前言
博客编写人:Willam
博客编写时间:2017/3/29
博主邮箱:2930526477@qq.com(有志同道合之人,可以加qq交流交流编程心得)1、代码实现的介绍
下面我将会实现哈希表的查找代码:
其中我会采取的散列构造函数为最常用的构造函数:除留取余数法
而解决冲突的方法采用以下三种,分别实现:
- 线性探测
- 二次探测
- 链地址法
如果需要了解哈希表的详细介绍,可参考博客:哈希表的详解
2、线性探测的实现
- linear.h文件的代码
/************************************************************/
/* 程序作者:Willam */
/* 程序完成时间:2017/3/29 */
/* 有任何问题请联系:[email protected] */
/************************************************************/
//@尽量写出完美的程序
//#pragma once是一个比较常用的C/C++杂注,
//只要在头文件的最开始加入这条杂注,
//就能够保证头文件只被编译一次。
#ifndef MY_H_FILE //如果没有定义这个宏
#define MY_H_FILE //定义这个宏
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Keytype;
//每次都是取质数最接近的质数
struct Hash {
Keytype * elem; //记录哈希表中的元素
bool * isfull; //记录哈希表是否有元素了
int count; //哈希表中元素的个数
int sizeindex;
};
bool searchHash(Hash t, Keytype k, int & p, int &c,int * hashsize);
bool insertHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize);
bool DeleteHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize);
void print(Hash t, int * hashsize);
#endif
- linear.cpp文件的代码
#include"linear.h"
//查找对应的关键字
bool searchHash(Hash t, Keytype k, int & p,int &c,int * hashsize) {
p = k%hashsize[t.sizeindex];
while (t.isfull[p] && t.elem[p] != k && c < hashsize[t.sizeindex]-1) {
++c;
//继续往下寻找下一个散列结点
p=(k+c) % hashsize[t.sizeindex];
}
if (t.elem[p] == k) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool insertHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize) {
int p;
int c = 0;
if (searchHash(t, k, p,c,hashsize)) {
return false;
}
else if (c==hashsize[t.sizeindex]-1) {//此时哈希表已经满,得重新分配了
//首先是把之前的内容保存起来
int temp;
temp=hashsize[t.sizeindex];
Keytype * elem = new Keytype[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
bool * isfull=new bool[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
for (int i = 0; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
elem[i] = t.elem[i];
isfull[i] = t.isfull[i];
}
delete t.elem;
delete t.isfull;
++t.sizeindex;
//重新分配空间
t.elem= new Keytype[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
t.isfull=new bool[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < temp; ++i) {
t.elem[i]=elem[i];
t.isfull[i] = isfull[i];
}
for (; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
t.isfull[i] = false;
}
}
else {
//cout << p << endl;
//直接插入对应的位置
t.elem[p] = k;
++t.count;
t.isfull[p] = true;
}
}
bool DeleteHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize) {
int p;
int c = 0;
if (!searchHash(t, k, p, c,hashsize)) {//没找到要删除的元素
return false;
}
else {
t.isfull[p] = false;
--t.count;
}
}
void print(Hash t, int * hashsize) {
cout << "当前的表的长度:" << hashsize[t.sizeindex] << endl;
cout << "Hash表的元素个数为:" << t.count << endl;
cout << "打印整个表:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
if(t.isfull[i])
cout << t.elem[i] << " ";
else {
cout << "^" << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}- main.cpp文件的代码
#include"linear.h"
int hashsize[]={ 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107,
109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223,
227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293, 307, 311, 313, 317, 331, 337,
347, 349, 353, 359, 367, 373, 379, 383, 389, 397, 401, 409, 419, 421, 431, 433, 439, 443, 449, 457,
461, 463, 467, 479, 487, 491, 499, 503, 509, 521, 523, 541, 547, 557, 563, 569, 571, 577, 587, 593,
599, 601, 607, 613, 617, 619, 631, 641, 643, 647, 653, 659, 661, 673, 677, 683, 691, 701, 709, 719,
727, 733, 739, 743, 751, 757, 761, 769, 773, 787, 797, 809, 811, 821, 823, 827, 829, 839, 853, 857,
859, 863, 877, 881, 883, 887, 907, 911, 919, 929, 937, 941, 947, 953, 967, 971, 977, 983, 991, 997 };
int main() {
Hash t;
t.count = 0;
t.sizeindex = 0;
t.elem = new Keytype[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
t.isfull = new bool[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
cout << "请先输入10个数" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
t.isfull[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
insertHash(t,temp,hashsize);
//print(t, hashsize);
}
print(t,hashsize);
cout << "输入需要查找的数:" << endl;
int key;
cin >> key;
int p;
int c = 0;
if (searchHash(t, key,p,c, hashsize)) {
cout << "查找成功" << endl;
cout << "为第" << p+1 << "个元素" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "查找失败" << endl;
}
cout << "输入需要删除的数:" << endl;
cin >> key;
if (DeleteHash(t, key, hashsize)) {
cout << "删除成功,删除后的结果:" << endl;
print(t, hashsize);
}
else {
cout << "删除失败" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}输入:
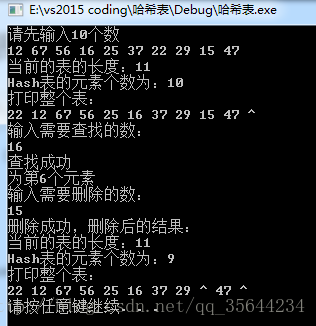
12 67 56 16 25 37 22 29 15 47
16
15输出:
3、二次探测的实现
对于二次探测,其实它和线性探测的插入删除代码都是一样的,只是查找过程中单位的移动量不同,所以我们只要修改对应的查找函数就可以了,修改成如下:
//查找对应的关键字
bool searchHash(Hash t, Keytype k, int & p,int &c,int * hashsize) {
p = k%hashsize[t.sizeindex];
while (t.isfull[p] && t.elem[p] != k && c < hashsize[t.sizeindex]-1) {
//++c;
//二次探测和线性探测的区别
if (c == 0) {
c=1;
p = (k + c) % hashsize[t.sizeindex];
}
else if (c > 0) {
c = -c;
p = (k - c*c) % hashsize[t.sizeindex];
}
else if (c < 0) {
c = -c + 1;
p = (k + c*c) % hashsize[t.sizeindex];
}
//继续往下寻找下一个散列结点
}
if (t.elem[p] == k) {
return true;
}
return false;
}输入:
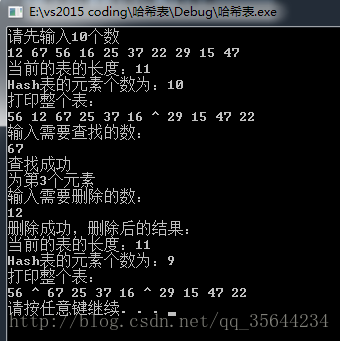
12 67 56 16 25 37 22 29 15 47
67
12输出:
4、链地址法的实现
- List.h文件的代码
#pragma once
/************************************************************/
/* 程序作者:Willam */
/* 程序完成时间:2017/3/29 */
/* 有任何问题请联系:[email protected] */
/************************************************************/
//@尽量写出完美的程序
//#pragma once是一个比较常用的C/C++杂注,
//只要在头文件的最开始加入这条杂注,
//就能够保证头文件只被编译一次。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Keytype;
struct Node {
Keytype data; //每个结点的值
Node * next; //下一个结点
Node() {
next = NULL;
}
};
//每次都是取质数最接近的质数
struct Hash {
Node * elem; //头结点链表
int sizeindex;
};
bool searchHash(Hash t, Keytype k, Node* & p, Node * & pre, int * hashsize);
bool insertHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize);
bool DeleteHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize);
void print(Hash t, int * hashsize);
- List.cpp文件的代码
#include"List.h"
bool searchHash(Hash t, Keytype k, Node * & p, Node * & pre, int * hashsize) {
int index = k%hashsize[t.sizeindex];
Node * head = t.elem[index].next;
pre = NULL;
while (head)
{//变量整个结点
p = head;
if (head->data == k) {
return true;
}
pre = head;
head = head->next;
}
return false;
}
//插入
bool insertHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize) {
Node * p;
Node * pre;
if (searchHash(t, k, p,pre, hashsize)) {
return false;
}
else {
Node * s = new Node;
s->data = k;
if (pre == NULL) {
int index = k%hashsize[t.sizeindex];
t.elem[index].next = s;
return true;
}
p->next = s;
}
return true;
}
//删除结点
bool DeleteHash(Hash & t, Keytype k, int * hashsize) {
Node * p;
Node * pre;
if (!searchHash(t, k, p,pre,hashsize)) {
return false;
}
else {
if (pre == NULL) {
int index = k%hashsize[t.sizeindex];
t.elem[index].next =p->next;
return true;
}
else {
pre->next = p->next;
delete p;
}
}
return true;
}
void print(Hash t, int * hashsize) {
Node * p;
for (int i = 0; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
cout << i << " ";
p = t.elem[i].next;
while (p) {
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "^" << endl;
}
}- main.cpp文件的代码
#include"list.h"
int hashsize[]={ 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107,
109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223,
227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293, 307, 311, 313, 317, 331, 337,
347, 349, 353, 359, 367, 373, 379, 383, 389, 397, 401, 409, 419, 421, 431, 433, 439, 443, 449, 457,
461, 463, 467, 479, 487, 491, 499, 503, 509, 521, 523, 541, 547, 557, 563, 569, 571, 577, 587, 593,
599, 601, 607, 613, 617, 619, 631, 641, 643, 647, 653, 659, 661, 673, 677, 683, 691, 701, 709, 719,
727, 733, 739, 743, 751, 757, 761, 769, 773, 787, 797, 809, 811, 821, 823, 827, 829, 839, 853, 857,
859, 863, 877, 881, 883, 887, 907, 911, 919, 929, 937, 941, 947, 953, 967, 971, 977, 983, 991, 997 };
int main() {
Hash t;
t.sizeindex = 0;
t.elem = new Node[hashsize[t.sizeindex]];
cout << "请先输入10个数" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < hashsize[t.sizeindex]; ++i) {
t.elem[i].next = NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
insertHash(t,temp,hashsize);
//print(t, hashsize);
}
print(t,hashsize);
cout << "输入需要查找的数:" << endl;
int key;
cin >> key;
Node *p;
Node *pre;
int c = 0;
if (searchHash(t, key,p,pre, hashsize)) {
cout << "查找成功" << endl;
cout << p->data << endl;
}
else {
cout << "查找失败" << endl;
}
cout << "输入需要删除的数:" << endl;
cin >> key;
if (DeleteHash(t, key, hashsize)) {
cout << "删除成功,删除后的结果:" << endl;
print(t, hashsize);
}
else {
cout << "删除失败" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}输入:
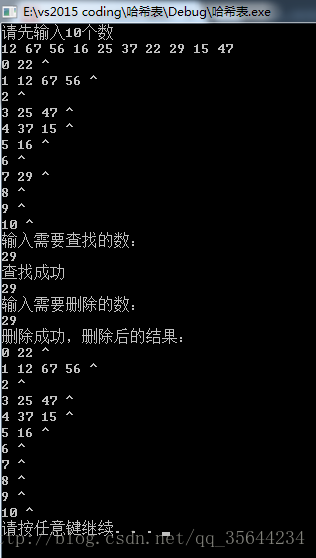
12 67 56 16 25 37 22 29 15 47
29
29输出: