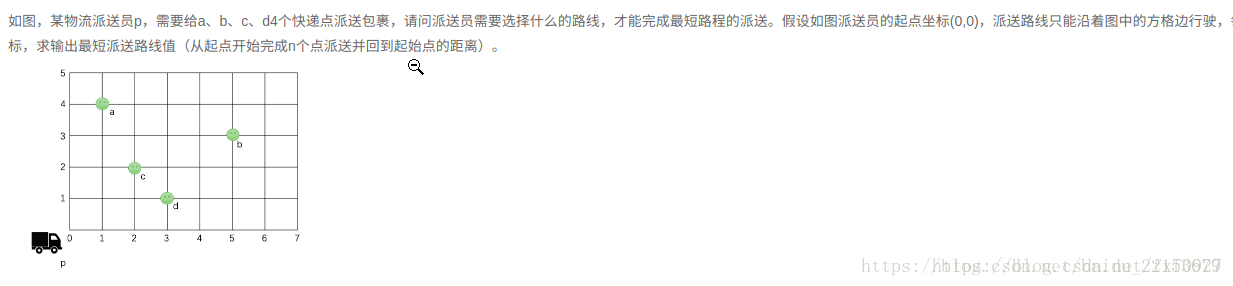
如图,某物流派送员p,需要给a、b、c、d4个快递点派送包裹,请问派送员需要选择什么的路线,才能完成最短路程的派送。假设如图派送员的起点坐标(0,0),派送路线只能沿着图中的方格边行驶,每个小格都是正方形,且边长为1,如p到d的距离就是4。随机输入n个派送点坐标,求输出最短派送路线值(从起点开始完成n个点派送并回到起始点的距离)。
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* DFS,BFS,包括其他递归方法,保证其完整正确性首先要具有递归出口;
* 其次,要考虑递归过程中是否携带 “状态记录”,若携带应注意记录的维护(自主维护还是递归栈“自己维护”)。
* 由此引出一个,编程中的高效思想,即尽可能地不要直接使用形参。提倡方法内将参数进行拷贝,如此有利于
* 状态与递归层次的对应关系(eg:下面代码中count+1优于count++,后者在回溯时需要--count);
* 当然,这不是一个“死规矩”,一些全局状态就需要我们在回溯的时候小心维护————恢复现场。其实操作系统本身
* 也是如此工作的,保留现场出现在指令中断、函数调用等多种场合。
*/
class Point{
int px;
int py;
boolean visited;
public Point(int px, int py) {
this.px = px;
this.py = py;
this.visited = false;
}
public int getLength(Point p){
return Math.abs(px - p.px) + Math.abs(py - p.py);
}
}
public class Main {
static final Point START = new Point(0,0);
static int minpath = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static int calculate(Point point,Point[] points,int sum,int count){
for(int i=0;i<points.length;i++){
if(points[i].visited==false){
points[i].visited=true;
count++;
sum +=point.getLength(points[i]);
if(count==points.length){
sum+=points[i].getLength(start);
if(sum<min){
min = sum;
}
}
calculate(points[i],points,sum,count);
points[i].visited=false;
sum-=point.getLength(points[i]);
count--;
}
}
return min;
}
private static int min =1000;
public static final Point start = new Point(0,0);
public static void main(String[] args){
Point[] points=new Point[4];
points[0]=new Point(1,4);
points[1]=new Point(2,2);
points[2]=new Point(3,1);
points[3]=new Point(5,3);
int min = calculate(START, points, 0, 0);
System.out.println(min);
}
}
