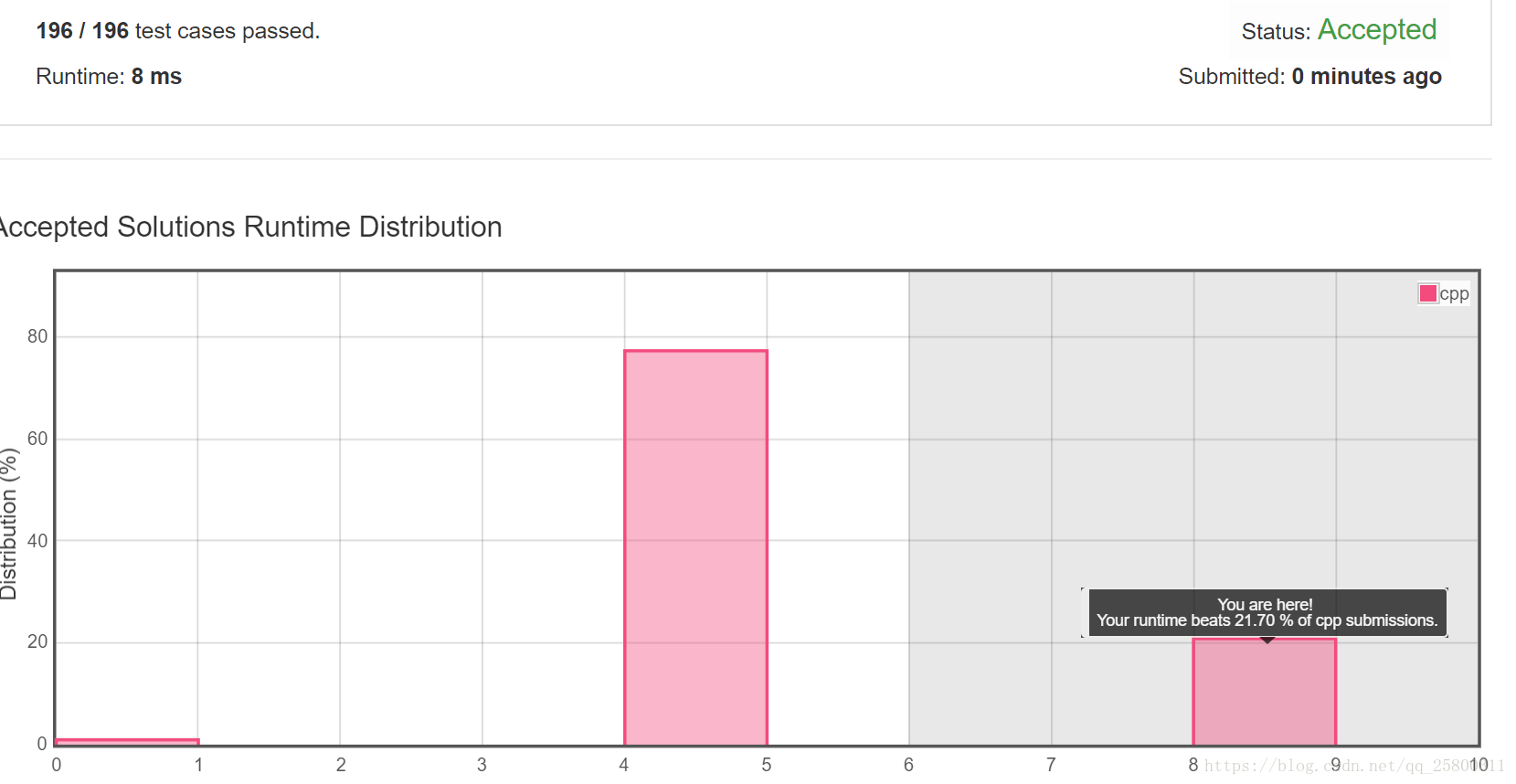
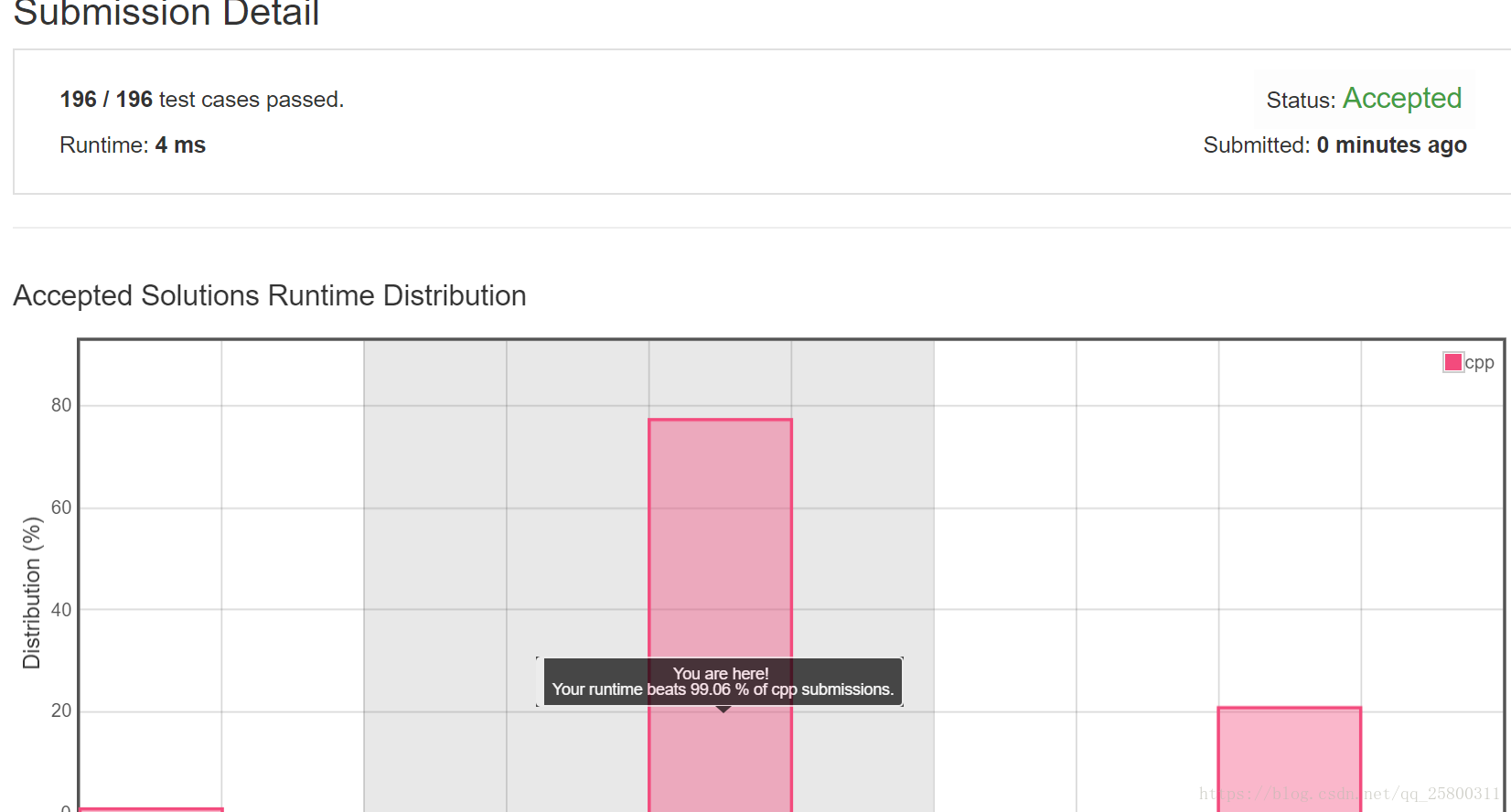
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return -1.
You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: -1方法一:找到升序的前半段和降序的后半段,采用二分查找法(自己想的,其实有点想复杂了)
L_record用来保存升序的前半段的起始为止,R_record用来保存降序的后半段的起始位置。
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1, mid,L_record = 0,R_record = right;
if (nums.size() <= 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (nums[i] == target)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
/*使用(left+right)/2会有整数溢出的问题
(问题会出现在当low+high的结果大于表达式结果类型所能表示的最大值时,
这样,产生溢出后再/2是不会产生正确结果的,而low+((high-low)/2)
不存在这个问题*/
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if ( nums[0] <= nums[mid]) {
if (mid > L_record) {
L_record = mid;
}
left = mid+1;
}
else if ( nums[0] > nums[mid]) {
if (mid < R_record) {
R_record = mid;
}
right = mid-1;
}
}
if (target >= nums[0] && target <= nums[L_record]) {
left = 0;
right = L_record;
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
else if (target >= nums[R_record] && target <= nums[nums.size() - 1]) {
left = R_record;
right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
else {
for (int i = L_record; i <= R_record; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == target)
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};方法二:直接对二分查找进行改进
二分搜索法,如果当前nums[mid] < nums[l],说明mid在旋转节点的右边,那么如果target也在mid和r之间就将l = mid + 1表示在mid + 1到r的区域找,否则将r = mid – 1在l到mid – 1的区域寻找;如果当前nums[mid] > nums[r],说明mid在旋转节点的左边,那么如果target也在l和mid之间就将r = mid – 1,在l~mid-1的区域内寻找,否则在mid+1~r的区域内寻找;否则说明当前区间的顺序是正确的,就判断target和mid的大小关系,如果比mid所指数字大则在右边找,否则在左边找
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
if (target >= nums[left] && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
}
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
else {
if (target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
}
else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
//未找到,返回-1
return -1;
}
};方法三:The -INF and INF method
Explanation
Let's say nums looks like this: [12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
Because it's not fully sorted, we can't do normal binary search. But here comes the trick:
-
If target is let's say 14, then we adjust
numsto this, where "inf" means infinity:
[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf, inf] -
If target is let's say 7, then we adjust
numsto this:
[-inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, -inf, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
And then we can simply do ordinary binary search.
Of course we don't actually adjust the whole array but instead adjust only on the fly only the elements we look at. And the adjustment is done by comparing both the target and the actual element against nums[0].
Code
If nums[mid] and target are "on the same side" of nums[0], we just take nums[mid]. Otherwise we use -infinity or +infinity as needed.
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int lo = 0, hi = nums.size();
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
double num = (nums[mid] < nums[0]) == (target < nums[0])
? nums[mid]
: target < nums[0] ? -INFINITY : INFINITY;
if (num < target)
lo = mid + 1;
else if (num > target)
hi = mid;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}