版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/huanghaocs/article/details/78797524
二叉树的存储
二叉树主要是用二叉链表来存储,二叉链表有一个数据域data和两个指针域lchild、rchild构成,分别存放左孩子和右孩子的指针。二叉链表的结点结构定义如下:
class BiTNode {
int data; // 数据域
BiTNode left; // 左孩子指针
BiTNode right; // 右孩子指针
}二叉树的创建
这里用整型数组来代表二叉树的结点,如arr=[1,2,4,0,0,5,0,0,3,6,0,0,0],这里的顺序是按照二叉树的前序遍历结果顺序存储,构建的二叉树如下图所示。这里的0表示空结点。
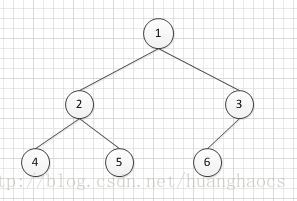
下面来具体实现二叉树的建立过程:
public class TestBiTree {
static int count = 0; //定义计数变量
/*通过数组来构建二叉树,二叉链表*/
public BiTNode createBiTree(BiTNode root, int[] arr, int i){
if(i<arr.length){
if(arr[i] == 0)
root = null;
else{
BiTNode left = new BiTNode();
BiTNode right = new BiTNode();
root.data = arr[i];
root.left = createBiTree(left, arr, ++count);
root.right = createBiTree(right, arr, ++count);
}
}
return root;
}
// 返回二叉树的深度
public int TreeDepth(BiTNode root){
if(root == null)
return 0;
int leftDepth = TreeDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = TreeDepth(root.right);
if(leftDepth > rightDepth)
return leftDepth+1;
else
return rightDepth+1;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
BiTNode root = new BiTNode();
int arr[] = {1,2,4,0,0,5,0,0,3,6,0,0,0};
TestBiTree testBiTree = new TestBiTree();
root = testBiTree.createBiTree(root, arr, count);
}
}二叉树的遍历
(一) 前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历的递归方法。
/*前序遍历二叉树*/
public void PreOrderTraverse(BiTNode root){
if(root == null)
return;
System.out.println(root.data);
PreOrderTraverse(root.left);
PreOrderTraverse(root.right);
}
// 输出结果:1 2 4 5 3 6
/*中序遍历二叉树*/
public void InOrderTraverse(BiTNode root){
if(root == null)
return;
InOrderTraverse(root.left);
System.out.println(root.data);
InOrderTraverse(root.right);
}
// 输出结果:4 2 5 1 6 3
/*后序遍历二叉树*/
public void PostOrderTraverse(BiTNode root){
if(root == null)
return;
PostOrderTraverse(root.left);
PostOrderTraverse(root.right);
System.out.println(root.data);
}
// 输出结果:4 5 2 6 3 1(二) 二叉树的层次遍历。每次把二叉树的一层遍历完整
/*层次遍历二叉树*/
public void LevelTraverse(BiTNode root){
Queue<BiTNode> queue = new LinkedList<BiTNode>(); // 定义一个队列存放结点
if(root == null)
return;
queue.offer(root); // 根节点入队列
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BiTNode biTNode = queue.poll();
if(biTNode.left != null)
queue.offer(biTNode.left); // 左孩子结点入队列
if(biTNode.right != null)
queue.offer(biTNode.right); // 右孩子结点入队列
System.out.println(biTNode.data); // 取出队列首节点
}
}
// 输出结果:1 2 3 4 5 6(三) 二叉树的“Z”字形层次遍历
// Z字形层次遍历二叉树
public List<List<Integer>> ZigzagLevelTraverse(BiTNode root){
List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>(); //集合中每个元素表示每一层的遍历结果
Queue<BiTNode> queue = new LinkedList<BiTNode>(); // 队列来存储每一层的结点
boolean flag = true; // flag来标识队列是从头入队,还是从尾入队
if(root == null)
return result;
queue.offer(root); // 根节点入队列
while(queue.size() != 0){
int size = queue.size(); // 计算队列长度
List<Integer> level = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // 一层的遍历结果
for(int i=0;i<size; i++){
root = queue.remove(); // 出队列,从队列中删除一个结点
if(root.left != null){
queue.offer(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
queue.offer(root.right);
}
if(flag){
level.add(root.data); // 从队尾入队列
}else{
level.add(0, root.data); // 从队头入队列
}
}
flag = !flag;
result.add(level);
}
return result;
}
// 输出结果:[[1],[3,2],[4,5,6]]