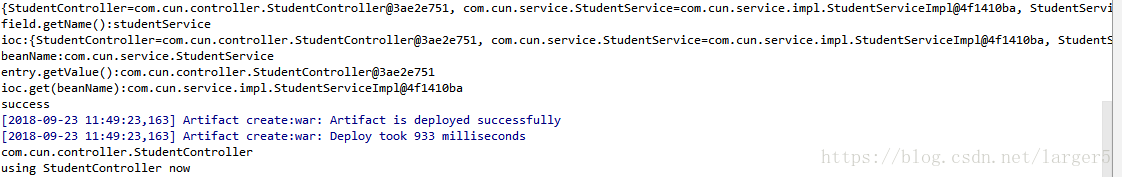
测试效果:
package com.cun.controller;
import annotation.CunAutowired;
import annotation.CunController;
import annotation.CunRequestMapping;
import com.cun.service.StudentService;
@CunController
@CunRequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@CunAutowired
private StudentService studentService;
@CunRequestMapping("/index")
public void index() {
System.out.println("using " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " now");
}
}
① 浏览器访问 url
② console 输出
四、小结
1、通过模仿 SpringMVC 的过程,提高了 Java 反射 API 的熟练度:
一年前只是知道 Java 有反射这回事,而且在众多大咖的赞叹下,略知其挺有逼格的。
现在才真切体会到,反射确实挺有作为,名副其实。
2、看了很多关于 SpringMVC 处理流程文章,还不如自己写个 Hello World 级别 SpringMVC 有印象。