我的LeetCode代码仓:https://github.com/617076674/LeetCode
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/description/
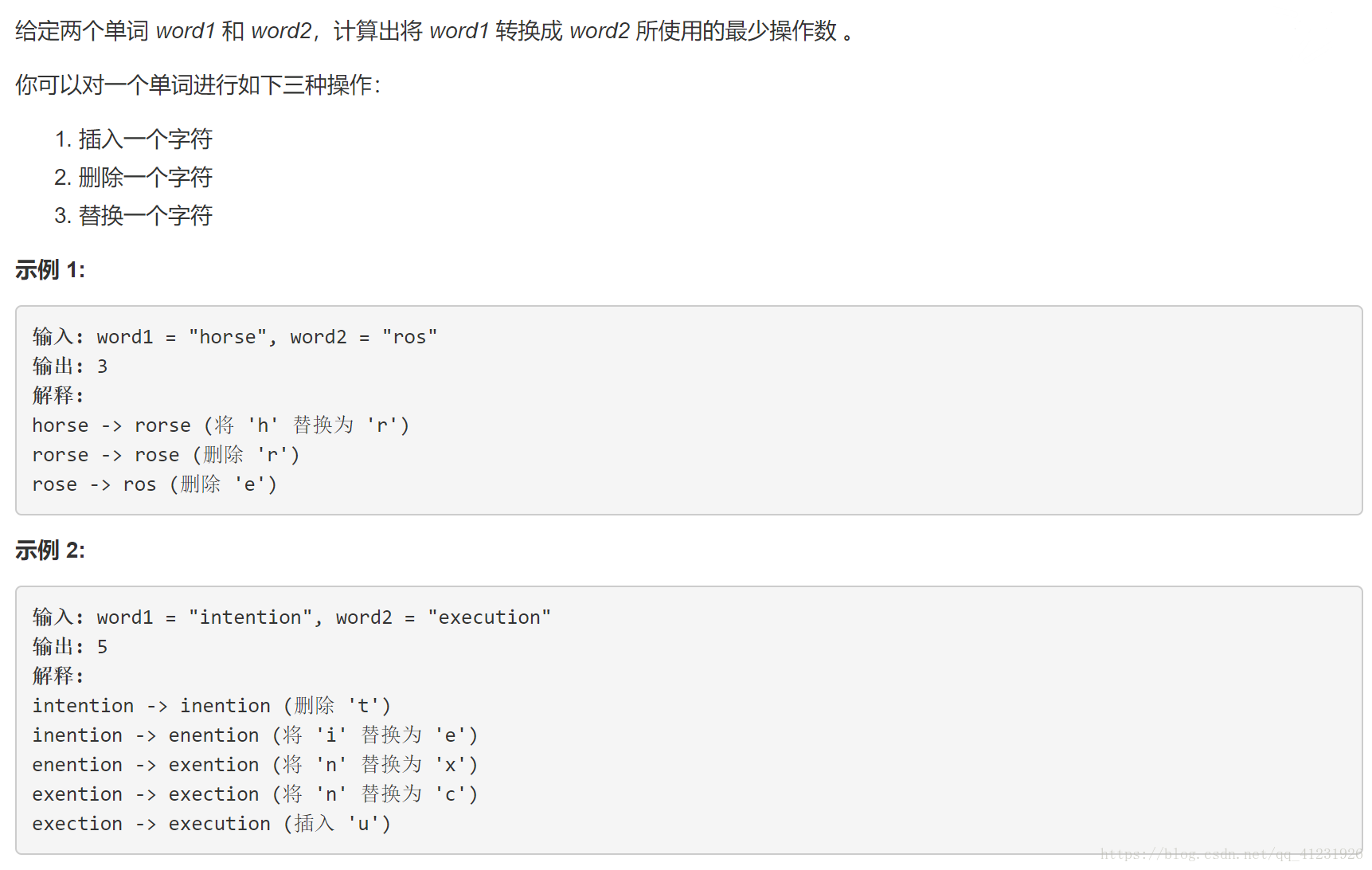
题目描述:
知识点:动态规划
思路:动态规划
一看到题目的时候,我其实是懵的,感觉无从下手。但其实本题是一个经典的动态规划问题。
状态定义:
f(x, y) -------- 代表word1中[0, x - 1]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 1]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤。
状态转移:
(1)如果x == 0或者y == 0,说明转换的字符串之中有一个是空串,其转换为另一个字符串所需要的最少操作数显然就是另一个字符串的长度。因此对于x == 0的情况,f(0, y) = y。对于y == 0的情况,f(x, 0) = x。
(2)如果x和y均不为0且word1.charAt(x - 1) == word2.charAt(y - 1),显然f(x, y) = f(x - 1, y - 1)。
因为此时我们不需要考虑word1.charAt(x - 1)与word2.charAt(y - 1)之间的转换,word1中[0, x - 1]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 1]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤和word1中[0, x - 2]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 2]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤相同。
(3)如果x和y均不为0且word1.charAt(x - 1) != word2.charAt(y - 1),这又分为三种情况
a.如果是从f(x - 1, y - 1)状态转移过来的,f(x - 1, y - 1)代表word1中[0, x - 2]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 2]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤。从f(x, y)转移到f(x - 1, y - 1)需多走一步,即修改word1中x - 1位置的字符使其和word2中y - 1的字符相等。此时f(x, y) = f(x - 1, y - 1) + 1。
b.如果是从f(x - 1, y)状态转移过来的,f(x - 1, y)代表word1中[0, x - 2]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 1]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤。从f(x, y)转移到f(x - 1, y)需多走一步,即在word1中删除第x - 1位置的字符。此时f(x, y) = f(x - 1, y) + 1。
c.如果是从f(x, y - 1)状态转移过来的,f(x, y - 1)代表word1中[0, x - 1]范围内的字符串转换成word2中[0, y - 2]范围内的字符串所需要的最少操作步骤。从f(x, y)转移到f(x, y - 1)需多走一步,即在word2中删除第y - 1位置的字符。此时f(x, y) = f(x, y - 1) + 1。
由于题目要求的是最少操作数,因此应该取a、b、c三种情况中的最小值。
时间复杂度和空间复杂度均是O(m * n),其中m为word1字符串的长度,n为word2字符串的长度。
JAVA代码:
public class Solution {
//dynamic programming
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
int[][] distances = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) {
distances[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {
distances[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n + 1; j++) {
if(word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)){
distances[i][j] = distances[i - 1][j - 1];
}else{
distances[i][j] = Math.min(distances[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(distances[i - 1][j], distances[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
}
}
return distances[m][n];
}
}LeetCode解题报告: