直接上代码额。。搜索、删除、添加节点主要用到的是函数嵌套递归的思想,而且考虑的角度从整个树转变为每一个节点如何操作。
Tree.h
#ifndef TREE_H
#define TREE_H
#include"Node.h"
class Tree
{
public:
Tree();
~Tree();
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);
bool AddNode(int nodeIndex,int diretion,Node*pNode);
bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode);
void PreorderTraversal();//前序遍历
void InorderTraversal();//中序
void PostorderTraversal();//后序
private:
Node *m_pRoot;
};
#endifTree.cpp
#include"Tree.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Tree::Tree()
{
m_pRoot = new Node;//不在树根放有意义的值
}
Tree::~Tree()
{
DeleteNode(0,NULL);
//m_pRoot->DeleteNode();//也可以
}
Node *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
return m_pRoot->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
//Node *pSearchNode = m_pRoot;
//while(1){
// while(pSearchNode->pLKid != NULL){
// pSearchNode = pSearchNode->pLKid;
// }
// if(pSearchNode->index == nodeIndex){
// return pSearchNode;
// }else if((pSearchNode->index)%2 == 0){
// pSearchNode = pSearchNode->pFather;
// }else{
// pSearchNode = pSearchNode->pFather->pRKid;
// }
// if(pSearchNode == m_pRoot){
// cout << "没有对应该下标的节点" << endl;
// return NULL;
// }
//}
}
bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex,int diretion,Node*pNode)
{
Node *pCurrentNode = SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if(pCurrentNode == NULL){
cout << "没有该下标对应的节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if(diretion == 0){//左孩子
if(pCurrentNode->pLKid != NULL){
cout << "该节点左孩子不为NULL,无法添加" << endl;
return false;
}
Node *pNewNode = new Node;//这里可以添加一个判断申请内存是否成功
pNewNode->data = pNode->data;
pNewNode->index = pNode->index;
pNewNode->pFather = pCurrentNode;
pCurrentNode->pLKid = pNewNode;
return true;
}
if(diretion != 0){//右孩子
if(pCurrentNode->pRKid != NULL){
cout << "该节点右孩子不为NULL,无法添加" << endl;
return false;
}
Node *pNewNode = new Node;
pNewNode->index = pNode->index;
pNewNode->data = pNode->data;
pNewNode->pFather = pCurrentNode;
pCurrentNode->pRKid = pNewNode;
return true;
}
cout << "异常" << endl;//以防有誤
return false;
}
bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode)//如果pNode等于NULL,则只用删除节点就行,不用取出来。
{
Node *pCurrentNode = SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if(pCurrentNode == NULL){
cout << "没有该下标对应的节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if(pNode != NULL){
pNode->data = pCurrentNode->data;
}
pCurrentNode->DeleteNode();
return true;
}
void Tree::PreorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PreorderTraversal();
}
void Tree::InorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->InorderTraversal();
}
void Tree::PostorderTraversal()
{
m_pRoot->PostorderTraversal();
}Node.h
#ifndef NODE_H
#define NODE_H
//#include"Person.h"//实验后发现比下一句好,如果用下一句,则Person data;会显示不允许使用不完整的定义
//class Person;
class Node
{
public://为了方便都定义在public下
Node();
Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);//关心到每个节点自己的搜索检查
void DeleteNode();//关心到每个节点自己的删除
void PreorderTraversal();//每一个节点的前序遍历
void InorderTraversal();
void PostorderTraversal();
int index;
int data;
Node *pLKid;
Node *pRKid;
Node *pFather;
//Node();直接用默认
//~Node();
};
#endif
Node.cpp
#include"Node.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Node::Node()
{
index = 0;
data = 0;
pLKid = NULL;
pRKid = NULL;
pFather = NULL;
}
Node *Node::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if(index == nodeIndex)return this;
Node* temp = NULL;
if(pLKid != NULL){//减少程序冗余
//if(pLKid->index == nodeIndex){
// return pLKid;
//}else{
temp = pLKid->SearchNode(nodeIndex);//嵌套的方式
if(temp != NULL)return temp;
//}
}
if(pRKid != NULL){
/*if(pRKid->index == nodeIndex){
return pRKid;
}else{*/
temp = pRKid->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if(temp != NULL)return temp;
//}
}
return NULL;
}
void Node::DeleteNode()//先删除左右孩子,再和父节点断开联系,再自杀。。。
{
if(pLKid != NULL){
pLKid->DeleteNode();
};
if(pRKid != NULL){
pRKid->DeleteNode();
};
if(pFather != NULL){
if(pFather->pRKid == this){
pFather->pRKid = NULL;
}else{
pFather->pLKid = NULL;
}
}
delete this;
}
void Node::PreorderTraversal()
{
cout << index << "," << data << endl;
if(pLKid != NULL){
pLKid->PreorderTraversal();
}
if(pRKid != NULL){
pRKid->PreorderTraversal();
}
//cout << pLKid->index << "," << pLKid->data << endl;
//cout << pRKid->index << "," << pRKid->data << endl;
}
void Node::InorderTraversal()
{
if(pLKid != NULL){
pLKid->InorderTraversal();
}
cout << index << "," << data << endl;
if(pRKid != NULL){
pRKid->InorderTraversal();
}
}
void Node::PostorderTraversal()
{
if(pLKid != NULL){
pLKid->PostorderTraversal();
}
if(pRKid != NULL){
pRKid->PostorderTraversal();
}
cout << index << "," << data << endl;
}
demo.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>//system
#include"Node.h"
#include"Tree.h"
using namespace std;
/*
(0)
(1)5 (2)8
(3)2 (4)6 (5)9 (6)7
(7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14)
3层
前序遍历:0 1 3 4 2 5 6
中序:3 1 4 0 5 2 6
后序:3 4 1 5 6 2 0
4层
0 1 3 7 8 4 9 10 2 5 11 12 6 13 14
7 3 8 1 9 4 10 0 11 5 12 2 13 6 14
7 8 3 9 10 4 1 11 12 5 13 14 6 2 0
*/
int main()
{
Node *node1 = new Node;
node1->index = 1;
node1->data = 5;
Node *node2 = new Node;
node2->index = 2;
node2->data = 8;
Node *node3 = new Node;
node3->index = 3;
node3->data = 2;
Node *node4 = new Node;
node4->index = 4;
node4->data = 6;
Node *node5 = new Node;
node5->index = 5;
node5->data = 9;
Node *node6 = new Node;
node6->index = 6;
node6->data = 7;
//测试4层
Node *node7 = new Node;
node7->index = 7;
node7->data = 10;
Node *node8 = new Node;
node8->index = 8;
node8->data = 11;
Node *node9 = new Node;
node9->index = 9;
node9->data = 7;
Node *node10 = new Node;
node10->index = 10;
node10->data = 7;
Node *node11 = new Node;
node11->index = 11;
node11->data = 7;
Node *node12 = new Node;
node12->index = 12;
node12->data = 7;
Node *node13 = new Node;
node13->index = 13;
node13->data = 7;
Node *node14 = new Node;
node14->index = 14;
node14->data = 7;
Tree *tree = new Tree;
tree->AddNode(0,0,node1);
tree->AddNode(0,1,node2);
tree->AddNode(1,0,node3);
tree->AddNode(1,1,node4);
tree->AddNode(2,0,node5);
tree->AddNode(2,1,node6);
//4层
tree->AddNode(3,0,node7);
tree->AddNode(3,1,node8);
tree->AddNode(4,0,node9);
tree->AddNode(4,1,node10);
tree->AddNode(5,0,node11);
tree->AddNode(5,1,node12);
tree->AddNode(6,0,node13);
tree->AddNode(6,1,node14);
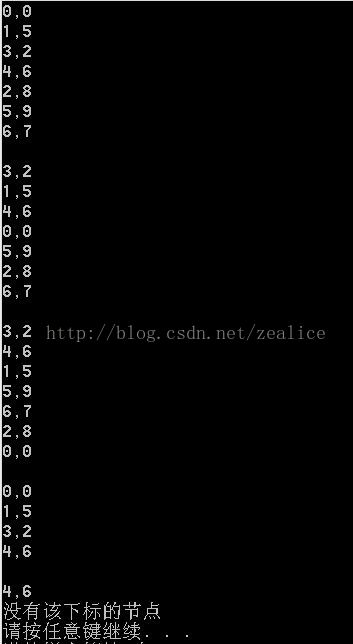
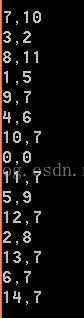
tree->PreorderTraversal();
cout << endl;
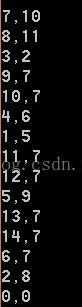
tree->InorderTraversal();
cout << endl;
tree->PostorderTraversal();
cout << endl;
tree->DeleteNode(2,NULL);
tree->PreorderTraversal();
cout << endl;
Node * test = tree->SearchNode(4);
cout << test->index << "," << test->data << endl;
test = tree->SearchNode(6);
if(test == NULL)cout << "没有该下标的节点" << endl;
delete tree;//不用delete那些节点,已经在delete tree 中释放了
system("pause");
return 0;
}三层的结果:
四层结果:
前序遍历:
中序:
后序:
删除和搜索: