版权声明:本文为hzy原创文章,未经博主允许不可随意转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/Binary_Heap/article/details/82709295
Splay是一种能快速分裂与合并的平衡树,常用于解决某些序列问题.
rotate : 单旋
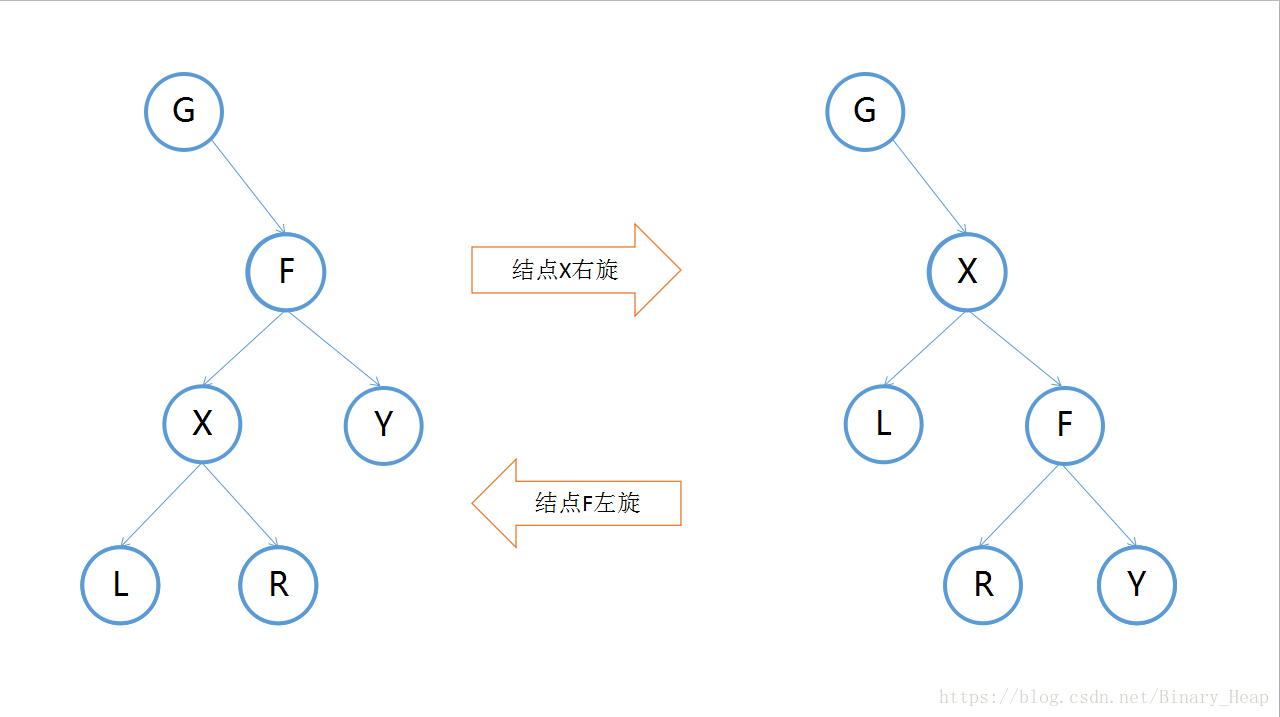
先理解一下右旋,左旋与右旋是完全对称的操作.
如图,右旋的作用就是一个结点是左儿子,它旋转到父亲的位置,并且可以发现旋转后依然满足二叉搜索树的性质
双旋
双旋就是一次往上旋两层,保证复杂度,而单旋不保证.
定义 表示 是左子树还是右子树。
如果 ,即x与父亲与父亲的父亲三点共线,旋转父亲与自己
否则,旋转自己两次.
还要注意一下最后的边界细节.
Splay : 伸展
好像双旋说完伸展就没啥好讲的了。。
伸展操作是把某个结点 通过旋转到达某个结点 ,保证 在 的子树中。
直接不断双旋,如果父亲已经是 ,旋一次并停止旋转.
代码 (Luogu P3391)
声明:本代码来自神犇_ ,稍作了修改。
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int son[N][2], fa[N], sz[N], n, m;
bool rev[N];
//pushdown the tag
void pdn(int x) {
if(rev[x]) {
rev[x] = 0;
std :: swap(son[x][0], son[x][1]);
rev[son[x][0]] ^= 1;
rev[son[x][1]] ^= 1;
}
}
//direction
int dir(int x) {
return son[fa[x]][1] == x;
}
//update the size
void upd(int x) {
sz[x] = 1 + sz[son[x][0]] + sz[son[x][1]];
}
void rotate(int x) {
int f = fa[x], d = dir(x);
if(fa[x] = fa[f]) son[ fa[x] ][dir(f)] = x;
if(son[f][d] = son[x][d ^ 1]) fa[ son[f][d] ] = f;
fa[son[x][d ^ 1] = f] = x;
upd(f), upd(x);
}
int st[N];
//move x to 'to'
void splay(int x, int to_f = 0) {
int top = 0;
for(int i = x; fa[i]; i = fa[i])
st[top ++] = fa[i];
while(top --) pdn(st[top]);
pdn(x);
for(; fa[x] != to_f; rotate(x))
if(fa[ fa[x] ] != to_f)
rotate(dir(x) == dir(fa[x]) ? fa[x] : x);
}
//find the kth and move it to the root
int kth(int k, int x) {
int o = x;
while(1) {
pdn(o);
if(sz[son[o][0]] == k - 1) break ;
if(sz[son[o][0]] >= k) o = son[o][0];
else {
k -= 1 + sz[son[o][0]];
o = son[o][1];
}
}
splay(o, fa[x]);
return o;
}
void reverse(int l, int r) {
splay(1);
int y = kth(r + 1, 1);
kth(l - 1, son[y][0]);
rev[son[son[y][0]][1]] ^= 1;
}
void print(int x) {
if(!x) return ;
pdn(x);
print(son[x][0]);
if(2 <= x && x <= n + 1)
printf("%d ", x - 1);
print(son[x][1]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n + 2; ++ i) {
if(fa[i] = i - 1) son[i - 1][1] = i;
sz[i] = (n + 2) - (i - 1);
rev[i] = 0;
}
for(int l, r; m --; ) {
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
reverse(l + 1, r + 1);
}
splay(1);
print(1);
return 0;
}分裂 : split
假设序列要分成左边 个,右边 。
先把排名第 的结点旋转到根。这时候 的右子树就是右边部分了。把右子树切掉,剩下的就是左边部分。
void split(int x, int s, int &l, int &r) {
if(s == 0) {
l = 0;
r = x;
return ;
}
int y = kth(s, x);
l = y;
if(r = son[l][1]) fa[ son[l][1] ] = 0;
son[l][1] = 0;
upd(l);
}合并 : merge
假设 要接在 的后面.
把 中的最大结点旋转到根,根据二叉搜索树的性质,此时根没有右子树。把右子树设成 就行.
int merge(int x, int y) {
if(!x) return y;
kth(sz[x], x);
if(son[x][1] = y) fa[son[x][1]] = x;
upd(x);
return x;
}