前言
布局优化对于每个项目总是必不可少,本文主要介绍使用抽象布局标签(include, viewstub, merge)、去除不必要的嵌套和View节点、减少不必要的infalte及其他Layout方面可调优点,顺带提及布局调优相关工具(hierarchy viewer和lint)。
抽象布局标签
< include >标签
include标签常用于将布局中的公共部分提取出来供其他layout共用,以实现布局模块化,这在布局编写方便提供了大大的便利。
下面以在一个布局main.xml中用include引入另一个布局foot.xml为例。main.mxl代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/simple_list_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/dp_80" />
<include layout="@layout/foot.xml" />
</RelativeLayout>其中include引入的foot.xml为公用的页面底部,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_40"
android:layout_above="@+id/text"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_40"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="@string/app_name" />
</RelativeLayout>< include >标签唯一需要的属性是layout属性,指定需要包含的布局文件。可以定义android:id和android:layout_*属性来覆盖被引入布局根节点的对应属性值。注意重新定义android:id后,子布局的顶结点i就变化了。
< viewstub >标签
viewstub标签同include标签一样可以用来引入一个外部布局,不同的是,viewstub引入的布局默认不会扩张,即既不会占用显示也不会占用位置,从而在解析layout时节省cpu和内存。
viewstub常用来引入那些默认不会显示,只在特殊情况下显示的布局,如进度布局、网络失败显示的刷新布局、信息出错出现的提示布局等。
下面以在一个布局main.xml中加入网络错误时的提示页面network_error.xml为例。main.mxl代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
……
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/network_error_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout="@layout/network_error" />
</RelativeLayout>其中network_error.xml为只有在网络错误时才需要显示的布局,默认不会被解析,示例代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/network_setting"
android:layout_width="@dimen/dp_160"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="@string/network_setting" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/network_refresh"
android:layout_width="@dimen/dp_160"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/network_setting"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/dp_10"
android:text="@string/network_refresh" />
</RelativeLayout>在java中通过(ViewStub)findViewById(id)找到ViewStub,通过stub.inflate()展开ViewStub,然后得到子View,如下:
private View networkErrorView;
private void showNetError() {
// not repeated infalte
if (networkErrorView != null) {
networkErrorView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
return;
}
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub)findViewById(R.id.network_error_layout);
networkErrorView = stub.inflate();
Button networkSetting = (Button)networkErrorView.findViewById(R.id.network_setting);
Button refresh = (Button)findViewById(R.id.network_refresh);
}
private void showNormal() {
if (networkErrorView != null) {
networkErrorView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
在上面showNetError()中展开了ViewStub,同时我们对networkErrorView进行了保存,这样下次不用继续inflate。这就是后面第三部分提到的减少不必要的infalte。
viewstub标签大部分属性同include标签类似。
上面展开ViewStub部分代码
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub)findViewById(R.id.network_error_layout);
networkErrorView = stub.inflate();也可以写成下面的形式
View viewStub = findViewById(R.id.network_error_layout);
viewStub.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); // ViewStub被展开后的布局所替换
networkErrorView = findViewById(R.id.network_error_layout); // 获取展开后的布局效果一致,只是不用显示的转换为ViewStub。通过viewstub的原理我们可以知道将一个view设置为GONE不会被解析,从而提高layout解析速度,而VISIBLE和INVISIBLE这两个可见性属性会被正常解析。
< merge >标签
在使用了include后可能导致布局嵌套过多,多余不必要的layout节点,从而导致解析变慢,不必要的节点和嵌套可通过hierarchy viewer(下面布局调优工具中有具体介绍)或设置->开发者选项->显示布局边界查看。
merge标签可用于两种典型情况:
- 布局顶结点是FrameLayout且不需要设置background或padding等属性,可以用merge代替,因为Activity内容试图的parent view就是个FrameLayout,所以可以用merge消除只剩一个。
- 某布局作为子布局被其他布局include时,使用merge当作该布局的顶节点,这样在被引入时顶结点会自动被忽略,而将其子节点全部合并到主布局中。
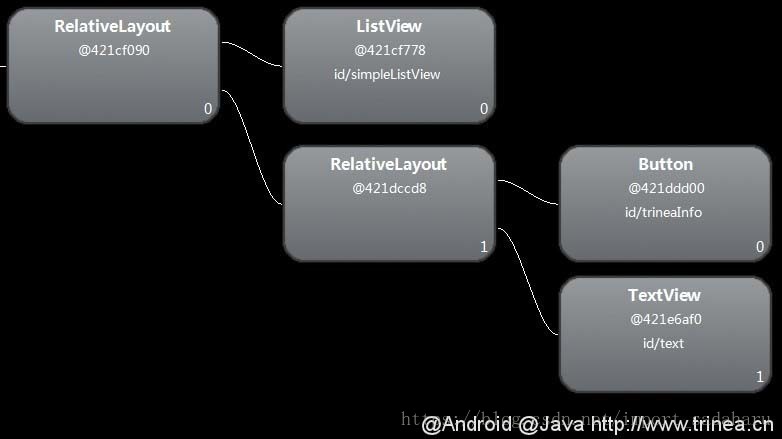
以< include >标签的示例为例,用hierarchy viewer查看main.xml布局如下图:
可以发现多了一层没必要的RelativeLayout,将foot.xml中RelativeLayout改为merge,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_40"
android:layout_above="@+id/text"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="@dimen/dp_40"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="@string/app_name" />
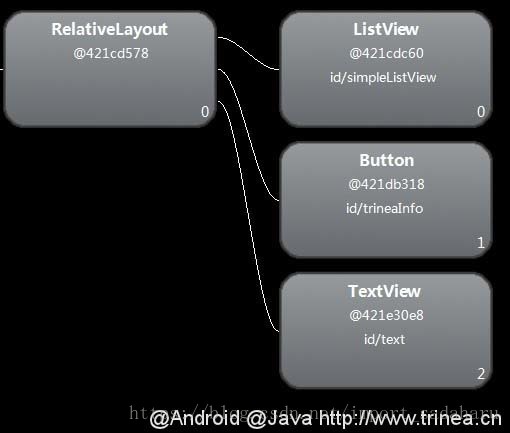
</merge>运行后再次用hierarchy viewer查看main.xml布局如下图:
这样就不会有多余的RelativeLayout节点了。
优化
去除不必要的嵌套和View节点
- 首次不需要使用的节点设置为GONE或使用viewstub
- 使用RelativeLayout代替LinearLayout
大约在Android4.0之前,新建工程的默认main.xml中顶节点是LinearLayout,而在之后已经改为RelativeLayout,因为RelativeLayout性能更优,且可以简单实现LinearLayout嵌套才能实现的布局。
4.0及以上Android版本可通过设置->开发者选项->显示布局边界打开页面布局显示,看看是否有不必要的节点和嵌套。4.0以下版本可通过hierarchy viewer查看。
减少不必要的infalte
对于inflate的布局可以直接缓存,用全部变量代替局部变量,避免下次需再次inflate
如上面ViewStub示例中的
if (networkErrorView != null) {
networkErrorView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
return;
}其他优化点
用SurfaceView或TextureView代替普通View
SurfaceView或TextureView可以通过将绘图操作移动到另一个单独线程上提高性能。
普通View的绘制过程都是在主线程(UI线程)中完成,如果某些绘图操作影响性能就不好优化了,这时我们可以考虑使用SurfaceView和TextureView,他们的绘图操作发生在UI线程之外的另一个线程上。
因为SurfaceView在常规视图系统之外,所以无法像常规试图一样移动、缩放或旋转一个SurfaceView。TextureView是Android4.0引入的,除了与SurfaceView一样在单独线程绘制外,还可以像常规视图一样被改变。
使用RenderJavascript
RenderScript是Adnroid3.0引进的用来在Android上写高性能代码的一种语言,语法给予C语言的C99标准,他的结构是独立的,所以不需要为不同的CPU或者GPU定制代码代码。
使用OpenGL绘图
Android支持使用OpenGL API的高性能绘图,这是Android可用的最高级的绘图机制,在游戏类对性能要求较高的应用中得到广泛使用。
Android 4.3最大的改变,就是支持OpenGL ES 3.0。相比2.0,3.0有更多的缓冲区对象、增加了新的着色语言、增加多纹理支持等等,将为Android游戏带来更出色的视觉体验。
尽量为所有分辨率创建资源
减少不必要的硬件缩放,这会降低UI的绘制速度,可借助Android asset studio
布局调优工具
hierarchy viewer
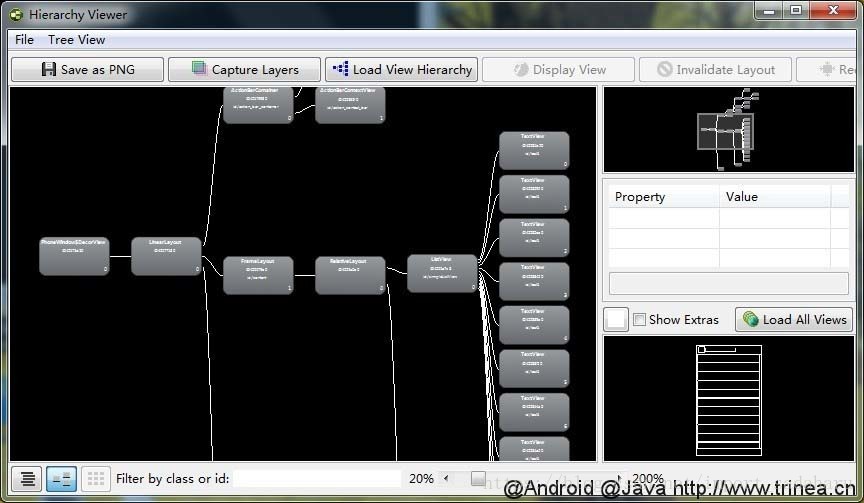
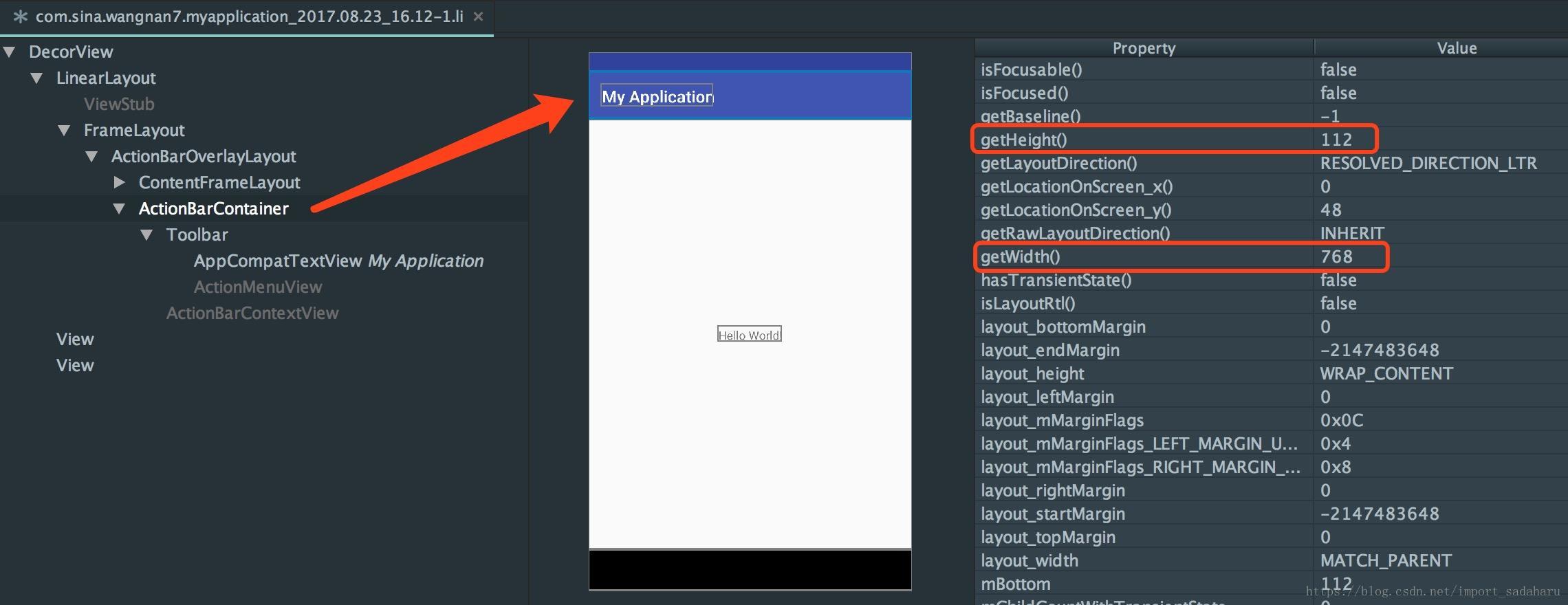
hierarchy viewer可以方便的查看Activity的布局,各个View的属性、measure、layout、draw的时间,如果耗时较多会用红色标记,否则显示绿色。
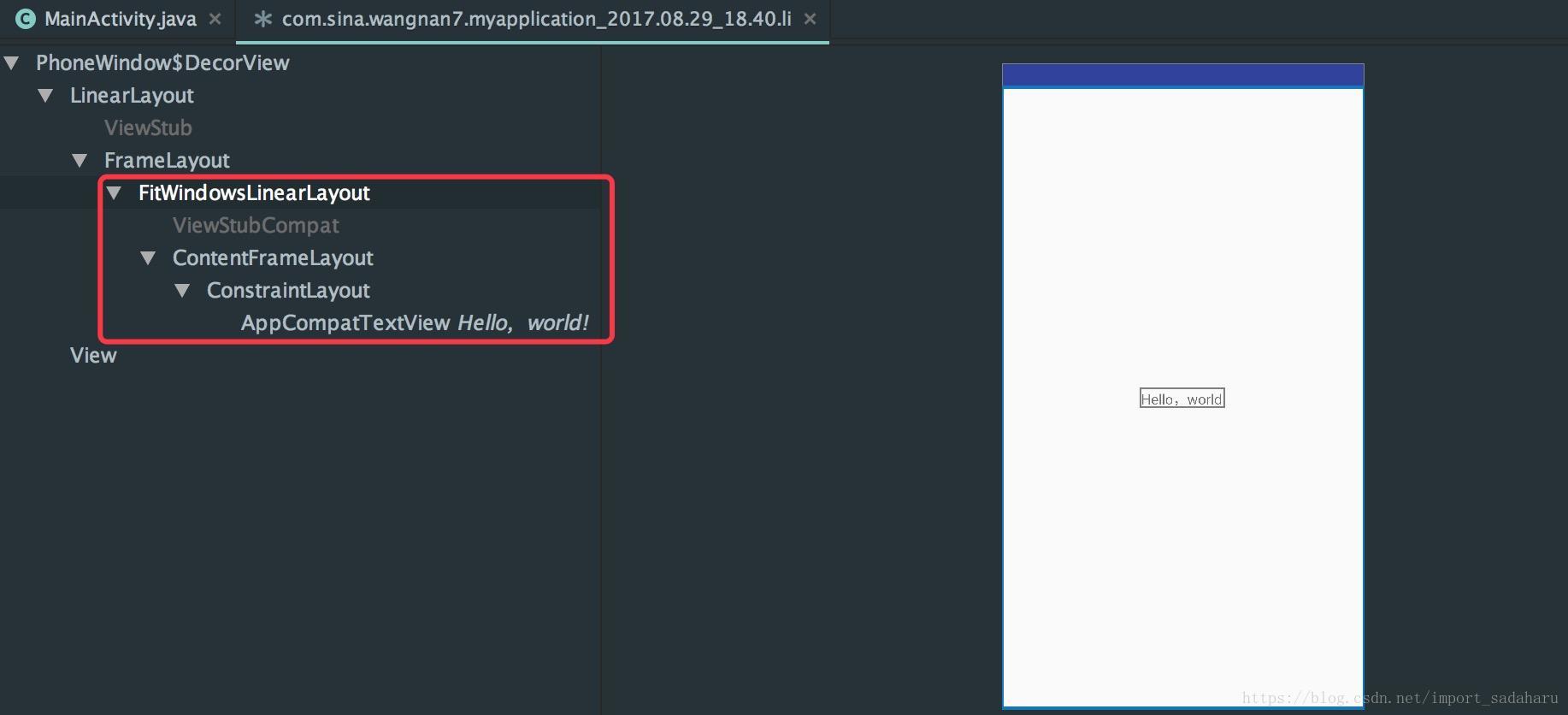
hierarchy viewer.bat位于/tools/目录下。使用可见:Using Hierarchy Viewer , 示例图如下:
layoutopt
layoutopt是一个可以提供layout及其层级优化提示的命令行,在sdk16以后已经被lint取代,在Windows->Show View->Other->Android->Lint Warnings查看lint优化提示,lint具体介绍可见Improving Your Code with lint。
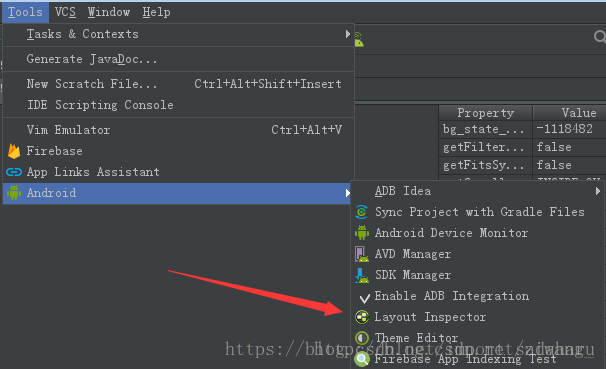
Layout Inspector
Android Studio 的面板上选择 Tools -> Android -> Layout Inspector 即可
这个工具也十分强大,可以直接对着你的视图查看整个的层级
你也可以查看一个View的详细的信息