前言:之前已经梳理了WiFi的启动、扫描,扫描到了AP,是时候看下连接AP的流程了。
1. WIFI AP简介
WiFi AP即WIFI Acess Point,它的安全性分无、WEP、WPA/WPA2 PSK和 802.1x EAP,我们日常生活中用的最多的应该是WPA/WPA2 PSK,连接该类型的热点的时候只需要输入对应的密码就好了。本文梳理也只梳理这种最常见类型的AP连接流程,当然也是从Settings-SettingsLib-framework。
2. WIFI AP连接流程梳理
Settings-SettingsLib-framework。
2.1 Settings
之前有提及到Wifi AP在设置 wifi 界面是以设置比较特色的组件Preference所呈现的,真正名称是
/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/wifi/LongPressAccessPointPreference.java
public class LongPressAccessPointPreference extends AccessPointPreference {
private final Fragment mFragment;
public LongPressAccessPointPreference(AccessPoint accessPoint, Context context,
UserBadgeCache cache, boolean forSavedNetworks, Fragment fragment) {
super(accessPoint, context, cache, forSavedNetworks);
mFragment = fragment;
}
public LongPressAccessPointPreference(AccessPoint accessPoint, Context context,
UserBadgeCache cache, boolean forSavedNetworks, int iconResId, Fragment fragment) {
super(accessPoint, context, cache, iconResId, forSavedNetworks);
mFragment = fragment;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(final PreferenceViewHolder view) {
super.onBindViewHolder(view);
if (mFragment != null) {
view.itemView.setOnCreateContextMenuListener(mFragment);
view.itemView.setTag(this);
view.itemView.setLongClickable(true);
}
}
}在WifiSettings里以如下方法初始化
@NonNull
private LongPressAccessPointPreference createLongPressActionPointPreference(
AccessPoint accessPoint) {
return new LongPressAccessPointPreference(accessPoint, getPrefContext(), mUserBadgeCache,
false, R.drawable.ic_wifi_signal_0, this);
}可以看到长按后弹出来的menu是由WifiSettings这个fragment负责创建的,看下具体方法:
@Override
public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View view, ContextMenuInfo info) {
Preference preference = (Preference) view.getTag();
if (preference instanceof LongPressAccessPointPreference) {
mSelectedAccessPoint =
((LongPressAccessPointPreference) preference).getAccessPoint();
menu.setHeaderTitle(mSelectedAccessPoint.getSsid());
if (mSelectedAccessPoint.isConnectable()) {
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_ID_CONNECT, 0, R.string.wifi_menu_connect);
}
WifiConfiguration config = mSelectedAccessPoint.getConfig();
// Some configs are ineditable
if (isEditabilityLockedDown(getActivity(), config)) {
return;
}
if (mSelectedAccessPoint.isSaved() || mSelectedAccessPoint.isEphemeral()) {
// Allow forgetting a network if either the network is saved or ephemerally
// connected. (In the latter case, "forget" blacklists the network so it won't
// be used again, ephemerally).
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_ID_FORGET, 0, R.string.wifi_menu_forget);
}
if (mSelectedAccessPoint.isSaved()) {
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_ID_MODIFY, 0, R.string.wifi_menu_modify);
NfcAdapter nfcAdapter = NfcAdapter.getDefaultAdapter(getActivity());
if (nfcAdapter != null && nfcAdapter.isEnabled() &&
mSelectedAccessPoint.getSecurity() != AccessPoint.SECURITY_NONE) {
// Only allow writing of NFC tags for password-protected networks.
menu.add(Menu.NONE, MENU_ID_WRITE_NFC, 0, R.string.wifi_menu_write_to_nfc);
}
}
}
}主要看下MENU_ID_CONNECT对应的事件处理
@Override
public boolean onContextItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
if (mSelectedAccessPoint == null) {
return super.onContextItemSelected(item);
}
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case MENU_ID_CONNECT: {
boolean isSavedNetwork = mSelectedAccessPoint.isSaved();
if (isSavedNetwork) {
connect(mSelectedAccessPoint.getConfig(), isSavedNetwork);
} else if (mSelectedAccessPoint.getSecurity() == AccessPoint.SECURITY_NONE) {
/** Bypass dialog for unsecured networks */
mSelectedAccessPoint.generateOpenNetworkConfig();
connect(mSelectedAccessPoint.getConfig(), isSavedNetwork);
} else {
showDialog(mSelectedAccessPoint, WifiConfigUiBase.MODE_CONNECT);
}
return true;
}继而调用到了connect方法
protected void connect(final int networkId, boolean isSavedNetwork) {
// Log subtype if configuration is a saved network.
mMetricsFeatureProvider.action(getActivity(), MetricsEvent.ACTION_WIFI_CONNECT,
isSavedNetwork);
mWifiManager.connect(networkId, mConnectListener);
}这次没有调用到SettingsLib,直接就到WifiManager了。
另外还传入了一个用于回调的listener,用于通知用户连接成功与否。
mConnectListener = new WifiManager.ActionListener() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
}
@Override
public void onFailure(int reason) {
Activity activity = getActivity();
if (activity != null) {
Toast.makeText(activity,
R.string.wifi_failed_connect_message,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
};2.2 framework
还是从WifiManager开始梳理
2.2.1 WifiManager
/**
* Connect to a network with the given networkId.
*
* This function is used instead of a enableNetwork(), saveConfiguration() and
* reconnect()
*
* @param networkId the ID of the network as returned by {@link #addNetwork} or {@link
* getConfiguredNetworks}.
* @param listener for callbacks on success or failure. Can be null.
* @throws IllegalStateException if the WifiManager instance needs to be
* initialized again
* @hide
*/
public void connect(int networkId, ActionListener listener) {
if (networkId < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Network id cannot be negative");
getChannel().sendMessage(CONNECT_NETWORK, networkId, putListener(listener));
}看下getChannel()获取的是什么
private synchronized AsyncChannel getChannel() {
if (mAsyncChannel == null) {
Messenger messenger = getWifiServiceMessenger();
if (messenger == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"getWifiServiceMessenger() returned null! This is invalid.");
}
mAsyncChannel = new AsyncChannel();
mConnected = new CountDownLatch(1);
Handler handler = new ServiceHandler(mLooper);
mAsyncChannel.connect(mContext, handler, messenger);
try {
mConnected.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "interrupted wait at init");
}
}
return mAsyncChannel;
} /**
* Get a reference to WifiService handler. This is used by a client to establish
* an AsyncChannel communication with WifiService
*
* @return Messenger pointing to the WifiService handler
* @hide
*/
public Messenger getWifiServiceMessenger() {
try {
return mService.getWifiServiceMessenger();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}这相当于是给WifiServiceImpl的handler发送一个CONNECT_NETWORK的消息。
AsyncTask原理参照:https://blog.csdn.net/u010961631/article/details/48179305
2.2.2 WifiServiceImpl
/**
* Get a reference to handler. This is used by a client to establish
* an AsyncChannel communication with WifiService
*/
@Override
public Messenger getWifiServiceMessenger() {
enforceAccessPermission();
enforceChangePermission();
mLog.info("getWifiServiceMessenger uid=%").c(Binder.getCallingUid()).flush();
return new Messenger(mClientHandler);
}看起来是mClientHandler负责处理WifiManager发来的CONNECT_NETWORK消息。
处理如下所示:
case WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK: {
if (checkChangePermissionAndReplyIfNotAuthorized(
msg, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED)) {
WifiConfiguration config = (WifiConfiguration) msg.obj;
int networkId = msg.arg1;
Slog.d(TAG, "CONNECT "
+ " nid=" + Integer.toString(networkId)
+ " uid=" + msg.sendingUid
+ " name="
+ mContext.getPackageManager().getNameForUid(msg.sendingUid));
if (config != null) {
if (DBG) Slog.d(TAG, "Connect with config " + config);
/* Command is forwarded to state machine */
mWifiStateMachine.sendMessage(Message.obtain(msg));
} else if (config == null
&& networkId != WifiConfiguration.INVALID_NETWORK_ID) {
if (DBG) Slog.d(TAG, "Connect with networkId " + networkId);
mWifiStateMachine.sendMessage(Message.obtain(msg));
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "ClientHandler.handleMessage ignoring invalid msg=" + msg);
replyFailed(msg, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.INVALID_ARGS);
}
}
break;
}继而调用WifiStateMachine(config没传过来,自然是null)
2.2.3 WifiStateMachine
看了下是ConnectModeState会对CONNECT_NETWORK消息作对应的连接处理。
case WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK:
/**
* The connect message can contain a network id passed as arg1 on message or
* or a config passed as obj on message.
* For a new network, a config is passed to create and connect.
* For an existing network, a network id is passed
*/
netId = message.arg1;
config = (WifiConfiguration) message.obj;
mWifiConnectionStatistics.numWifiManagerJoinAttempt++;
boolean hasCredentialChanged = false;
// New network addition.
if (config != null) {
result = mWifiConfigManager.addOrUpdateNetwork(config, message.sendingUid);
if (!result.isSuccess()) {
loge("CONNECT_NETWORK adding/updating config=" + config + " failed");
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_FAIL;
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.ERROR);
break;
}
netId = result.getNetworkId();
hasCredentialChanged = result.hasCredentialChanged();
}
if (!connectToUserSelectNetwork(
netId, message.sendingUid, hasCredentialChanged)) {
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_FAIL;
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.NOT_AUTHORIZED);
break;
}
mWifiMetrics.logStaEvent(StaEvent.TYPE_CONNECT_NETWORK, config);
broadcastWifiCredentialChanged(WifiManager.WIFI_CREDENTIAL_SAVED, config);
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_SUCCEEDED);
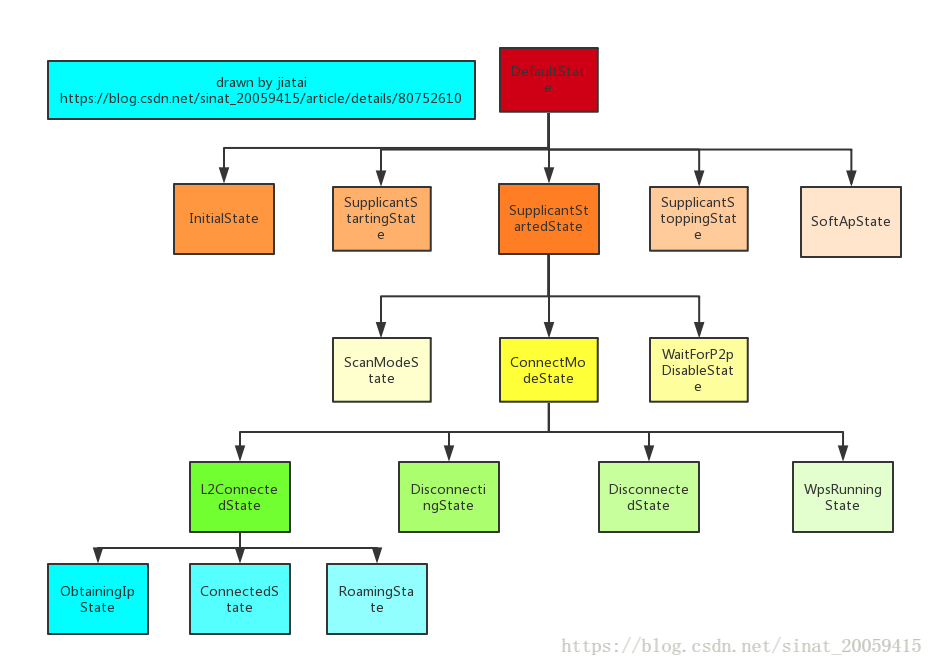
break;分析扫描流程的时候WifiStateMachine会change到SupplicantStartedState状态,这里正好看下何时会进入ConnectModeState。
有两个状态会变过来
分别是
L2ConnectedState
case CMD_IP_CONFIGURATION_SUCCESSFUL:
handleSuccessfulIpConfiguration();
reportConnectionAttemptEnd(
WifiMetrics.ConnectionEvent.FAILURE_NONE,
WifiMetricsProto.ConnectionEvent.HLF_NONE);
if (getCurrentWifiConfiguration() == null) {
// The current config may have been removed while we were connecting,
// trigger a disconnect to clear up state.
mWifiNative.disconnect();
transitionTo(mDisconnectingState);
} else {
sendConnectedState();
transitionTo(mConnectedState);
}
break;和 RoamingState
case WifiMonitor.NETWORK_CONNECTION_EVENT:
if (mAssociated) {
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) {
log("roaming and Network connection established");
}
mLastNetworkId = lookupFrameworkNetworkId(message.arg1);
mLastBssid = (String) message.obj;
mWifiInfo.setBSSID(mLastBssid);
mWifiInfo.setNetworkId(mLastNetworkId);
int reasonCode = message.arg2;
mWifiConnectivityManager.trackBssid(mLastBssid, true, reasonCode);
sendNetworkStateChangeBroadcast(mLastBssid);
// Successful framework roam! (probably)
reportConnectionAttemptEnd(
WifiMetrics.ConnectionEvent.FAILURE_NONE,
WifiMetricsProto.ConnectionEvent.HLF_NONE);
// We must clear the config BSSID, as the wifi chipset may decide to roam
// from this point on and having the BSSID specified by QNS would cause
// the roam to fail and the device to disconnect.
// When transition from RoamingState to DisconnectingState or
// DisconnectedState, the config BSSID is cleared by
// handleNetworkDisconnect().
clearTargetBssid("RoamingCompleted");
// We used to transition to ObtainingIpState in an
// attempt to do DHCPv4 RENEWs on framework roams.
// DHCP can take too long to time out, and we now rely
// upon IpClient's use of IpReachabilityMonitor to
// confirm our current network configuration.
//
// mIpClient.confirmConfiguration() is called within
// the handling of SupplicantState.COMPLETED.
transitionTo(mConnectedState);
} else {
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_DISCARD;
}
break;算了,还是看下连接流程吧。。
case WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK:
/**
* The connect message can contain a network id passed as arg1 on message or
* or a config passed as obj on message.
* For a new network, a config is passed to create and connect.
* For an existing network, a network id is passed
*/
netId = message.arg1;
config = (WifiConfiguration) message.obj;
mWifiConnectionStatistics.numWifiManagerJoinAttempt++;
boolean hasCredentialChanged = false;
// New network addition.
if (config != null) {
result = mWifiConfigManager.addOrUpdateNetwork(config, message.sendingUid);
if (!result.isSuccess()) {
loge("CONNECT_NETWORK adding/updating config=" + config + " failed");
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_FAIL;
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.ERROR);
break;
}
netId = result.getNetworkId();
hasCredentialChanged = result.hasCredentialChanged();
}
if (!connectToUserSelectNetwork(
netId, message.sendingUid, hasCredentialChanged)) {
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_FAIL;
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.NOT_AUTHORIZED);
break;
}
mWifiMetrics.logStaEvent(StaEvent.TYPE_CONNECT_NETWORK, config);
broadcastWifiCredentialChanged(WifiManager.WIFI_CREDENTIAL_SAVED, config);
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_SUCCEEDED);
break;首先看到了我们熟悉的addOrUpdateNetwork,其次是连接方法connectToUserSelectNetwork
/**
* Initiates connection to a network specified by the user/app. This method checks if the
* requesting app holds the NETWORK_SETTINGS permission.
*
* @param netId Id network to initiate connection.
* @param uid UID of the app requesting the connection.
* @param forceReconnect Whether to force a connection even if we're connected to the same
* network currently.
*/
private boolean connectToUserSelectNetwork(int netId, int uid, boolean forceReconnect) {
logd("connectToUserSelectNetwork netId " + netId + ", uid " + uid
+ ", forceReconnect = " + forceReconnect);
if (mWifiConfigManager.getConfiguredNetwork(netId) == null) {
loge("connectToUserSelectNetwork Invalid network Id=" + netId);
return false;
}
if (!mWifiConfigManager.enableNetwork(netId, true, uid)
|| !mWifiConfigManager.checkAndUpdateLastConnectUid(netId, uid)) {
logi("connectToUserSelectNetwork Allowing uid " + uid
+ " with insufficient permissions to connect=" + netId);
} else {
// Note user connect choice here, so that it will be considered in the next network
// selection.
mWifiConnectivityManager.setUserConnectChoice(netId);
}
if (!forceReconnect && mWifiInfo.getNetworkId() == netId) {
// We're already connected to the user specified network, don't trigger a
// reconnection unless it was forced.
logi("connectToUserSelectNetwork already connecting/connected=" + netId);
} else {
mWifiConnectivityManager.prepareForForcedConnection(netId);
startConnectToNetwork(netId, uid, SUPPLICANT_BSSID_ANY);
}
return true;
}瞄一眼WifiConnectivityManager
/**
* Handler to prepare for connection to a user or app specified network
*/
public void prepareForForcedConnection(int netId) {
localLog("prepareForForcedConnection: netId=" + netId);
clearConnectionAttemptTimeStamps();
clearBssidBlacklist();
}回来看下startConnectToNetwork
/**
* Automatically connect to the network specified
*
* @param networkId ID of the network to connect to
* @param uid UID of the app triggering the connection.
* @param bssid BSSID of the network
*/
public void startConnectToNetwork(int networkId, int uid, String bssid) {
sendMessage(CMD_START_CONNECT, networkId, uid, bssid);
}ConnectModeState继续处理发来的CMD_START_CONNECT消息
case CMD_START_CONNECT:
/* connect command coming from auto-join */
netId = message.arg1;
int uid = message.arg2;
bssid = (String) message.obj;
synchronized (mWifiReqCountLock) {
if (!hasConnectionRequests()) {
if (mNetworkAgent == null) {
loge("CMD_START_CONNECT but no requests and not connected,"
+ " bailing");
break;
} else if (!mWifiPermissionsUtil.checkNetworkSettingsPermission(uid)) {
loge("CMD_START_CONNECT but no requests and connected, but app "
+ "does not have sufficient permissions, bailing");
break;
}
}
}
config = mWifiConfigManager.getConfiguredNetworkWithPassword(netId);
logd("CMD_START_CONNECT sup state "
+ mSupplicantStateTracker.getSupplicantStateName()
+ " my state " + getCurrentState().getName()
+ " nid=" + Integer.toString(netId)
+ " roam=" + Boolean.toString(mIsAutoRoaming));
if (config == null) {
loge("CMD_START_CONNECT and no config, bail out...");
break;
}
mTargetNetworkId = netId;
setTargetBssid(config, bssid);
reportConnectionAttemptStart(config, mTargetRoamBSSID,
WifiMetricsProto.ConnectionEvent.ROAM_UNRELATED);
if (mWifiNative.connectToNetwork(config)) {
mWifiMetrics.logStaEvent(StaEvent.TYPE_CMD_START_CONNECT, config);
lastConnectAttemptTimestamp = mClock.getWallClockMillis();
targetWificonfiguration = config;
mIsAutoRoaming = false;
if (isLinkDebouncing()) {
transitionTo(mRoamingState);
} else if (getCurrentState() != mDisconnectedState) {
transitionTo(mDisconnectingState);
}
} else {
loge("CMD_START_CONNECT Failed to start connection to network " + config);
reportConnectionAttemptEnd(
WifiMetrics.ConnectionEvent.FAILURE_CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiMetricsProto.ConnectionEvent.HLF_NONE);
replyToMessage(message, WifiManager.CONNECT_NETWORK_FAILED,
WifiManager.ERROR);
break;
}
break;这里调用了WifiNative的connectToNetwork
2.2.4 WifiNative
/**
* Add the provided network configuration to wpa_supplicant and initiate connection to it.
* This method does the following:
* 1. Abort any ongoing scan to unblock the connection request.
* 2. Remove any existing network in wpa_supplicant(This implicitly triggers disconnect).
* 3. Add a new network to wpa_supplicant.
* 4. Save the provided configuration to wpa_supplicant.
* 5. Select the new network in wpa_supplicant.
* 6. Triggers reconnect command to wpa_supplicant.
*
* @param configuration WifiConfiguration parameters for the provided network.
* @return {@code true} if it succeeds, {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean connectToNetwork(WifiConfiguration configuration) {
// Abort ongoing scan before connect() to unblock connection request.
mWificondControl.abortScan();
return mSupplicantStaIfaceHal.connectToNetwork(configuration);
}如注释所示,这个方法做了6件事:
1. 中止任何正在进行的扫描来不阻塞连接请求
2.删除wpa_supplicant中的任何现有网络(这会隐式触发断开连接)
3.在wpa_supplicant中添加一个新的网络
4.在wpa_supplicant中保存提供的configuration
5.在wpa_supplicant中选择新的网络
6.触发wpa_supplicant 的重新连接命令
abortScan我就暂时不看了,反正和scan的命令差不多流程,我也看不下去=-=
2.2.5 SupplicantStaIfaceHal
/**
* Add the provided network configuration to wpa_supplicant and initiate connection to it.
* This method does the following:
* 1. If |config| is different to the current supplicant network, removes all supplicant
* networks and saves |config|.
* 2. Select the new network in wpa_supplicant.
*
* @param config WifiConfiguration parameters for the provided network.
* @return {@code true} if it succeeds, {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean connectToNetwork(@NonNull WifiConfiguration config) {
synchronized (mLock) {
logd("connectToNetwork " + config.configKey());
if (WifiConfigurationUtil.isSameNetwork(config, mCurrentNetworkLocalConfig)) {
logd("Network is already saved, will not trigger remove and add operation.");
} else {
mCurrentNetworkRemoteHandle = null;
mCurrentNetworkLocalConfig = null;
if (!removeAllNetworks()) {
loge("Failed to remove existing networks");
return false;
}
Pair<SupplicantStaNetworkHal, WifiConfiguration> pair =
addNetworkAndSaveConfig(config);
if (pair == null) {
loge("Failed to add/save network configuration: " + config.configKey());
return false;
}
mCurrentNetworkRemoteHandle = pair.first;
mCurrentNetworkLocalConfig = pair.second;
}
if (!mCurrentNetworkRemoteHandle.select()) {
loge("Failed to select network configuration: " + config.configKey());
return false;
}
return true;
}
}2.2.6 SupplicantStaNetworkHal
/**
* Trigger a connection to this network.
*
* @return true if it succeeds, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean select() {
synchronized (mLock) {
final String methodStr = "select";
if (!checkISupplicantStaNetworkAndLogFailure(methodStr)) return false;
try {
SupplicantStatus status = mISupplicantStaNetwork.select();
return checkStatusAndLogFailure(status, methodStr);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
handleRemoteException(e, methodStr);
return false;
}
}
}emmm,看不下去了,看下这个类的注释,hal 层的东西
/**
* Wrapper class for ISupplicantStaNetwork HAL calls. Gets and sets supplicant sta network variables
* and interacts with networks.
* Public fields should be treated as invalid until their 'get' method is called, which will set the
* value if it returns true
* To maintain thread-safety, the locking protocol is that every non-static method (regardless of
* access level) acquires mLock.
*/- ISupplicantStaNetwork HAL调用的包装类。 获取并设置请求者网络变量并与网络交互。
- 公共字段应被视为无效,直到调用它们的'get'方法,如果返回true,则将设置该值。
- 为了保持线程安全,锁定协议是每个非静态方法(无论访问级别)都获取mLock。
3. 总结
连接流程:
1. 中止任何正在进行的扫描来达到不阻塞连接请求的目的
2.删除wpa_supplicant中的任何现有网络(这会隐式触发断开连接)
3.在wpa_supplicant中添加一个新的网络
4.在wpa_supplicant中保存提供的configuration
5.在wpa_supplicant中选择新的网络
6.触发wpa_supplicant 的重新连接命令
至于最后到hal层、wpa_supplicant都不知道怎么看。。。emmm,C和C++也要重头再学一遍了