2017年学习的数据结构作的笔记,一些算法思想(伪代码实现)在日常学习中仍显得很重要,很多很多,在此记录整理不断补充,反复看反复理解反复记忆,加油!
1、判别读入的一个以'@'为结束符的字符序列是否为"回文"(palindrome,正反相同)
status palindrome()
{
initStack(s);//调用初始化s栈函数
initQueue(Q);//初始化队列Q
while((ch=getchar())!='@')
{
push(s,ch);//字符ch入s栈
enQueue(Q,ch);//字符ch入Q队列
}
while(!StackEmpty(s))
{
pop(s,ch1);//s栈栈顶元素ch1出栈
deQueue(Q,ch2);//Q队列队首元素ch2出队列
if(ch1=ch2)
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}2、栈实现表达式中括号匹配
int match(char exp[],int n)//表达式存放在exp[]中
{
//定义一个栈并初始化
char stack[Maxsize];
int top=-1;
//表达式从左向右开始遍历
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
if(exp[i]=='(')
stack[++top]='(';//入栈'('符号
if(exp[i]==')')
{
if(top==-1)
return 0;//判栈空,说明有多余')',匹配不成功
else
--top;//相当于'('=Stack[top--],出栈
}
}
if(top==-1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}3、求后缀表达式(suffix expression)的数值
//表达式中不同运算符进行不同操作
int suffixExp(int a, char op,int b)
{
if(op=='+') return a+b;
if(op=='-') return a-b;
if(op=='*') return a*b;
if(op=='/')
{
if(b==0)
{
printf("ERROR");
return 0;
}
else
return a/b;
}
}
//后缀表达式
int com(char exp[])
{
int a,b,c;//a,b为操作数,c保存结果
char op;//op取运算符
int stack[Maxsize];
int top=-1;
for(int i=0;exp[i]!='\0';++i)
{
if(exp[i]>='0'&exp[i]<='9')
stack[++top]=exp[i]-'0';//栈中是整数型,数组中是字符型,将字符型减去‘0’,得到整数型
else //遇到运算符
{
op=exp[i];
b=stack[top--];//第1个弹出的数在右边
a=stack[to--];//第2个弹出的数在左边
c=op[a,op,b];//位置不可变,因为除法有要求的
stack[++top]=c;
}
}
return stack[top];
}4、用不带头结点的单链表存储链栈
//初始化栈
void initStack(LNode *&1st)
{
1st=Null;//1st为第1个结点,即栈顶元素
}
//判栈空
int isEmpty(LNode *1st)
{
if(1st==Null)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//进栈
void push(LNode *&1st,int x)
{
LNode *p;
p=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
p->next=Null;
p->data=x;
p->next=1st;
1st=p;
}
//出栈
int pop(LNode *&1st,int &x)
{
LNode *p;
if(1st==Null)
return 0;
p=1st;
x=p->data;
1st=p->next;
free(p);
return 1;
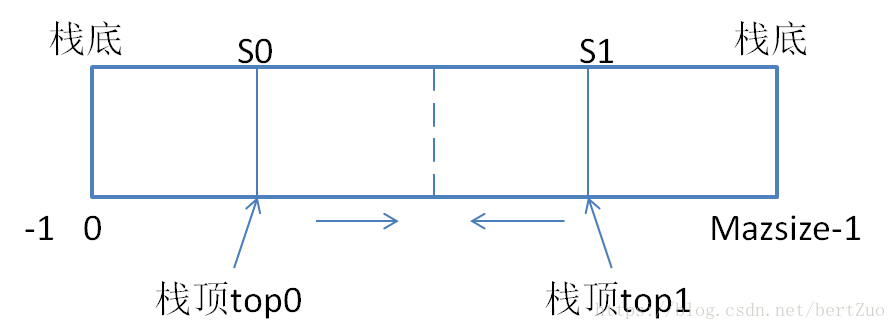
}5、共享一个存储区的共享栈S0,S1,入栈操作
int push(SeqStack &st,int stNo,int x)//stNo是栈编号
{
if(st.top[0]+1<st.top[1])//存储区未满
{
if(stNo==0)
{//x元素进S0栈,在存储区elem[0...maxsize-1]中的下标是增加的
++(st.top[0]);
st.elem[st.top[0]]=x;
return 1;
}
else if(stNo==1)
{//x元素进S1栈,在存储区elem[0...maxsize-1]中的下标是减小的
--(st.top[1]);
st.elem[st.top[1]]=x;
return 1;
}
else return -1;//栈编号有误
}
else return 0;//存储区已满
}6、共享一个存储区的共享栈S0,S1,出栈操作
int pop(SeqStack &st,int stNo,int &x)
{
if(stNo==0)
{
if(st.top[0]!=-1)//S0栈不空,可出栈操作
{
x=st.elem[st.top[0]];
--(st.top[0]);
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
else if(stNo==1)
{
if(st.top[1]!=Maxsize)
{
x=st.elem[st.top[1]];
++(st.top[1]);
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
else return -1;
}7、两个栈模拟一个队列,入队列操作
int enQueue(SeqStack &s1,SeqStack &s2,int x)
{
int y;
//若s1满则看s2是否为空
if(s1.top==Maxsize-1)
{
//s2也不为空,全都满了,无法入元素操作
if(!isEmpty(s2)) return 0;
else if(isEmpty(s2))
{
//当s1栈不空时,循环进行s1栈的栈顶元素出栈再入栈s2栈
while(!isEmpty(s1))
{
pop(s1,y);//s1栈顶元素y出栈
push(s2,y);//元素y入s2栈
}
push(s1,x);
return 1;
}
}
else//若s1没有满则元素x直接入栈
{
push(s1,x);
return 1;
}
}8、两个栈模拟一个队列,出队列操作
int deQueue(SeqStack &s1,SeqStack &s2,int &x)
{
int y;
//s2栈不空可直接出元素
if(!isEmpty(s2))
{
pop(s2,x);//s2栈栈顶元素出栈
return 1;
}
else//若s2栈为空则看s1是否为空
{
if(isEmpty(s1))
{
while(!isEmpty(s1))
{
pop(s1,y);
push(s2,y);
}
pop(s2,x);
return 1;
}
}
}