最近在和小伙伴一同做一个有关投资者情绪分析的项目,除了实现一些文本挖掘的算法外,其实这个项目绝大部分的任务量是在文本数据的获取上,也就是网络爬虫。以前虽学了些H5+CSS网络开发的技术,但网络爬虫接触很少,索性花了点时间把爬虫技术从头到尾学了一遍。这不到一个月来,利用闲余时间完成了百度指数、东方财富网和新浪微博的批量爬虫。这三个网站的爬虫较之传统网站都不是省油的灯,例如,百度指数网上的指数数据无法直接提取、东方财富网是经过Javascript渲染过后的网页并且还需经过先从文章列表中提取文章链接再爬取链接中的文章的两步爬取过程、新浪微博反爬虫太强并且微博提取过程中牵涉到一些模拟网页动作链的实现;做的过程中着实碰壁不少,后续拟撰写几篇博客一一解读,并总结我这段时间的爬虫经验与心得。会了自然通,我个人觉得爬虫主要还是流程代码的实现,还是比较简单的,不过学习爬虫有助于理解网页结构、理解网页开发的原理,我个人也推荐学一些简单的爬虫实现,一定会有收获。
今天先说百度指数爬虫的实现,代码修改自这篇博客https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26877377/article/details/80860722(后面称作baseline代码),在此表示感谢。百度指数爬虫的难点有二:
(1)模拟登陆。这个还算好,因为一次登录后浏览器直接生成会话,后续无需重复登录,所以也不用完全实现自动化模拟登陆,就像baseline代码中实现的一样,先使用selenium模拟登陆,再加上一个input等待人工确认是否登录完毕,若需要输手机验证码就手动输一下后确认登录。
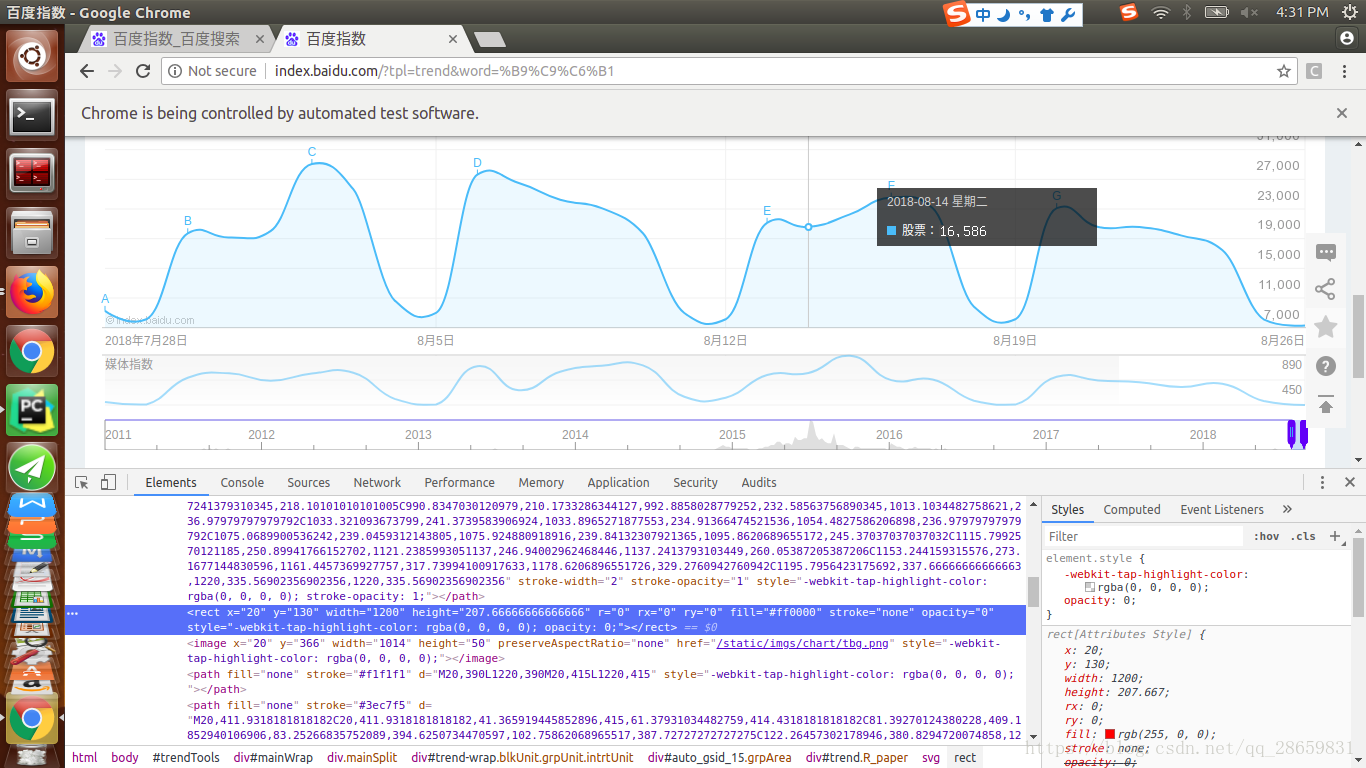
(2)百度指数获取。百度指数的数据并不是以数值形式存储在网页上的,只有当鼠标出现在曲线上才会跳出百度指数,因此需要模拟鼠标移动截图跳出来的百度指数,再通过图像识别方法获取百度指数。
Baseline代码已基本实现了这两个难点的操作,我又继续优化了三个地方:
(1)Baseline代码过多地使用time.sleep()函数等待页面加载,可以使用selenium.webdriver.support.ui.WebDriverWait显示等待页面的某个元素是否存在来判断页面是否加载完毕。
- Baseline代码模拟登录:
# 源代码模拟登陆操作
# 输入账号密码
# 输入账号密码
account = []
try:
fileaccount = open("../baidu/account.txt", encoding='UTF-8')
accounts = fileaccount.readlines()
for acc in accounts:
account.append(acc.strip())
fileaccount.close()
except Exception as err:
print(err)
input("请正确在account.txt里面写入账号密码")
exit()
print(account[0])
print(account[1])
time.sleep(2)
browser.find_element_by_id("TANGRAM__PSP_3__footerULoginBtn").click()
time.sleep(2)
browser.find_element_by_id("TANGRAM__PSP_3__userName").send_keys(account[0])
time.sleep(2)
browser.find_element_by_id("TANGRAM__PSP_3__password").send_keys(account[1])
# 点击登陆登陆
# id="TANGRAM__PSP_3__submit"
browser.find_element_by_id("TANGRAM__PSP_3__submit").click()- 改进的模拟登陆:
# 改进的显示等待
# 输入账号密码
# 输入账号密码
account = []
try:
fileaccount = open("./account.txt", encoding='UTF-8')
accounts = fileaccount.readlines()
for acc in accounts:
account.append(acc.strip())
fileaccount.close()
except Exception as err:
print(err)
input("请正确在account.txt里面写入账号密码")
exit()
print(account[0])
print(account[1])
footer_login_btn = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "TANGRAM__PSP_3__footerULoginBtn")))
footer_login_btn.click()
username_input = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "TANGRAM__PSP_3__userName")))
password_input = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "TANGRAM__PSP_3__password")))
login_btn = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "TANGRAM__PSP_3__submit")))
username_input.send_keys(account[0])
password_input.send_keys(account[1])
login_btn.click()(2)使用百度云人工智能图像文字识别API,基础文字识别每天有50000次免费调用,精度比pytesseract.image_to_string()的ocr识别高多了,此外baseline代码只提取了百度指数的数值,没有提取时间,我也加进去了,修改了图片截取大小,在百度云API识别图片后用正则化提取出了时间。
- Baseline代码的图像截取与识别过程
imgelement = browser.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="viewbox"]')
# 找到图片坐标
locations = imgelement.location
# 跨浏览器兼容
scroll = browser.execute_script("return window.scrollY;")
top = locations['y'] - scroll
# 找到图片大小
sizes = imgelement.size
# 构造关键词长度
add_length = (len(keyword) - 2) * sizes['width'] / 15
# 构造指数的位置
rangle = (
int(locations['x'] + sizes['width'] / 4 + add_length), int(top + sizes['height'] / 2),
int(locations['x'] + sizes['width'] * 2 / 3), int(top + sizes['height']))
time.sleep(2)
# 截取当前浏览器
path = "../baidu/" + str(num)
browser.save_screenshot(str(path) + ".png")
# 打开截图切割
img = Image.open(str(path) + ".png")
jpg = img.crop(rangle)
jpg.save(str(path) + ".jpg")
# 将图片放大一倍
# 原图大小73.29
jpgzoom = Image.open(str(path) + ".jpg")
(x, y) = jpgzoom.size
x_s = 146
y_s = 58
out = jpgzoom.resize((x_s, y_s), Image.ANTIALIAS)
out.save(path + 'zoom.jpg', 'png', quality=95)
# 图像识别
try:
image = Image.open(str(path) + "zoom.jpg")
code = pytesseract.image_to_string(image) # pytesseract的ocr识别,精度一般
if code:
index.append(code)
else:
index.append("")
except:
index.append("")
num = num + 1- 改进的图像截取与识别过程
# 原代码图像截取与识别过程
imgelement = browser.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="viewbox"]')
# 找到viewbox坐标
locations = imgelement.location
# 跨浏览器兼容
scroll = browser.execute_script("return window.scrollY;")
top = locations['y'] - scroll
# 找到viewbox大小
sizes = imgelement.size
# 构造文本与数据位置
rangle = (
int(locations['x']), int(top),
int(locations['x'] + sizes['width']), int(top + sizes['height']))
# 截取当前浏览器
if day <= 180:
file = './' + keyword + '_' + str(day) + '/image/'
else:
file = './' + keyword + '_' + 'all' + '/image/'
if not os.path.exists(file):
os.makedirs(file)
path = file + str(num)
browser.save_screenshot(str(path) + "_raw.png")
# 打开截图切割
img = Image.open(str(path) + "_raw.png")
jpg = img.crop(rangle)
jpg.save(str(path) + "_cropped.png")
# 图像识别
try:
image = get_file_content(str(path) + "_cropped.png")
code = client.basicGeneral(image) # 百度云文字识别api
print('code : ', code)
if day <= 180:
r1 = re.compile('(\d+).*')
r2 = re.compile('\D+(\d+)')
else:
r1 = re.compile('(\d+\D\d+).*')
r2 = re.compile('\D+(\d+)')
dict = {}
dict['time'] = r1.findall(code['words_result'][0].get('words').strip().replace('-', ''))[0]
dict['index'] = int(r2.findall(code['words_result'][1].get('words').strip().replace(',', '').replace('■', ''))[0])
print('dict: ', dict)
index.append(dict)
except:
index.append("")
num = num + 1(3)Baseline代码中设置的鼠标移动的动作链的步长并不具有普适性,可能这套步长设置只适合他的浏览器却不适合其他的,可能因为步长过大而漏掉了一些指数。那么我宁愿将步长设置的很小,尽管会有重复,但是可以保证每一个指数都被提取到,后续再判断去重即可。虽然采取小步长会很慢,但是百度指数一次提取后便可复用以后只需更新最新的,所以慢就慢点吧,可以晚上睡觉时候一次性设置好关键词条跑完。
- Baseline代码动作链步长设置
# 源代码动作链步长设置
for i in range(day):
# 坐标偏移量
ActionChains(browser).move_to_element_with_offset(xoyelement, x_0, y_0).perform()
# 构造规则
if day == 7:
x_0 = x_0 + 202.33
elif day == 30:
x_0 = x_0 + 41.68
elif day == 90:
x_0 = x_0 + 13.64
elif day == 180:
x_0 = x_0 + 6.78
elif day == 1000000:
x_0 = x_0 + 3.37222222
time.sleep(2)
- 改进的动作链步长设置
# 改进的动作链步长设置
ActionChains(browser).move_to_element_with_offset(xoyelement, 1100, 50).perform()
time.sleep(1)
while True:
# 坐标偏移量
ActionChains(browser).move_to_element_with_offset(xoyelement, x_0, y_0).perform()
time.sleep(1)
# 构造规则
if day == 1:
x_0 = x_0 + 20
if x_0 > 1200:
break
elif day == 7:
x_0 = x_0 + 40
if x_0 > 1200:
break
elif day == 30:
x_0 = x_0 + 20
if x_0 > 1200:
break
elif day == 90:
x_0 = x_0 + 5
if x_0 > 1200:
break
elif day == 180:
x_0 = x_0 + 3
if x_0 > 1200:
break
else:
x_0 = x_0 + 1
if x_0 > 1200:
break综上,便是基于baseline代码的改进,再次感谢baseline代码给我的基础。改进的完整代码请戳我的github:https://github.com/shaoniangu/Baidu_index_spider。后续几篇博客将陆续完成。

-------------------------------------------
Youzhi Gu,master student
Foresight Control Center
College of Control Science & Engineering
Zhejiang University
Email: [email protected],[email protected]