随机数模块random
python3.7
手册
https://docs.python.org/3/library/random.html#module-random
部分图片转自wiki
常用函数
random.seed()
random.seed(a=None, version=2)
- 设置随机种子 ,用于同步不同运行环境的随机数。
random.getstate()
random.getstate()
- 获得当前状态,用于恢复状态
random.setstate()
random.setstate(state)
- 恢复状态
>>> import random
>>> s=random.getstate()
>>> random.random()
0.15441857485858956
>>> random.random()
0.6330314601528841
>>> random.setstate(s)
>>> random.random()
0.15441857485858956
>>> random.random()
0.6330314601528841
>>> random.random()
0.04725013105129261random.getrandbits()
random.getrandbits(k)
- 生成占内存k位以内的随机整数,硬核秃头专属。
>>> import random
>>> random.getrandbits(10)
674
>>> random.getrandbits(10)
10
>>> random.getrandbits(10)
745
>>> random.getrandbits(10)
560
>>> random.getrandbits(10)
162random.random()
random.random()
- 随机产生一个[0,1.)数字。
>>> random()
0.37444887175646646random.uniform()
random.uniform(a, b)
- 产生一个a、b区间的随机数。
>>> uniform(2.5, 10.0)
3.1800146073117523random.randrange()
random.randrange(start, stop[, step])
- 整数随机。
- 功能等同于
choice(range(start, stop, step))。
>>> randrange(10) # 0到9随机
7
>>> randrange(0, 101, 2) # 0到100随机偶数
26random.randint()
random.randint(a, b)
- 返回一个[a,b]的随机整数。
- 功能等同于
randrange(a, b+1)。
random.choice()
random.choice(seq)
- 返回对象中的一个随机元素。
random.choices()
random.choices(population, weights=None, *, cum_weights=None, k=1)
- 随机选择,是
random.choice(seq)的升级版本。
>>> choice(['win', 'lose', 'draw'])
'draw'random.sample()
random.sample(population, k)
- 随机取样
>>> sample([10, 20, 30, 40, 50], k=4)
[40, 10, 50, 30]- choices与sample的区别:
- choices在抽取随机元素时是包含重复元素的,即:一个元素可能会被抽取多次。
- 反之,在sample中,抽取的元素是不重复的。
- 所以,在抽取元素大于样本集总数时,choices会继续而sample会报错:
>>> import random
>>> random.choices([1,2,3,4],k=4)
[4, 3, 4, 4]
>>> random.sample([1,2,3,4],k=4)
[3, 1, 2, 4]
>>> random.choices([1,2,3,4],k=5)
[3, 3, 2, 3, 2]
>>> random.sample([1,2,3,4],k=5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module>
random.sample([1,2,3,4],k=5)
File "F:\python\lib\random.py", line 321, in sample
raise ValueError("Sample larger than population or is negative")
ValueError: Sample larger than population or is negative
>>> random.shuffle()
random.shuffle(x[, random])
- 打乱序列
>>> deck = 'ace two three four'.split()
>>> shuffle(deck)
>>> deck
['four', 'two', 'ace', 'three']不同的分布模式
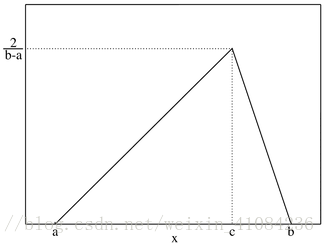
random.triangular(low, high, mode)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triangular_distribution
random.betavariate(alpha, beta)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_distribution
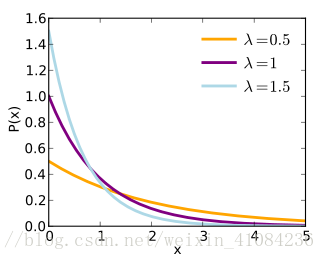
random.expovariate(lambd)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exponential_distribution
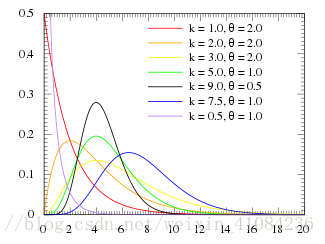
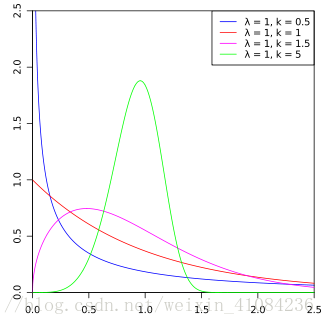
random.gammavariate(alpha, beta)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_distribution
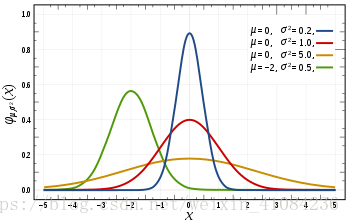
random.gauss(mu, sigma)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution
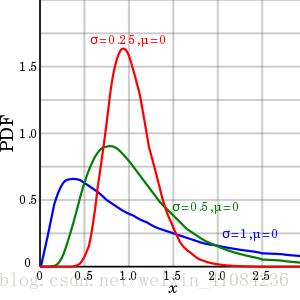
random.lognormvariate(mu, sigma)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log-normal_distribution
random.normalvariate(mu, sigma)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution
random.vonmisesvariate(mu, kappa)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Mises_distribution
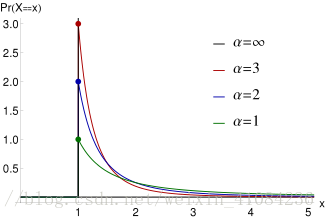
random.paretovariate(alpha)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_distribution
random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weibull_distribution
- random.triangular(low, high, mode)
- 以三角分布的概率分布返回随机数。
- 以三角分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter() # 方便偷懒,用Counter统计次数。
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.triangular(0,9,7)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
================= RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\blank.py =================
Counter({'7': 1963, '6': 1946, '5': 1617, '4': 1264, '8': 1105, '3': 944, '2': 668, '1': 323, '9': 138, '0': 32})
0
1***
2*******
3*********
4*************
5****************
6*******************
7********************
8***********
9*
- random.betavariate(alpha, beta)
- 以beta分布的概率分布返回0到1之间的随机数。
- 以beta分布的概率分布返回0到1之间的随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.betavariate(2,5)*10))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
Counter({'2': 2424, '3': 2173, '1': 1941, '4': 1512, '5': 1000, '6': 416, '0': 316, '7': 167, '8': 48, '9': 3})
0***
1*******************
2************************
3**********************
4***************
5**********
6****
7**
8
9
- random.expovariate(lambd)
- 以指数分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.expovariate(1)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============== RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\expovariate.py ==============
Counter({'0': 3950, '1': 3862, '2': 1403, '3': 484, '4': 192, '5': 73, '6': 18, '7': 12, '8': 4, '9': 2})
0****************************************
1***************************************
2**************
3*****
4**
5*
6
7
8
9- random.gammavariate(alpha, beta)
- 以gamma分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.gammavariate(9,0.5)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============== RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\gammavariate.py ==============
Counter({'4': 2671, '5': 2244, '3': 2054, '6': 1303, '2': 698, '7': 616, '8': 236, '1': 103, '9': 89, '0': 32})
0
1*
2*******
3*********************
4***************************
5**********************
6*************
7******
8**
9*
- random.gauss(mu, sigma)
- 以高斯分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.gauss(5,1)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
================= RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\gauss.py =================
Counter({'5': 3803, '4': 2429, '6': 2418, '3': 660, '7': 582, '2': 59, '8': 41, '9': 6, '1': 2})
0
1
2*
3*******
4************************
5**************************************
6************************
7******
8
9- random.lognormvariate(mu, sigma)
- 以对数正态分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.triangular(5,0.02)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============= RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\lognormvariate.py =============
Counter({'3': 3232, '2': 3168, '4': 1626, '1': 1621, '0': 178, '5': 175})
0**
1****************
2********************************
3********************************
4****************
5**
6
7
8
9
random.normalvariate(mu, sigma)
- 同
random.gauss(mu, sigma)
- 同
random.vonmisesvariate(mu, kappa)
- 以von Mises分布的概率分布返回随机数。
- 又作圆上正态分布
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.vonmisesvariate(3.14,2)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(7):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============ RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\vonmisesvariate.py ============
Counter({'3': 4795, '4': 2609, '2': 1732, '5': 437, '1': 296, '6': 87, '0': 44})
0
1***
2*****************
3************************************************
4**************************
5****
6*- random.paretovariate(alpha)
- 以Pareto分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.paretovariate(2)))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============= RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\paretovariate.py =============
Counter({'1': 5644, '2': 2853, '3': 830, '4': 347, '5': 179, '6': 82, '7': 76, '8': 45, '9': 36, '0': 27})
0
1********************************************************
2*****************************
3********
4***
5**
6*
7*
8
9- random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta)
- 以Weibull分布的概率分布返回随机数。
import random
import collections
counter=collections.Counter()
for i in range(10000):
step=str(round(random.weibullvariate(1,5)*5))
counter.update(step)
print(counter)
for i in range(10):
print(str(i),end='')
value=round(counter[str(i)]/100.)
for j in range(value):
print('*',end='')
print('')
============= RESTART: F:\PyWorkspace\LeetCode\weibullvariate.py =============
Counter({'5': 3601, '4': 2847, '6': 1753, '3': 1247, '2': 294, '7': 239, '1': 17, '8': 2})
0
1
2***
3************
4****************************
5************************************
6******************
7**
8
9