①C语言版
亮点:
1.qsort(b, j, sizeof(char), cmp);
C语言标准库函数
2.while(处理括号 || 处理否定 || 处理合取 ... );
可以消除运算符优先级的问题,但是还是解决不了同级运算符的先后问题。
如:p+q*r会变成p+(q*r)
3.模拟辗转相除法给变元赋值
代码简单明了,但是效率比不上位运算
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "ctype.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
int cmp(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*((char*) a) - *((char*) b));
}
int getalpha(char a[],char b[])
{
char tmpc=' ';
int n=strlen(a),i=0,j=0,k=0;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(isalpha(a[i])) //改进1:使用isalpha()函数判断大小写,简洁明了
// if(((a[i]>='a')&&(a[i]<='z'))||((a[i]>='A')&&(a[i]<='Z')))
{
for(k=0; k<j; k++)
{
if(b[k]==a[i])
{
break;
}
}
if(k>=j)
{
b[j]=a[i];
j++;
}
}
}
qsort(b,j,sizeof(char),cmp); //改进2:用快排代替冒泡排序,提高效率
/* for(i=0; i<j-1; i++)
{
for(k=0; k<j-i-1; k++)
{
if(b[k]>b[k+1])
{
tmpc=b[k];
b[k]=b[k+1];
b[k+1]=tmpc;
}
}
}
*/
b[j]='\0';
return j;
}
void fillValue(char a[],char varchar[],int nvar,
char valchar[],char resultchar[])
{
//a是原始公式,varchar是变元列表如pqrs,
//valchar是变元的某次取值
int nLen=strlen(a),i=0,j=0,k=0;
for(i=0; i<nLen; i++)
resultchar[i]=a[i];
resultchar[i]='\0';
for(i=0; i<nLen; i++)
{
//原公式中的每个字符
for(j=0; j<nvar; j++)
{
//公式中的字符是第几个变元
if(resultchar[i]==varchar[j])
{
//是第j个变元,其值换成第j个值
resultchar[i]=valchar[j];
break;
}
}
}
}
bool negatecal(char a[]) //改进5:将函数返回类型改为bool,若在字符串中存在!1或!0,就把第一个!1或!0改成0或1,然后返回true;如果没找到,返回false
//void negatecal(char a[]) //...下面的函数进行完全相同的修改
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while(i<strlen(a))
{
//如果当前位置起形如"!1"则换成"1"
j=i;
_result=0;
if((j+1<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='!')&&(a[j+1]=='1'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+1<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='!')&&(a[j+1]=='0'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
if(_result==1)
{
//如果有运算则后面的往前移
j++;
while(a[j+1]!='\0')
{
//后面的字符往前移1格
a[j]=a[j+1];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1; //改进5
}
else
{
//没有!0或!1则看下一个指针
i++;
}
}
return 0; //改进5
}
bool kuanhao(char a[])
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while (i<strlen(a)) //如果当前位置起形如(1)则换成1
{
j=i;
_result=0;
if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='(')&&(a[j+1]=='1')&&(a[j+2]==')'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='(')&&(a[j+1]=='0')&&(a[j+2]==')'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
if (_result==1)
{
j++;
while (a[j+2]!='\0')
{
a[j]=a[j+2];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool conYsh(char a[])
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while (i<strlen(a)) //如果当前位置其形如1*1则换成"1"
{
j=i;
_result=0;
if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='*')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='*')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='*')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='*')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
if (_result==1)
{
j++;
while (a[j+2]!='\0')
{
a[j]=a[j+2];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool biCondYsh (char a[]) //1=1
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while(i<strlen(a))
{
j=i;
_result=0;
if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='=')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='=')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='=')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='=')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
if(_result==1)
{
j++;
while(a[j+2]!='\0')
{
a[j]=a[j+2];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool condYsh(char a[]) //1-1
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while(i<strlen(a))
{
j=i;
_result=0;
if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='-')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='0')&&(a[j+1]=='-')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='-')&&(a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j]='0';
_result=1;
}
else if((j+2<strlen(a))&&(a[j]=='1')&&(a[j+1]=='-')&&(a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j]='1';
_result=1;
}
if(_result==1)
{
j++;
while(a[j+2]!='\0')
{
a[j]=a[j+2];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool disConjYsh(char a[])
{
int _result=0,i=0,j=0;
while (i<strlen(a))
{
j = i;
_result =0;
if ((j+2<strlen(a)) && (a[j]=='0') && (a[j+1]=='+')&& (a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j] = '0' ;
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a)) && (a[j]=='0') && (a[j+1]=='+')&& (a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j] = '1';
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a)) && (a[j]=='1') && (a[j+1]=='+')&& (a[j+2]=='0'))
{
a[j] ='1' ;
_result=1;
}
else if ((j+2<strlen(a)) && (a[j]=='1') && (a[j+1]=='+')&& (a[j+2]=='1'))
{
a[j] ='1' ;
_result=1;
}
if (_result==1)
{
j ++;
while (a[j+2]!='\0')
{
a[j]=a[j+2];
j++;
}
a[j]='\0';
return 1;
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
char pstate[120],pstate0[120],charList[120],charVal[120];
char minItem[1024][52],truetable[1024]; //最多10个变量
int i=0,nold=0,nnew=0,nvar=1,nRow=1,j=0,iMinItem=0;
// int flagsum=1;
printf("请输入公式(析+,合*,条-,双=,否定!01) \n");
gets(pstate0);
fflush(stdin);
nold=strlen(pstate0)+1;
nnew=strlen(pstate0);
strcpy(pstate,pstate0); //改进3:strcpy函数拷贝字符串,简单快捷
/* for(i=0; i<nnew; i++)
{
pstate[i]=pstate0[i];
}
pstate[i]='\0';
*/
nvar=getalpha(pstate,charList);
//真值表各个变元的值
nRow=1;
for(i=0; i<nvar; i++)
{
charVal[i]='0';
nRow=nRow*2;
}
charVal[i]='\0';
//真值表的首行
printf("\n");
for(i=0; i<nvar; i++)
printf("%4c",charList[i]);
printf("%15c%s\n",' ',pstate);
for(i=0; i<nvar; i++)
printf("%4c",'-');
printf("|");
for(i=0; i<60; i++)
printf("%c",'-');
printf("\n");
int num; //为改进4作铺垫
for(i=0; i<nRow; i++)
{
num = i;
for(j=nvar-1; j>=0; j--) //改进4:new algorithm: 模拟"辗转相除法"给charList赋值,更简洁明了
{
charVal[j] = num % 2 + '0';
num /= 2;
}
//真值表各行
for(j=0; j<nvar; j++)
printf("%4c",charVal[j]);
//将值填入到公式中
pstate[0]='\0';
fillValue(pstate0,charList,nvar,charVal,pstate);
while(negatecal(pstate)||kuanhao(pstate)||conYsh(pstate)||disConjYsh(pstate)||condYsh(pstate)||biCondYsh(pstate));
//改进5:利用||的短路性质,保证处理顺序:否定、括号、合取析取、条件。消除了原代码的BUG
/* nold=strlen(pstate0)+1; //原来处理字符串的办法
nnew=strlen(pstate);
while(nnew<nold)
{
nold=strlen(pstate);
negatecal(pstate); //否定
kuanhao(pstate); // (A)
conYsh(pstate); //1*1
biCondYsh(pstate); //1=1
condYsh(pstate); //1-1
disConjYsh(pstate); //1+1
nnew=strlen(pstate);
}
*/
if(strlen(pstate)==1)
{
if(pstate[0]=='1')
{
for (j=0; j<nvar; j++)
minItem[iMinItem][j]=charVal[j];
minItem[iMinItem][j]='\0';
iMinItem++;
}
truetable[i]=pstate[0];
}
printf("%20c%s",' ',pstate);
printf("\n");
/* flagsum=1; //原算法:进位法
for(j=nvar-1; j>=0; j--)
{
if(charVal[j]=='1')
{
if(flagsum==1)
{
charVal[j]='0';
flagsum=1;
}
else //1+0=1 不变
{
break;
}
}
else if(charVal[j]=='0')
{
if(flagsum==1)
{
charVal[j]='1';
flagsum=0;
} //0+0结束
else
{
break;
}
}
}
*/
}
for (i=0; i<iMinItem; i++)
{
if (i==0)
printf("m%s",minItem[i]);
else
printf("+m%s",minItem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for (i=0; i<iMinItem; i++)
{
if(i==0)
{
printf("(");
for (j=0; j<nvar; j++)
{
if (j==0)
{
if (minItem[i][j]=='1')
printf("%c",charList[j]);
else
printf("!%c",charList[j]);
}
else
{
if (minItem[i][j]=='1')
printf("*%c",charList[j]);
else
printf("*!%c",charList[j]);
}
}
printf(")");
}
else
{
printf("+(");
for(j=0; j<nvar; j++)
{
if (j==0)
{
if (minItem[i][j]=='1')
printf("%c",charList[j]);
else
printf("!%c",charList[j]);
}
else
{
if (minItem[i][j]=='1')
printf("*%c",charList[j]);
else
printf("*!%c",charList[j]);
}
}
printf(")");
}
}
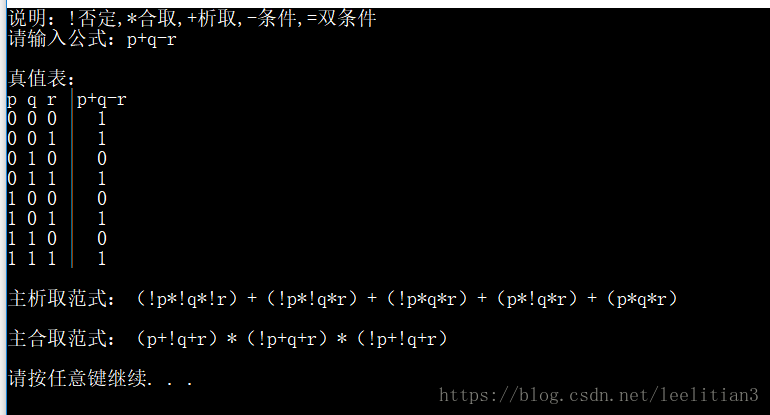
}运行结果展示:
②C++11版
亮点:
1.使用map容器储存变元—>0/1的映射
2.合理使用STL中的string::find和replace函数
3.增加判断了公式是否合法
// !否定,*合取,+析取,-条件,=双条件
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
map<char, bool> letter; //用红黑树结构建立 p/q/r -> 0/1 的映射 //优点:查找方便且速度快,按字典顺序排序
vector<int> minum;
vector<int> maxum;
void setLetter( int num ) //set p/q/r with 0/1
{
for (auto p = letter.rbegin(); p != letter.rend(); ++p) //new algorithm:模拟辗转相除法给p/q/r赋值
{
p->second = num % 2;
num /= 2;
}
}
bool rps( string& a, string f, string r ) //replace f with r in string a
{
if (a.find( f ) != string::npos) //string::find
{
a.replace( a.find( f ), f.length(), r ); //string::replace
return true;
}
return false;
}
void setString( string& a ) //replace p/q/r with 0/1 in string
{
for (auto &p : a)
if (islower( p ))
{
if (letter[p]) p = '1';
else p = '0';
}
}
int getResult( string& tmp ) //get the result true/false
{
//利用||判断符的"短路性",按照运算符优先级给原字符串替换,消除了原版本的bug
while (rps( tmp, "(0)", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "(1)", "1" ) ||
rps( tmp, "!0", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "!1", "0" ) ||
rps( tmp, "0+0", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "0+1", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "1+0", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "1+1", "1" ) ||
rps( tmp, "0*0", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "0*1", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "1*0", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "1*1", "1" ) ||
rps( tmp, "0-0", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "0-1", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "1-0", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "1-1", "1" ) ||
rps( tmp, "0=0", "1" ) || rps( tmp, "0=1", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "1=0", "0" ) || rps( tmp, "1=1", "1" )
);
if (tmp == "1") return 1;
else if (tmp == "0") return 0;
else return -1;
}
void print( int num, bool isMax, int count ) //print the min_item or max_item
{
int temp = 0;
setLetter( num );
for (auto p = letter.begin(); p != letter.end(); ++p, ++temp)
{
if (p->second ^ isMax) cout << p->first; //异或运算:若是小项,则输出值为0的变元;若是大项,输出值为1的变元
else cout << "!" << p->first;
if (temp != count - 1)
{
if (isMax) cout << "+";
else cout << "*";
}
}
}
int main()
{
string input, tmp;
cout << "说明:!否定,*合取,+析取,-条件,=双条件" << endl;
cout << "请输入公式:";
cin >> input;
tmp = input;
for (auto p : input)
if (islower( p )) letter[p] = 0; //把字母建立到map容器中去
setString( tmp );
if (getResult( tmp ) == -1) //首先判断公式是否合法
{
cout << input << " 不合法!" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << endl << "真值表:" << endl;
for (auto p : letter)
cout << p.first << ' ';
cout << '|' << input << endl;
int count = pow( 2, letter.size() );
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) //for i = 0 to 2^letter_number
{
tmp = input;
setLetter( i );
setString( tmp );
for (auto p : letter)
cout << p.second << ' ';
cout << '|';
for (int j = 0; j < input.size() / 2; ++j)
cout << ' ';
if (getResult( tmp )) //如果结果为1
{
cout << 1 << endl;
minum.push_back( i ); //储存到小项数组
}
else
{
cout << 0 << endl;
maxum.push_back( i );
}
}
//print 主合/主析
cout << endl << "主析取范式:";
if (minum.size() == 1) print( minum[0], false, letter.size() );
else
{
for (auto p = minum.begin(); p != minum.end(); ++p)
{
cout << "(";
print( *p, false, letter.size() );
cout << ")";
if (p != minum.end() - 1) cout << "+";
}
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "主合取范式:";
if (maxum.size() == 1) print( maxum[0], true, letter.size() );
else
{
for (auto p = maxum.begin(); p != maxum.end(); ++p)
{
cout << "(";
print( *p, true, letter.size() );
cout << ")";
if (p != maxum.end() - 1) cout << "*";
}
}
cout << endl << endl;
system( "pause" );
return 0;
}