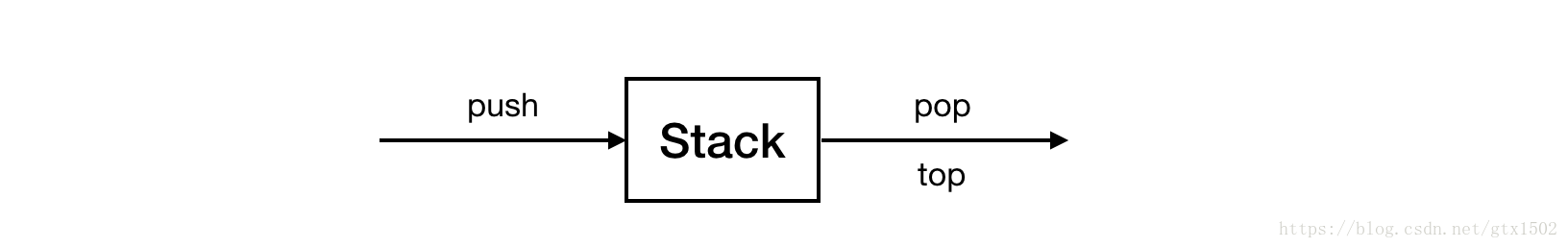
1 栈模型
1.1 定义
栈(stack)是限制插入和删除只能在一个位置上进行的表(list),该位置是表的末端,称为栈的顶(top)。
LIFO(先进后出)表
1.2 基本操作
push(进栈) :插入元素
pop(出栈):删除元素
1.3 特性
- 只有栈顶元素可以访问
top:查询栈顶元素 - 以非常快的常数时间运行
2 栈的实现
2.1 栈的链表实现
这里用之前写的双链表实现,实际上单链表就可以实现栈。
栈的链表实现
package chapter2.stack.stack_linkedList;
import chapter2.linkedList.MyLinkedList;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
public class LinkedListStack {
private MyLinkedList linkedList;
LinkedListStack() {
linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
}
/**
* 插入元素
*
* @param object 要插入的元素
*/
public void push(Object object) {
linkedList.add(object);
}
/**
* 移除栈顶元素
*
* @return 栈顶元素
*/
public Object pop() {
if (linkedList.size() == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
Object oldElement = linkedList.get(linkedList.size() - 1);
linkedList.remove(linkedList.size() - 1);
return oldElement;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
*
* @return 为空:true 非空:false
*/
public boolean empty() {
return linkedList.size() == 0;
}
/**
* 查看栈顶元素(java的Stack实现中为peek方法)
*
* @return 栈顶元素
*/
public Object top() {
if (linkedList.size() == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return linkedList.get(linkedList.size() - 1);
}
}
测试类
package chapter2.stack.stack_linkedList;
public class TestStack_linkedList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedListStack linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack();
linkedListStack.push("a");
linkedListStack.push("b");
System.out.println("pop:" + linkedListStack.pop());
System.out.println("top is:" + linkedListStack.top());
linkedListStack.pop();
System.out.println("empty:" + linkedListStack.empty());
//linkedListStack.top(); 此处会有EmptyStackException
}
}
输出
pop:b
top is:a
empty:true2.2 栈的数组实现
栈的数组实现
package chapter2.stack.stack_array;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
public class ArrayStack {
private Object[] data; //栈数据
private int top; //栈顶位置
private int maxSize; //Stack最大容量
ArrayStack(int size) {
maxSize = size;
data = new Object[size];
top = -1;
}
/**
* 插入元素
*
* @param object 要插入的元素
*/
public void push(Object object) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈已满");
return;
}
top++;
data[top] = object;
}
/**
* 移除栈顶元素
*
* @return 栈顶元素
*/
public Object pop() {
if (empty()) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
Object topData = data[top];
top--;
return topData;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
*
* @return 为空:true 非空:false
*/
public boolean empty() {
return top == -1;
}
/**
* 查看栈顶元素(java的Stack实现中为peek方法)
*
* @return 栈顶元素
*/
public Object top() {
if (empty()) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return data[top];
}
private boolean isFull() {
return top + 1 == maxSize;
}
}测试类
package chapter2.stack.stack_array;
public class TestStack_array {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//为了测试栈空间用尽的情况设置得比较小,实际应用时可以设大一些
ArrayStack arrayStack = new ArrayStack(5);
arrayStack.push("a");
arrayStack.push("b");
arrayStack.push("c");
arrayStack.push("d");
arrayStack.push("e");
arrayStack.push("f");
System.out.println("top is:" + arrayStack.top());
System.out.println("pop:" + arrayStack.pop());
arrayStack.pop();
arrayStack.pop();
arrayStack.pop();
arrayStack.pop();
System.out.println("empty:" + arrayStack.empty());
//arrayStack.top(); //此处会有EmptyStackException
}
}
输出
栈已满
top is:e
pop:e
empty:true2.3 比较
数组实现栈的方式避免了使用链,较为流行。
3 栈的应用
3.1 平衡符号
作用
检测符号(括号、注释符号)是否成对,可用于编译器检查实现方式
- 建一个空栈。
- 从头到尾逐个字符读入文件。
- 遇到开放符号,将其推入栈中。
- 遇到封闭符号:若栈空,则报错;否则弹出栈元素。若弹出的符号不是其对应的开放符号,则报错。
- 在文件结尾,如果栈非空则报错。
3.2 后缀表达式
- 不需要知道任何优先规则
- 计算一个后缀表达式花费时间为 O(N)
- 过程:遇到数字推入栈中;遇到运算符则弹出两个数字并计算,把计算结果推入栈中
例:1 2 3 * +(对应中缀表达式为 1 + 2 * 3)
1. 把 1,2,3 依次推入栈中

2. 读到 * 号,把 3 和 2 弹出,然后把它们的积 6 推入栈中

3. 读到 + 号,把 6 和 1 弹出,然后把它们的和 7 推入栈中

4. 计算结果为 7
3.3 中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
package chapter2.stack.infixToPostfix;
import chapter2.stack.stack_array.ArrayStack;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class InfixToPostfix {
private ArrayStack stack;
private Map<Character, Integer> map;
InfixToPostfix() {
stack = new ArrayStack(20);
map = new HashMap();
map.put('+', 1);
map.put('-', 1);
map.put('*', 2);
map.put('/', 2);
map.put('(', 0);
}
String parse(String infix) {
String postfix = "";
for (int i = 0; i < infix.length(); i++) {
char ch = infix.charAt(i);
if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
if (i > 0 && !Character.isDigit(infix.charAt(i - 1))) {
postfix += ' ';
}
postfix += ch;
} else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/' || ch == '(') {
if (stack.empty()) {
stack.push(ch);
} else if (map.get(ch) > map.get(stack.top()) || ch == '(') { //当前运算符优先级高于栈中运算符,或当前运算符为(,入栈
stack.push(ch);
} else {
for (int j = i; j >= 0 && !stack.empty(); j--) { //依次弹出优先级比当前运算符低的运算符,遇到(停止
if (stack.top() == '(' || map.get(ch) > map.get(stack.top())) {
break;
}
char pop = (char) stack.pop();
if (pop == '(') {
break;
} else {
postfix += ' ';
postfix += pop;
}
}
stack.push(ch);
}
} else if (ch == ')') {
for (int j = i; j >= 0 && !stack.empty(); j--) {
char pop = (char) stack.pop();
if (pop == '(') {
break;
} else {
postfix += ' ';
postfix += pop;
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法字符" + ch);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < infix.length() && !stack.empty(); i++) {
char pop = (char) stack.pop();
postfix += ' ';
postfix += pop;
}
return postfix;
}
}测试
package chapter2.stack.infixToPostfix;
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
InfixToPostfix infixToPostfix=new InfixToPostfix();
String s1=infixToPostfix.parse("6+(1+20*3)*5");
String s2=infixToPostfix.parse("3+(2-5)*6/3");
String s3=infixToPostfix.parse("1+((2+3)*4)-5");
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
}
}
输出
6 1 20 3 * + 5 * +
3 2 5 - 6 * 3 / +
1 2 3 + 4 * + 5 -