SystemServer进程Android用户空间核心的的进程, framework层的很多services都是在SystemServer中进行创建并启动的. SystemServer也是由Zygote进行孵化的. 在将解启动zygote进程一文中知道启动zygote就会进入framework/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp的main函数中
在init.rc中zygote有四个参数:-Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server,各自的意义如下:
-Xzygote:该参数将作为虚拟机启动时所需的参数;
/system/bin:代表虚拟机程序所在目录;
--zygote:指明以ZygoteInit.java类中的main函数作为虚拟机执行入口;
--start-system-server:告诉Zygote进程启动SystemServer进程;
在app_main.cpp的main函数中会使用这些参数。前两个参数主要对虚拟机的设置,后面的参数主要处理systemServer
#if defined(__LP64__) //判断系统为64为还是32为, 进行赋予不同的进程名
static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = "ro.product.cpu.abilist64";
static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = "zygote64";
#else
static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = "ro.product.cpu.abilist32";
static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = "zygote";
#endif
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option. //解析运行时的参数,从解析init.rc中获得
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true; //在zygote模式中启动
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME; //设置进程的名字
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true; //启动System Server
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true; //在application模式启动
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12); //参数中有进程名,就设置
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg); //设置className
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}根据上面获取的参数, 知道我们正在zygote mode
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache(); //创建data/dalvik-cache,设置环境
if (startSystemServer) { //startSystemServer为true
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i])); //将所有参数添加如args中
} if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote); //调用ZygoteInit
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
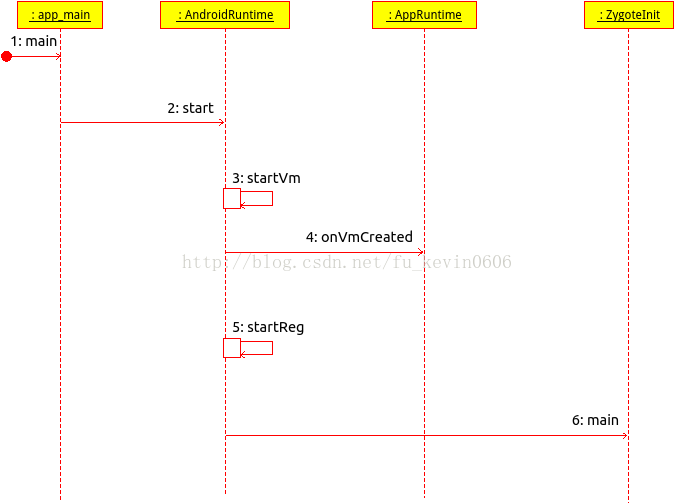
}由于AppRuntime派生与AndroidRuntime,故会调用AndroidRuntime的start函数,之后会启动虚拟机,并且对虚拟机进行初始化,注册JNI函数。最后根据在app_main中传递过来的启动类参数,获取它的静态main函数,启动ZygoteInit类的main函数。代码位置frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
/*
* Start the Android runtime. This involves starting the virtual machine
* and calling the "static void main(String[] args)" method in the class
* named by "className".
*
* Passes the main function two arguments, the class name and the specified
* options string.
*/
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
ALOGD(">>>>>> START %s uid %d <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)", getuid()); //在main.log中输出需要启动的className
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000; //在event log中输出android启动的时间
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
...........
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) { //启动虚拟机
return;
}
onVmCreated(env); //对虚拟机进行初始化
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) { //注册JNI函数
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
.......
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray); //调用ZygoteInit的main函数
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n"); //如果系统死掉会走到这里
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
在调用完ZygoteInit的main函数后,Zygote就进入了Java世界。
ZygoteInit代码位置frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java ,
在ZygoteInit的main函数中首先将从底层中传过来的参数获取出来.
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote"; //socketName为zygote
String abiList = null;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true; //start-system-server在参数列表中,故为true
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length()); //设置abiList
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) { //如果参数列表有socketName,就重新设置socketName
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}在ZygoteInit中通过RegisterZygoteSocket()进行注册Socket,用于进程间通信。
/**
* Registers a server socket for zygote command connections
*
* @throws RuntimeException when open fails
*/
private static void registerZygoteSocket(String socketName) {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName; //设置完整的socketName
try {
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName); //获取环境变量
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.setInt$(fileDesc); //设置文件描述符
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd); //根据文件描述符创建Server Socket
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
} 在Android系统中有很多的公共资源,所有的程序都会需要。而Zygote创建应用程序进程过程其实就是复制自身进程地址空间作为应用程序进程的地址空间,因此在Zygote进程中加载的类和资源都可以共享给所有由Zygote进程孵化的应用程序。所以就可以在Zygote中对公共类与资源进行加载,当应用程序启动时只需要加载自身特有的类与资源就行了,提高了应用软件的启动速度,这也看出面向对象编程中继承关系的好处。
static void preload() {
Log.d(TAG, "begin preload");
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "BeginIcuCachePinning"); //Systrace开始tag
beginIcuCachePinning();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK); //systrace结束tag
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadClasses");
preloadClasses(); //预加载Classes
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadResources");
preloadResources(); //预加载resources
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadOpenGL");
preloadOpenGL(); //预加载openGL
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
preloadSharedLibraries(); //预加载共享类库
preloadTextResources(); //预加载文本资源
// Ask the WebViewFactory to do any initialization that must run in the zygote process,
// for memory sharing purposes.
WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
endIcuCachePinning();
warmUpJcaProviders();
Log.d(TAG, "end preload");
} /**
* The path of a file that contains classes to preload.
*/
private static final String PRELOADED_CLASSES = "/system/etc/preloaded-classes";
private static void preloadClasses() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
InputStream is;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(PRELOADED_CLASSES); //将classes文件转变为文件输入流
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't find " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".");
return;
}
Log.i(TAG, "Preloading classes...");
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); //开始预加载时间
//.........
try {
BufferedReader br
= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is), 256); //封装成BufferReader
int count = 0;
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// Skip comments and blank lines.
line = line.trim();
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.equals("")) { //将没有用的行过滤掉
continue;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadClass " + line);
try {
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, "Preloading " + line + "...");
}
// Load and explicitly initialize the given class. Use
// Class.forName(String, boolean, ClassLoader) to avoid repeated stack lookups
// (to derive the caller's class-loader). Use true to force initialization, and
// null for the boot classpath class-loader (could as well cache the
// class-loader of this class in a variable).
Class.forName(line, true, null); //用反射将每一行的类没转化为class
count++;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Class not found for preloading: " + line);
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Problem preloading " + line + ": " + e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error preloading " + line + ".", t);
if (t instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) t;
}
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
}
throw new RuntimeException(t);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
}
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + count + " classes in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms."); //计算预加载classes一共花了多长时间
//......
} private static void preloadResources() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
try {
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
mResources.startPreloading();
if (PRELOAD_RESOURCES) {
Log.i(TAG, "Preloading resources...");
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); //记录开始预加载resources时间点
TypedArray ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray( //所需要加载的资源,其实就是在framework/base/core/res/res/values/arrays.xml中进行定义的
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_drawables); //获取需要预加载的drawables
int N = preloadDrawables(ar); //预加载drawables
ar.recycle();
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms."); //预加载drawables耗时情况
startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); //开始预加载colorState时间点
ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_color_state_lists); //获取预加载的color state lists
N = preloadColorStateLists(ar); //预加载color state
ar.recycle();
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resources in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime) + "ms."); //预加载resoures耗时
if (mResources.getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_freeformWindowManagement)) {
startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_freeform_multi_window_drawables);
N = preloadDrawables(ar);
ar.recycle();
Log.i(TAG, "...preloaded " + N + " resource in "
+ (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms.");
}
}
mResources.finishPreloading();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failure preloading resources", e);
}
} ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation(); //禁止创建线程commit 1ef8aef260c19236be023c429b41a46e7f5da8b0
Author: Andreas Gampe <[email protected]>
Date: Mon Apr 11 08:39:52 2016 -0700
Frameworks/base: Add no-thread marking to zygote
Use ZygoteHooks code to mark zygote initialization to not be
allowed to create threads. This is helpful when new classes are
found to be used by apps but cannot be preloaded as they spawn
threads. //根据注释可以看出,主要是由于担心用户新建线程提高预加载速度
//但是可能没做好同步工作, 当有的应用需要预加载的资源,但是多线程情况下还没有加载,发生问题
Bug: 27248115
Change-Id: I1dc3620d9e7d0054c672b993d89459fc4b353dfc
diff --git a/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java b/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
index 5980ab6..78b5d61 100644
--- a/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
+++ b/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
@@ -43,6 +43,7 @@ import com.android.internal.os.InstallerConnection.InstallerException;
import dalvik.system.DexFile;
import dalvik.system.PathClassLoader;
import dalvik.system.VMRuntime;
+import dalvik.system.ZygoteHooks;
import libcore.io.IoUtils;
@@ -597,6 +598,10 @@ public class ZygoteInit {
}
public static void main(String argv[]) {
+ // Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
+ // an error.
+ ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation(); //启动无多线程模式 .当在zygoteInit中新建线程系统挂掉
+
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
@@ -648,6 +653,8 @@ public class ZygoteInit {
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
+ ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation(); //停止无多线程模式
+
if (startSystemServer) {
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}并且循环进入监听模式, 监听创建进程的请求
if (startSystemServer) { //startSysteServer为true
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
runSelectLoop(abiList); //接受应用的socket链接请求
closeServerSocket(); //当退出循环时,系统出现问题, 所以也要将server socket关闭.之后Zygote等待客户端的创建进程请求.
/**
* Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
* worth at a time.
*
* @throws MethodAndArgsCaller in a child process when a main() should
* be executed.
*/
private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (i == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}