IO分为同步阻塞BIO、同步非阻塞NIO、异步非阻塞AIO
1、BIO
在JDK1.4出来之前,我们建立网络连接的时候采用BIO模式,需要先在服务端启动一个ServerSocket,然后在客户端启动Socket来对服务端进行通信,默认情况下服务端需要对每个请求建立一堆线程等待4请求,而客户端发送请求后,先咨询服务端是否有线程相应,如果没有则会一直等待或者遭到拒绝请求,如果有的话,客户端会线程会等待请求结束后才继续执行。
2、NIO
NIO本身是基于事件驱动思想来完成的,其主要想解决的是BIO的大并发问题: 在使用同步I/O的网络应用中,如果要同时处理多个客户端请求,或是在客户端要同时和多个服务器进行通讯,就必须使用多线程来处理。也就是说,将每一个客户端请求分配给一个线程来单独处理。这样做虽然可以达到我们的要求,但同时又会带来另外一个问题。由于每创建一个线程,就要为这个线程分配一定的内存空间(也叫工作存储器),而且操作系统本身也对线程的总数有一定的限制。如果客户端的请求过多,服务端程序可能会因为不堪重负而拒绝客户端的请求,甚至服务器可能会因此而瘫痪。NIO基于Reactor,当socket有流可读或可写入socket时,操作系统会相应的通知引用程序进行处理,应用再将流读取到缓冲区或写入操作系统。 也就是说,这个时候,已经不是一个连接就要对应一个处理线程了,而是有效的请求,对应一个线程,当连接没有数据时,是没有工作线程来处理的。
BIO与NIO一个比较重要的不同,是我们使用BIO的时候往往会引入多线程,每个连接一个单独的线程;而NIO则是使用单线程或者只使用少量的多线程,每个连接共用一个线程。NIO的最重要的地方是当一个连接创建后,不需要对应一个线程,这个连接会被注册到多路复用器上面,所以所有的连接只需要一个线程就可以搞定,当这个线程中的多路复用器进行轮询的时候,发现连接上有请求的话,才开启一个线程进行处理,也就是一个请求一个线程模式。
在NIO的处理方式中,当一个请求来的话,开启线程进行处理,可能会等待后端应用的资源(JDBC连接等),其实这个线程就被阻塞了,当并发上来的话,还是会有BIO一样的问题。HTTP/1.1出现后,有了Http长连接,这样除了超时和指明特定关闭的http header外,这个链接是一直打开的状态的,这样在NIO处理中可以进一步的进化,在后端资源中可以实现资源池或者队列,当请求来的话,开启的线程把请求和请求数据传送给后端资源池或者队列里面就返回,并且在全局的地方保持住这个现场(哪个连接的哪个请求等),这样前面的线程还是可以去接受其他的请求,而后端的应用的处理只需要执行队列里面的就可以了,这样请求处理和后端应用是异步的.当后端处理完,到全局地方得到现场,产生响应,这个就实现了异步处理
3、AIO
与NIO不同,当进行读写操作时,只须直接调用API的read或write方法即可。这两种方法均为异步的,对于读操作而言,当有流可读取时,操作系统会将可读的流传入read方法的缓冲区,并通知应用程序;对于写操作而言,当操作系统将write方法传递的流写入完毕时,操作系统主动通知应用程序。 即可以理解为,read/write方法都是异步的,完成后会主动调用回调函数。 在JDK1.7中,这部分内容被称作NIO.2
由于NIO的API较为复杂用起来多为不便,于是出现Netty,他对NIO的很多API进行了封装,更方便我们使用。
jdk1.7、netty-all-4.0.25.Final.jar
服务端代码
package com.swk.common.netty;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
/**
* Created by fuyuwei on 2017/9/15.
*/
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object o) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server channelRead...");
System.out.println(channelHandlerContext.channel().remoteAddress()+"--Server:"+o.toString());
channelHandlerContext.write("server write:"+o);
channelHandlerContext.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Throwable throwable) throws Exception {
throwable.printStackTrace();
channelHandlerContext.close();
}
}
package com.swk.common.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
/**
* Created by fuyuwei on 2017/9/15.
*/
public class NettyServer {
private int port;
public NettyServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap().group(bossGroup,workerGroup).
channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).
localAddress(port).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128).childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true);
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Server start listen at:"+port);
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port;
if(args.length > 0){
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}else{
port = 8080;
}
new NettyServer(port).start();
}
}
客户端代码
package com.swk.common.netty;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
/**
* Created by fuyuwei on 2017/9/15.
*/
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("NettyClientHandler Active...");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("NettyClientHandler read message:"+msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
package com.swk.common.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
/**
* Created by fuyuwei on 2017/9/15.
*/
public class NettyClient {
static final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
static final int PORT = 8080;
static final int SIZE = 256;
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).
option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true).
handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = socketChannel.pipeline();
p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST,PORT);
future.channel().writeAndFlush("Hello Netty Server,I am a common client");
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
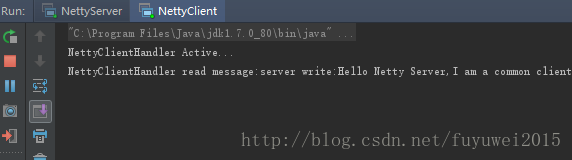
运行结果
先启动服务端,后运行客户端,服务端输出如下
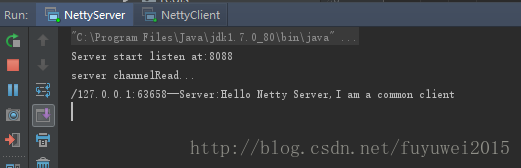
客户端输出如下