DirectBoot功能介绍
当手机已经通电开机但是用户并有解锁锁屏的时候,Android N运行于一个安全的模式,也就是Dierect Boot模式。
为了支持Dierect Boot模式,系统提供了两个存储数据的地方:
1.Credential encrypted storage,默认存储数据的地方,仅在用户解锁手机后可用。
2.Device encrypted storage,主要对应的就是Direct Boot使用的存储空间。在Direct Boot模式下和用户解锁手机后都可以使用的存储空间。
系统把部分系统数据和已经注册了相关权限的Apps的数据保存在device-encrypted store 。其他的数据默认保存到credential-encrypted store。
当手机开机,首先进入一个Dierect Boot的模式,在这个模式下只可以访问device-encrypted store下的数据,无法访问credential-encrypted store下的数据。当用户解锁后就都可以访问了。
一般情况下,应用是无法在Direct Boot模式下运行的
如果需要某个app能够在Direct Boot模式下运行,需要注册相关APP的组件。通常需要在这个模式下运行的app:
1.计划通知的应用,例如Clock
2.重要的用户通知的应用,例如sms
3.提供无障碍服务的应用,例如Talkback
应用组件申请在Direct Boot模式下运行:在AndroidManinfest.xml中设置 android:directBootAware="true"。
应用访问device encrypted storage:
创建Context.createDeviceEncryptedStorageContext().然后通过这个Context来使用device encrypted storage 的存储空间。
Context directBootContext = Context.createDeviceEncryptedStorageContext();
// Access appDataFilename that lives in device encrypted storage
FileInputStream inStream = directBootContext.openFileInput(appDataFilename);
// Use inStream to read content...监听广播ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED 。
或者接收ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED ,这个广播的意思是手机开机并且用户解锁。
也可调用UserManager.isUserUnlocked()方法来查询。
应用迁移已经存在的数据:
Context.migrateSharedPreferencesFrom()
Context.migrateDatabaseFrom()
两种方法在credential encrypted storage 和device encrypted storage存储空间之间去迁移preference 和database的数据.
启动FallbackHome流程
在分析7.0过程中发现在启动Launcher之前会先启动一个FallbackHome,之后才会启动Launcher,通过调查发现FallbackHome属于Settings中的一个activity,Settings的android:directBootAware为true,并且FallbackHome在category中配置了Home属性,而Launcher的android:directBootAware为false,所有只有FallbackHome可以在direct boot模式下启动。
<application android:label="@string/settings_label"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_settings"
............
android:directBootAware="true">
<!-- Triggered when user-selected home app isn't encryption aware -->
<activity android:name=".FallbackHome"
android:excludeFromRecents="true"
android:theme="@style/FallbackHome">
<intent-filter android:priority="-1000">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Intent getHomeIntent() {
Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
return intent;
}
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
&& mTopAction == null) {
// We are running in factory test mode, but unable to find
// the factory test app, so just sit around displaying the
// error message and don't try to start anything.
return false;
}
Intent intent = getHomeIntent();
ActivityInfo aInfo = resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId); //获取Home activity信息
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, true);
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked(intent, aInfo, reason); //启动FallbackHome
}
} else {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + intent, new Throwable());
}
return true;
}下面就要看具体什么时候发送ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED广播了。
代码位置packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/FallbackHome.java
* Copyright (C) 2015 The Android Open Source Project
package com.android.settings;
import android.app.Activity;
public class FallbackHome extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "FallbackHome";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Set ourselves totally black before the device is provisioned so that
// we don't flash the wallpaper before SUW
if (Settings.Global.getInt(getContentResolver(),
Settings.Global.DEVICE_PROVISIONED, 0) == 0) {
setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Black_NoTitleBar_Fullscreen);
}
registerReceiver(mReceiver, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED));
maybeFinish();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unregisterReceiver(mReceiver);
}
private BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
maybeFinish();
}
};
private void maybeFinish() {
if (getSystemService(UserManager.class).isUserUnlocked()) {
final Intent homeIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN)
.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
final ResolveInfo homeInfo = getPackageManager().resolveActivity(homeIntent, 0);
if (Objects.equals(getPackageName(), homeInfo.activityInfo.packageName)) {
Log.d(TAG, "User unlocked but no home; let's hope someone enables one soon?");
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 500);
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "User unlocked and real home found; let's go!");
finish();
}
}
}
private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
maybeFinish();
}
};
}
在开机将近尾声时WindowManagerService会调用enableScreenIfNeededLocked函数来判断是否将Screen enable。通过Handler发送ENABLE_SCREEN消息到主线程
void enableScreenIfNeededLocked() {
if (mDisplayEnabled) {
return;
}
if (!mSystemBooted && !mShowingBootMessages) {
return;
}
mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.ENABLE_SCREEN);
}在mH的handleMessage中处理消息ENABLE_SCREEN,调用函数performEnableScreen来处理。
final class H extends Handler {
........
public static final int ENABLE_SCREEN = 16;
........
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
case ENABLE_SCREEN: {
performEnableScreen();
break;
}
........
}1.checkWaitingForWindowsLocked所有Windows是否绘制完成
2.checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked开机动画时候完成
如果都完成了会通知AMS开机动画完成了,并且要enable Screen了。
public void performEnableScreen() {
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
if (mDisplayEnabled) { //如果设备已经enabled,返回
return;
}
if (!mSystemBooted && !mShowingBootMessages) { //如果不是系统启动,并且没有启动信息,返回
return;
}
// Don't enable the screen until all existing windows have been drawn.
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && checkWaitingForWindowsLocked()) { //如果不是强制设备enable,并且Windows还没有绘制完成,返回
return;
}
...........
if (!mForceDisplayEnabled && !checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked()) { //如果不是强制设备enable,并且开机动画还没有结束,返回
return;
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.WM_BOOT_ANIMATION_DONE, SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mDisplayEnabled = true;
if (DEBUG_SCREEN_ON || DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "******************** ENABLING SCREEN!");
// Enable input dispatch.
mInputMonitor.setEventDispatchingLw(mEventDispatchingEnabled);
}
try {
mActivityManager.bootAnimationComplete(); //通知ActivityManagerService开机动画完成
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
mPolicy.enableScreenAfterBoot(); //通知ActivityManagerService Screen可以enable
// Make sure the last requested orientation has been applied.
updateRotationUnchecked(false, false);
} private boolean checkWaitingForWindowsLocked() {
boolean haveBootMsg = false; //是否有启动message
boolean haveApp = false; //是否有APP
// if the wallpaper service is disabled on the device, we're never going to have
// wallpaper, don't bother waiting for it
boolean haveWallpaper = false; //是否有Wallpaper
boolean wallpaperEnabled = mContext.getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_enableWallpaperService)
&& !mOnlyCore; //Wallpaper是否可用
boolean haveKeyguard = true; //是否有Keyguard
// TODO(multidisplay): Expand to all displays?
final WindowList windows = getDefaultWindowListLocked(); //获取所有的Windows
final int N = windows.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
WindowState w = windows.get(i);
if (w.isVisibleLw() && !w.mObscured && !w.isDrawnLw()) {
return true;
}
if (w.isDrawnLw()) { 判断Window的属性
if (w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_BOOT_PROGRESS) {
haveBootMsg = true;
} else if (w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_APPLICATION) {
haveApp = true;
} else if (w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_WALLPAPER) {
haveWallpaper = true;
} else if (w.mAttrs.type == TYPE_STATUS_BAR) {
haveKeyguard = mPolicy.isKeyguardDrawnLw();
}
}
}
// If we are turning on the screen to show the boot message,
// don't do it until the boot message is actually displayed.
if (!mSystemBooted && !haveBootMsg) {
return true;
}
// If we are turning on the screen after the boot is completed
// normally, don't do so until we have the application and
// wallpaper.
if (mSystemBooted && ((!haveApp && !haveKeyguard) ||
(wallpaperEnabled && !haveWallpaper))) {
return true;
}
return false;
} private boolean checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked() {
if (SystemService.isRunning(BOOT_ANIMATION_SERVICE)) {
mH.removeMessages(H.CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED,
BOOT_ANIMATION_POLL_INTERVAL);
if (DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "checkBootAnimationComplete: Waiting for anim complete");
return false;
}
if (DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "checkBootAnimationComplete: Animation complete!");
return true;
} case CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED: {
final boolean bootAnimationComplete;
synchronized (mWindowMap) {
if (DEBUG_BOOT) Slog.i(TAG_WM, "CHECK_IF_BOOT_ANIMATION_FINISHED:");
bootAnimationComplete = checkBootAnimationCompleteLocked();
}
if (bootAnimationComplete) {
performEnableScreen();
}
} @Override
public void bootAnimationComplete() {
final boolean callFinishBooting;
synchronized (this) {
callFinishBooting = mCallFinishBooting;
mBootAnimationComplete = true; //设置mBootAnimationComplete为true
}
if (callFinishBooting) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "FinishBooting");
finishBooting(); //调用finishBooting
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}
final void finishBooting() {
synchronized (this) {
if (!mBootAnimationComplete) {
mCallFinishBooting = true;
return;
}
mCallFinishBooting = false;
}
................
// Let system services know.
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED);
...............
mUserController.sendBootCompletedLocked(
new IIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode,
String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
requestPssAllProcsLocked(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(),
true, false);
}
}
});具体流程图如下:
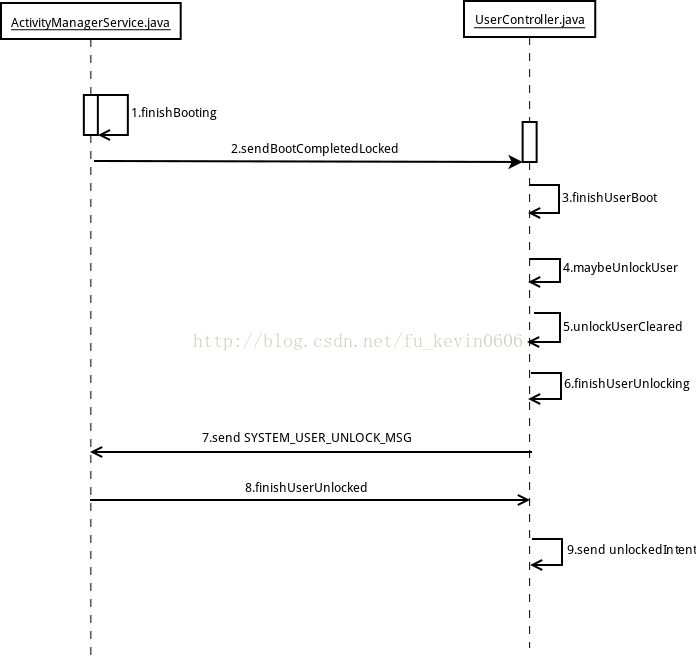
经过一系列的代码跳转,最终调用UserController的finishUserUnlocked函数来发送ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED广播。
void finishUserUnlocked(final UserState uss) {
.................
final Intent unlockedIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED);
unlockedIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, userId);
unlockedIntent.addFlags(
Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY | Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
mService.broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, unlockedIntent, null, null, 0, null,
null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID,
userId);
.................
}问题分析
就是因为现在启动Launcher时多了一个流程,导致启动launcher比原来6.0要慢。通过查看开机log可以看到从启动FallbackHome到启动google桌面花费了4s
18:10:50.653 769 1910 I ActivityManager: START u0 {act=android.intent.action.MAIN cat=[android.intent.category.HOME] flg=0x10000100 cmp=com.android.settings/.FallbackHome} from uid 0 on display 0
18:10:54.586 2029 2029 D FallbackHome: User unlocked and real home found; let's go!
18:10:54.615 769 2207 I ActivityManager: START u0 {act=android.intent.action.MAIN cat=[android.intent.category.HOME] flg=0x10000100 cmp=com.google.android.setupwizard/.SetupWizardActivity} from uid 0 on display 0
小结
Android 7.0新增了DirectBoot功能,AOSP中为实现该功能修改了开机代码流程,并且这部分流程并未根据设备是否支持DirectBoot做区分,只是流程上做了兼容,确保不支持DirectBoot的设备在这套流程下也能正常开机。
在这套流程下,用户解锁后才可进入非directBootAware应用,包括Launcher。com.android.settings/.FallbackHome中判断用户解锁状态,已解锁才会Finish掉去启动Launcher,未解锁就等待ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED广播后再去启动Launcher。非DirectBoot模式下耗时4s就是在等待finishBooting后的系统广播ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED。
目前已从APP和PackageManagerService的角度尝试修改,在开机流程中绕过FallbackHome,但验证失败:
1)去除FallbackHome的android.intent.category.Home属性会导致停留在开机动画之后的界面。因为此时仍旧处于未解锁状态,且Launcher非directBootAware应用,PMS中的限制导致此时无法启动Launcher;
2)修改FallbackHome和Launcher的优先级仍旧先启动FallbackHome;
3)将Launcher标记为directBootAware应用会导致开机后Launcher crash。因为Launcher中的widget仍旧是非directBootAware的,此时仍旧无法启动,除非将widget相关的APP都标记为directBootAware;
4)PMS依赖手机当前的状态,需要user解锁才能正常查询。如果强制修改,不考虑DirectBoot和当前启动状态,即使当前user未解锁,依然可以查询符合条件的component,修改后会有无法开机的现象。因为Launcher不是directBootAware的,当前手机user尚未解锁,涉及存储相关的解锁也未进行。
开机绕过FallbackHome涉及的修改面很多,并非通过修改APP或PMS可以实现,还涉及存储区域解锁以及用户状态和ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED广播的修改,对AOSP开机流程改动较大,暂时尚未有较好的优化方案,欢迎大神指教。