Birthday Toy
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 866 Accepted Submission(s): 456
Problem Description
AekdyCoin loves toys. It is AekdyCoin’s Birthday today and he gets a special “Toy”.
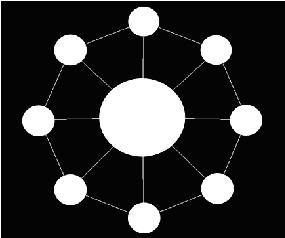
The “Toy” is in bulk and AekdyCoin has to make one by him. Let’s assume that the “Toy” has N small white beads and one Big bead .If someone want to make a “Toy”, he (or she) must always puts the Big bead in center, and then connect the other N small beads around it by using N sticks with equal length, and then the N small beads must be connected by N sticks with equal length, and it could be seen as a regular polygon. Figure 1 shows a “Toy” with 8 small white beads and one big white bead.
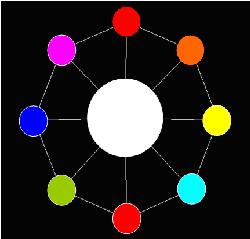
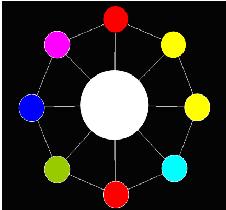
Now AekdyCoin has C kinds of available color, say blue, green, yellow, pink …etc. He wants to color these beads, but he thinks that must be too boring and stupid. So he colors these beads with one role: any adjacent beads couldn’t have same color. Figure 2 shows a legal situation, and Figure 3 shows an illegal situation.
It seems that the “Toy” becomes more interesting for AekdyCoin right now; however, he wants to color the big bead in center. Of course, he should follow the role above.
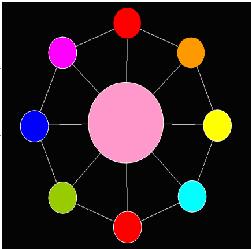
Now AekdyCoin begins to play with the “Toy”, he always colors the big beads and then the other small beads. He should color under the rule above. After several minutes, AekdyCoin finally makes a perfect “Toy”. Figure 4 shows a situation that is under the color rule.
AekdyCoin now want to know the different method to color the “Toy” whit at most K color. (“Toy” contains N small beads and one big bead.)
But, no, the problem is not so easy .The repetitions that are produced by rotation around the center of the circular necklace are all neglected. Figure 5 shows 8 “Toy”, they are regard as one method.
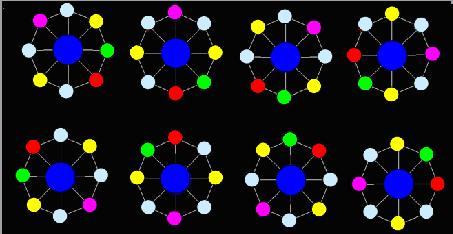
Now AekdyCoin will give you N and K, he wants you to help him calculate the number of different methods, because the number of method is so huge, so AekdyCoin just want you to tell him the remainder when divided by M.
In this problem, M = 1,000,000,007.
The “Toy” is in bulk and AekdyCoin has to make one by him. Let’s assume that the “Toy” has N small white beads and one Big bead .If someone want to make a “Toy”, he (or she) must always puts the Big bead in center, and then connect the other N small beads around it by using N sticks with equal length, and then the N small beads must be connected by N sticks with equal length, and it could be seen as a regular polygon. Figure 1 shows a “Toy” with 8 small white beads and one big white bead.

Now AekdyCoin has C kinds of available color, say blue, green, yellow, pink …etc. He wants to color these beads, but he thinks that must be too boring and stupid. So he colors these beads with one role: any adjacent beads couldn’t have same color. Figure 2 shows a legal situation, and Figure 3 shows an illegal situation.


It seems that the “Toy” becomes more interesting for AekdyCoin right now; however, he wants to color the big bead in center. Of course, he should follow the role above.
Now AekdyCoin begins to play with the “Toy”, he always colors the big beads and then the other small beads. He should color under the rule above. After several minutes, AekdyCoin finally makes a perfect “Toy”. Figure 4 shows a situation that is under the color rule.

AekdyCoin now want to know the different method to color the “Toy” whit at most K color. (“Toy” contains N small beads and one big bead.)
But, no, the problem is not so easy .The repetitions that are produced by rotation around the center of the circular necklace are all neglected. Figure 5 shows 8 “Toy”, they are regard as one method.

Now AekdyCoin will give you N and K, he wants you to help him calculate the number of different methods, because the number of method is so huge, so AekdyCoin just want you to tell him the remainder when divided by M.
In this problem, M = 1,000,000,007.
Input
The input consists of several test cases.(at least 1000)
Every case has only two integers indicating N, K
(3<=N<=10^9, 4<=K<=10^9)
Every case has only two integers indicating N, K
(3<=N<=10^9, 4<=K<=10^9)
Output
For each case, you should output a single line indicates the remainder of number of different methods after divided by M.
Sample Input
3 4 3 5 3 17 162 78923
Sample Output
8 40 19040 19469065
Source
N个小珠子加一个大珠子,大珠子放在中间,小的围着她形成一个等分的圆形,有k种颜色,在满足任意相邻珠子都不能同色的情况下的涂色方案数是多少,通过旋转能达到的算作一种方案。
不难想到先给大珠子一个颜色,然后求k-1种颜色涂n个小珠子的方案个数,最后乘上一个k就是答案。
ans=k/n * SUM{ C(g) } ,现在的问题是求C(g) ,也就是不动点个数,在朴素的题目里就是 k^x,但这里要求相邻珠子颜色不同就不能这么做了。先考虑把置换g分解成循环的形势,如果循环个数是1的话,不动点数量应该是0。f(i)=C(i) ,ans=k/n * SUM{f(gcd(i,n) | gcd(i,n)!=1 }
很容易想到对gcd分组利用欧拉函数减少运算次数。然后就是计算f了,这个f代表的问题等价于用k-1种颜色涂一个i珠子形成圆,相邻元素不同的方案数,用dp来求 f[i]=f[i-1]*(k-3)+f[i-2]*(k-2) (i>3) ,一个表示前一个环首尾元素不同,一个表示首尾元素相同,涵盖了所有情况。
n很大,这个递推式要用矩阵幂优化。
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
2670161 查看本文章


注意答案最后要减去gcd(i,n)==1的情况。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<map> 5 #include<set> 6 #include<vector> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<cmath> 9 using namespace std; 10 #define LL long long 11 #define PI acos(-1.0) 12 LL mod=1e9+7,N,K,F[5]; 13 vector<LL>prime; 14 bool isp[36000]; 15 struct matrix{ 16 LL a[2][2]; 17 matrix(){ 18 memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); 19 } 20 matrix operator*(matrix &tmp){ 21 matrix ans; 22 for(int i=0;i<2;++i){ 23 for(int j=0;j<2;++j){ 24 for(int k=0;k<2;++k){ 25 ans.a[i][j]+=a[i][k]*tmp.a[k][j]; 26 } 27 ans.a[i][j]%=mod; 28 } 29 } 30 return ans; 31 } 32 }A,U; 33 matrix qpow(matrix A,int b){ 34 matrix ans=U; 35 while(b){ 36 if(b&1) ans=ans*A; 37 A=A*A; 38 b>>=1; 39 } 40 return ans; 41 } 42 LL inv(LL n){ 43 if(n<=1) return n; 44 else return (mod-mod/n)*inv(mod%n)%mod; 45 } 46 LL phi(LL n){ 47 LL ans=n; 48 for(int i=0;prime[i]<=n;++i){ 49 if(n%prime[i]==0){ 50 ans=ans/prime[i]*(prime[i]-1); 51 while(n%prime[i]==0)n/=prime[i]; 52 } 53 } 54 if(n>1)ans=ans/n*(n-1); 55 return ans; 56 } 57 void init(){ 58 for(int i=2;i<=33333;++i){ 59 if(!isp[i]) prime.push_back(i); 60 for(int j=0;j<prime.size()&&i*prime[j]<=33333;++j){ 61 isp[i*prime[j]]=1; 62 if(i%prime[j]==0) break; 63 } 64 } 65 U.a[0][0]=U.a[1][1]=1; 66 } 67 LL f(LL n){ 68 if(n<=3)return F[n]; 69 matrix X=qpow(A,n-3); 70 return (X.a[0][0]*F[3]%mod+X.a[1][0]*F[2]%mod)%mod; 71 } 72 int main() 73 { 74 int t,i,j,k,d; 75 init(); 76 while(scanf("%lld%lld",&N,&K)!=EOF){ 77 78 A.a[0][0]=K-3; 79 A.a[0][1]=1; 80 A.a[1][0]=K-2; 81 A.a[1][1]=0; 82 F[1]=K-1; 83 F[2]=(K-1)*(K-2)%mod; 84 F[3]=F[2]*(K-3)%mod; 85 LL ans=0; 86 for(i=1;i*i<N;++i){ 87 if(N%i==0){ 88 ans=(ans+phi(N/i)*f(i))%mod; 89 ans=(ans+phi(i)*f(N/i))%mod; 90 } 91 } 92 if(i*i==N){ 93 ans=(ans+phi(i)*f(i))%mod; 94 } 95 ans=((ans-f(1)*phi(N))%mod+mod)%mod; 96 ans=ans*K%mod; 97 ans=ans*inv(N)%mod; 98 cout<<ans<<endl; 99 } 100 return 0; 101 }