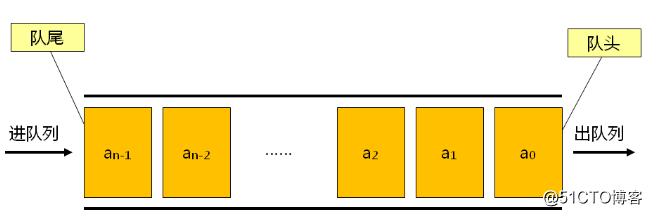
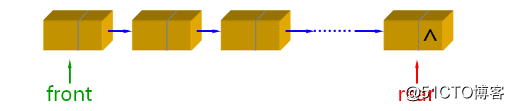
我们在上节博客中学习了栈的相关知识,今天我们来学习下队列。那么什么是队列呢?队里是一种特殊的线性表,队列仅能在线性表的两端进行操作;队头(Front)是取出数据元素的一端,队尾(Rear)是插入数据元素的一端。队列的特性是先进先出(First in first out),关系图如下所示
下来我们来看看队列的常用操作,如下
1、创建队列(Queue())
2、销毁队列(~Queue())
3、清空队列(clear())
4、进队列(add())
5、出队列(remove())
6、获取队头元素(front())
7、获取队列的长度(length())
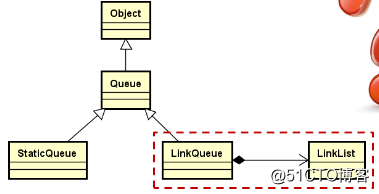
下来我们来看看队列的结构框图,如下
那么队列的顺序实现如下图所示
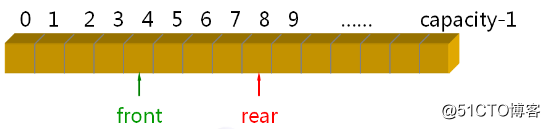
下来我们来看看 StaticQueue 设计要点:首先必须是类模板,使用原生数组作为队列的存储空间;使用模板参数决定队列的最大容量。
StaticQueue 实现要点是循环计数法,关键操作:1、进队列:m_space[m_rear] = e; m_rear = (m_rear + 1) % N;2、出队列:m_front = (m_front + 1) % N;
队列的状态:1、队空:(m_length == 0) && (m_fronmt == m_rear); 2、队满:(m_length == N) && (m_front == m_rear)。
下来我们来看看代码是怎样写的
Queue.h 源码
#ifndef QUEUE_H
#define QUEUE_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class Queue : public Object
{
public:
virtual void add(const T& e) = 0;
virtual void remove() = 0;
virtual T front() const = 0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
virtual int length() const = 0;
};
}
#endif // QUEUE_H
StaticQueue.h 源码
#ifndef STATICQUEUE_H
#define STATICQUEUE_H
#include "Queue.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T, int N >
class StaticQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
T m_space[N];
int m_front;
int m_rear;
int m_length;
public:
StaticQueue()
{
m_front = 0;
m_rear = 0;
m_length = 0;
}
int capacity() const
{
return N;
}
void add(const T& e)
{
if( m_length < N )
{
m_space[m_rear] = e;
m_rear = (m_rear + 1) % N;
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No space in current queue ...");
}
}
void remove()
{
if( m_length > 0 )
{
m_front = (m_front + 1) % N;
m_length--;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
T front() const
{
if( m_length > 0 )
{
return m_space[m_front];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
void clear()
{
m_front = 0;
m_rear = 0;
m_length = 0;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
};
}
#endif // STATICQUEUE_H
我们来写个测试代码来看看代码是否正确
#include <iostream>
#include "StaticQueue.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
StaticQueue<int, 5> queue;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
queue.add(i);
}
while( queue.length() > 0 )
{
cout << queue.front() << endl;
queue.remove();
}
return 0;
}
我们来看看结果
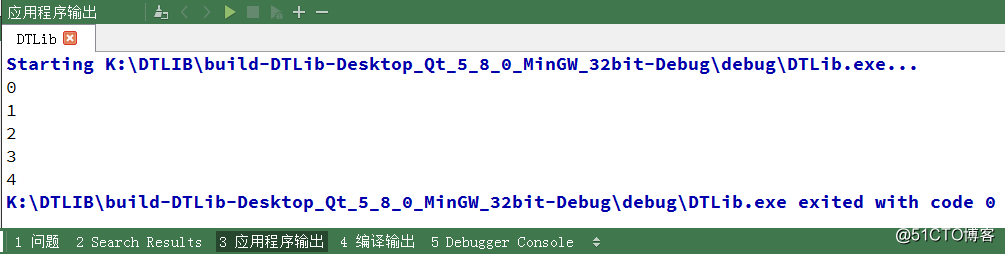
那么同样的参考我们上节实现的栈来说,目前实现的队列也存在一定的缺陷,那便是当数据元素为类类型时, StaticQueue 的对象在创建时会多次调用元素类型的构造函数,极大的影响了效率。所以我们需要实现链式队列来解决这个问题,实现的思路也很简单,参考前面的 StaticQueue 即可。下来我们来看看队列的链式存储实现结构图,如下所示
链式队列的设计要点如下:
1、类模板,抽象父类 Queue 的直接子类;
2、在内部使用链式结构实现元素的存储;
3、只在链表的头部和尾部进行操作。
结构图如下
下来我们来看看 LinkQueue 的源码是怎样写的
LinkQueue.h 源码
#ifndef LINKQUEUE_H
#define LINKQUEUE_H
#include "Queue.h"
#include "LinkList.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class LinkQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
LinkList<T> m_list;
public:
LinkQueue()
{
}
void add(const T& e) // O(n)
{
m_list.insert(e);
}
void remove() // O(1)
{
if( m_list.length() > 0 )
{
m_list.remove(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
T front() const // O(1)
{
if( m_list.length() > 0 )
{
return m_list.get(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
void clear() // O(n)
{
m_list.clear();
}
int length() const // O(1)
{
return m_list.length();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKQUEUE_H
我们来看看测试代码,如下
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkQueue.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
LinkQueue<int> lq;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
lq.add(i);
}
while( lq.length() > 0 )
{
cout << lq.front() << endl;
lq.remove();
}
return 0;
}
编译运行结果如下
我们已经实现了 LinkQueue 的代码,结果也是正确的。可是我们再看看它的效率是否很高呢?看看它们的时间复杂度,只有 add 和 clear 函数是 O(n) ,其他的都是 O(1)。因为在插入的时候我们必须遍历下整个链表,所以效率不是很高。再来对比下之前实现的 StaticQueue 的代码,它们的函数复杂度都是 O(1),那么是否有更好的解决办法吗?下来我们来看看队列链式存储实现的优化,如下图所示
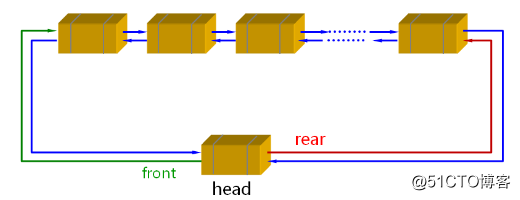
结构图如下图所示
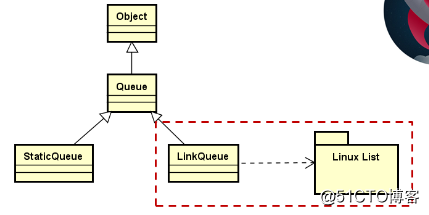
下来我们来看看基于 Linnx 内核链表的队列,源码如下
LinkQueue.h 源码
#ifndef LINKQUEUE_H
#define LINKQUEUE_H
#include "Queue.h"
#include "LinuxList.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template < typename T >
class LinkQueue : public Queue<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
list_head head;
T value;
};
list_head m_header;
int m_length;
public:
LinkQueue() // O(1)
{
m_length = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&m_header);
}
void add(const T& e) // O(1)
{
Node* node = new Node();
if( node != NULL )
{
node->value = e;
list_add_tail(&node->head, &m_header);
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No memory to add new element ...");
}
}
void remove() // O(1)
{
if( m_length > 0 )
{
list_head* toDel = m_header.next;
list_del(toDel);
m_length--;
delete list_entry(toDel, Node, head);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
T front() const // O(1)
{
if( m_length > 0 )
{
return list_entry(m_header.next, Node, head)->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(INvalidOPerationException, "No element in current queue ...");
}
}
void clear() // O(n)
{
while( m_length > 0 )
{
remove();
}
}
int length() const // O(1)
{
return m_length;
}
~LinkQueue() // O(n)
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKQUEUE_H
我们看看在上面的 add 函数中调用的是 Linux 内核中的 list_add_tail 函数,我们来看看它的时间复杂度为多少,它的源码如下
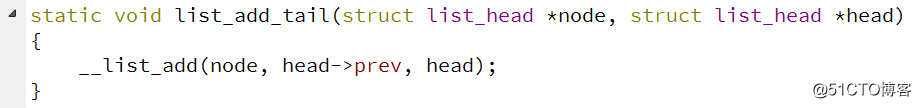
我们再来看看 __list_add 函数是怎样实现的,如下
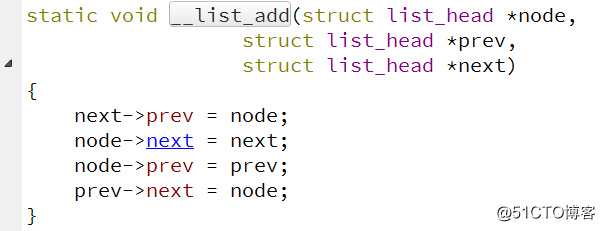
它的时间复杂度为 O(1),因而我们上面实现的 add 函数时间复杂度为 O(1)。比起之前实现的代码效率更高,我们来测试下此代码
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkQueue.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
LinkQueue<Test> lq;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
lq.add(i);
}
while( lq.length() > 0 )
{
cout << lq.front() << endl;
lq.remove();
}
return 0;
}
结果如下
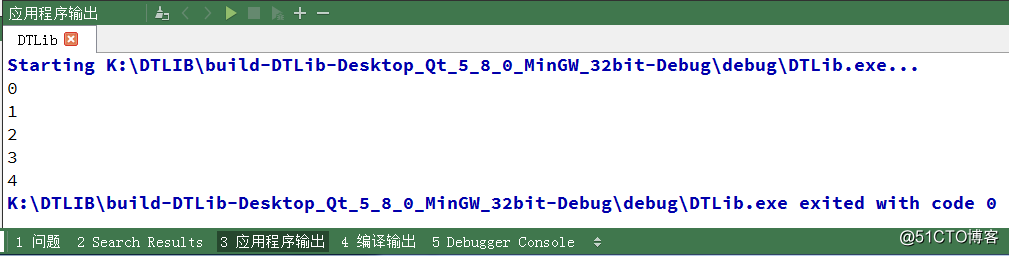
我们再来测试下当数据元素为类类型时,看看结果,测试代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkQueue.h"
#include "StaticQueue.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
class Test : public Object
{
public:
Test()
{
cout << "Test()" << endl;
}
~Test()
{
cout << "~Test()" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
LinkQueue<int> lq;
StaticQueue<Test, 5> sq;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
}
while( lq.length() > 0 )
{
lq.remove();
}
return 0;
}
我们看看结果怎样
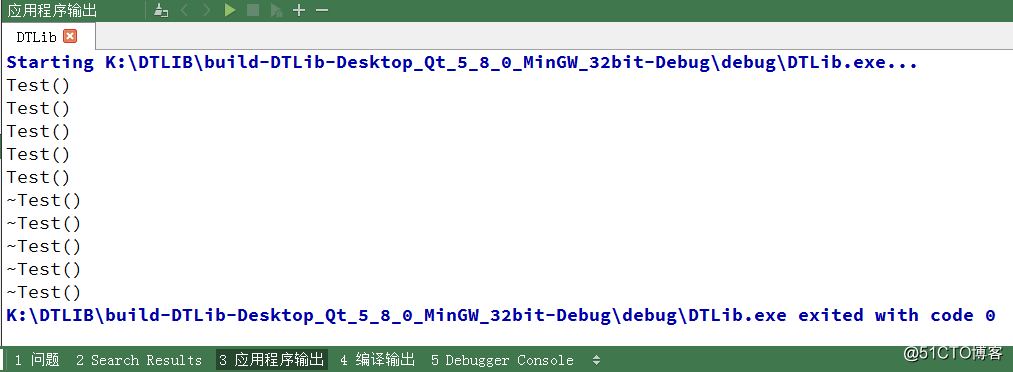
在 LinkQueue 的创建中没有 Test 类对象的生成,但是在 StaticQueue 中有类对象的生成。通过今天对队列的学习,总结如下:1、StaticQueue 在初始化时可能多次调用元素类型的构造函数;2、LinkList 的组合使用能够实现队列的功能,但是不够高效;3、LinkQueue 的最终实现组合使用了 Linux 内核链表;4、LinkQueue 中入队和出队操作可以在常量时间内完成。