前言:最近又需要学一下WiFi模块,我心里是虚的,但是还是要学呀。
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/csdn_of_coder/article/details/51541094
(里面也不少framework和WiFi的文章,我得过一遍,很对口)
aosp: Android O
1.wifi启动流程简介
用户可以通过systemUi和设置里的WiFi开关打开WiFi,这时候会调用到wifi framework的相关接口,继而再继续往下启用具体的硬件完成WiFi启动流程,我只对应用到framework层有些简单的了解,本篇也主要注重framework这一块,app层没啥好说的。
2.WiFi启动流程梳理
我之前是负责设置模块的,systemUi代码虽然看过,但是不是很熟,所以WiFi打开流程还是从设置的WiFi开关开始梳理吧,不考虑打开飞行模式后打开WiFi的情况=-=
2.1 设置启动WiFi
设置这边说到底其实就是监控WiFi开关的变化,然后根据开关走对应的逻辑处理。
两个比较重要的类:
1)WifiSettings:设置中wifi主界面所对应的代码
2)WifiEnabler:设置中负责wifi开关打开和关闭事件处理的类
/aosp/packages/apps/Settings$ vim ./src/com/android/settings/wifi/WifiSettings.java
/**
* @return new WifiEnabler or null (as overridden by WifiSettingsForSetupWizard)
*/
private WifiEnabler createWifiEnabler() {
final SettingsActivity activity = (SettingsActivity) getActivity();
return new WifiEnabler(activity, new SwitchBarController(activity.getSwitchBar()),
mMetricsFeatureProvider);
}/aosp/packages/apps/Settings$ vim ./src/com/android/settings/widget/SwitchBarController.java
public class SwitchBarController extends SwitchWidgetController implements
SwitchBar.OnSwitchChangeListener {
private final SwitchBar mSwitchBar;
public SwitchBarController(SwitchBar switchBar) {
mSwitchBar = switchBar;
}
... @Override
public void startListening() {
mSwitchBar.addOnSwitchChangeListener(this);
}...
@Override
public void onSwitchChanged(Switch switchView, boolean isChecked) {
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onSwitchToggled(isChecked);
}
}
/aosp/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/wifi/WifiEnabler.java
@VisibleForTesting
WifiEnabler(Context context, SwitchWidgetController switchWidget,
MetricsFeatureProvider metricsFeatureProvider,
ConnectivityManagerWrapper connectivityManagerWrapper) {
mContext = context;
mSwitchWidget = switchWidget;
mSwitchWidget.setListener(this);
mMetricsFeatureProvider = metricsFeatureProvider;
mWifiManager = (WifiManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
mConnectivityManager = connectivityManagerWrapper;
mIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
// The order matters! We really should not depend on this. :(
mIntentFilter.addAction(WifiManager.SUPPLICANT_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
mIntentFilter.addAction(WifiManager.NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
setupSwitchController();
}
public void setupSwitchController() {
final int state = mWifiManager.getWifiState();
handleWifiStateChanged(state);
if (!mListeningToOnSwitchChange) {
mSwitchWidget.startListening();
mListeningToOnSwitchChange = true;
}
mSwitchWidget.setupView();
}@Override
public boolean onSwitchToggled(boolean isChecked) {
//Do nothing if called as a result of a state machine event
if (mStateMachineEvent) {
return true;
}
// Show toast message if Wi-Fi is not allowed in airplane mode
if (isChecked && !WirelessUtils.isRadioAllowed(mContext, Settings.Global.RADIO_WIFI)) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, R.string.wifi_in_airplane_mode, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Reset switch to off. No infinite check/listenenr loop.
mSwitchWidget.setChecked(false);
return false;
}
// Disable tethering if enabling Wifi
if (mayDisableTethering(isChecked)) {
mConnectivityManager.stopTethering(ConnectivityManager.TETHERING_WIFI);
}
if (isChecked) {
mMetricsFeatureProvider.action(mContext, MetricsEvent.ACTION_WIFI_ON);
} else {
// Log if user was connected at the time of switching off.
mMetricsFeatureProvider.action(mContext, MetricsEvent.ACTION_WIFI_OFF,
mConnected.get());
}
if (!mWifiManager.setWifiEnabled(isChecked)) {
// Error
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(true);
Toast.makeText(mContext, R.string.wifi_error, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}看到这里其实发现应用层打开和关闭WiFi就是调用了下WifiManager的setWifiEabled(boolean)接口即可。
2.2 WiFi framework
看下WifiManager的setWifiEabled(boolean)接口
framework/base/wifi/java/android/net/wifi/WifiManager.java
/**
* Enable or disable Wi-Fi.
*
* Note: This method will return false if wifi cannot be enabled (e.g., an incompatible mode
* where the user has enabled tethering or Airplane Mode).
*
* Applications need to have the {@link android.Manifest.permission#CHANGE_WIFI_STATE}
* permission to toggle wifi. Callers without the permissions will trigger a
* {@link java.lang.SecurityException}.
*
* @param enabled {@code true} to enable, {@code false} to disable.
* @return {@code true} if the operation succeeds (or if the existing state
* is the same as the requested state). False if wifi cannot be toggled on/off when the
* request is made.
*/
public boolean setWifiEnabled(boolean enabled) {
try {
return mService.setWifiEnabled(mContext.getOpPackageName(), enabled);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}2.2.1 WifiService是什么
而mService是啥呢
IWifiManager mService;
/**
* Create a new WifiManager instance.
* Applications will almost always want to use
* {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService Context.getSystemService()} to retrieve
* the standard {@link android.content.Context#WIFI_SERVICE Context.WIFI_SERVICE}.
* @param context the application context
* @param service the Binder interface
* @hide - hide this because it takes in a parameter of type IWifiManager, which
* is a system private class.
*/
public WifiManager(Context context, IWifiManager service, Looper looper) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
mLooper = looper;
mTargetSdkVersion = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
}应用层的WifiManager都是这么来的
mWifiManager = (WifiManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);那真正的WifiManager实例是谁来new出来的呢?
有这么一个类:
/framework/base/core/java/android/app/SystemServiceRegistry.java
registerService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE, WifiManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<WifiManager>() {
@Override
public WifiManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
IWifiManager service = IWifiManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return new WifiManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), service,
ConnectivityThread.getInstanceLooper());
}});它有个静态代码块,大致如下,负责创建各种manager实例
final class SystemServiceRegistry {
...
// Not instantiable.
private SystemServiceRegistry() { }
static {
registerService(Context.ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE, AccessibilityManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<AccessibilityManager>() {
@Override
public AccessibilityManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
return AccessibilityManager.getInstance(ctx);
}});
registerService(Context.CAPTIONING_SERVICE, CaptioningManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<CaptioningManager>() {
@Override
public CaptioningManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
return new CaptioningManager(ctx);
}});
registerService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE, AccountManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<AccountManager>() {
@Override
public AccountManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE);
IAccountManager service = IAccountManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return new AccountManager(ctx, service);
}});
...
}而调用呢,则看我们之前说的应用层ContextImpl的getSystemService方法
// The system service cache for the system services that are cached per-ContextImpl.
final Object[] mServiceCache = SystemServiceRegistry.createServiceCache(); @Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name);
}SystemServiceRegistry
// Service registry information.
// This information is never changed once static initialization has completed.
private static final HashMap<Class<?>, String> SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES =
new HashMap<Class<?>, String>();
private static final HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS =
new HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>>();
/**
* Gets a system service from a given context.
*/
public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) {
ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name);
return fetcher != null ? fetcher.getService(ctx) : null;
}
/**
* Statically registers a system service with the context.
* This method must be called during static initialization only.
*/
private static <T> void registerService(String serviceName, Class<T> serviceClass,
ServiceFetcher<T> serviceFetcher) {
SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES.put(serviceClass, serviceName);
SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.put(serviceName, serviceFetcher);
}这里主要就弄清了一件事,WifiManager是aidl的客户端,具体逻辑还是要去看服务端的。即看下Service对应代码:
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);而之前在(四十一) SystemServer初探有说到WifiService
// Wifi Service must be started first for wifi-related services.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWifi");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS);
traceEnd(); private static final String WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.server.wifi.WifiService";ServiceManager是这样的:
public final class ServiceManager {
private static final String TAG = "ServiceManager";
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or <code>null</code> if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name, or throws
* {@link NullPointerException} if none is found.
*
* @hide
*/
public static IBinder getServiceOrThrow(String name) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
final IBinder binder = getService(name);
if (binder != null) {
return binder;
} else {
throw new ServiceNotFoundException(name);
}
}
...
/**
* This is only intended to be called when the process is first being brought
* up and bound by the activity manager. There is only one thread in the process
* at that time, so no locking is done.
*
* @param cache the cache of service references
* @hide
*/
public static void initServiceCache(Map<String, IBinder> cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
sCache.putAll(cache);
}可以看到Service的IBinder要么从cache里取出来的,要么getIServiceManager().getService(name)取到的,那就先看下initServiceCache是在哪里调用的?
./base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial) {
if (services != null) {
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}那bindApplication是在 哪里调用的呢?
AMS:
if (app.instr != null) {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
} else {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo,
null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
} /**
* Initialize the application bind args. These are passed to each
* process when the bindApplication() IPC is sent to the process. They're
* lazily setup to make sure the services are running when they're asked for.
*/
private HashMap<String, IBinder> getCommonServicesLocked(boolean isolated) {
// Isolated processes won't get this optimization, so that we don't
// violate the rules about which services they have access to.
if (isolated) {
if (mIsolatedAppBindArgs == null) {
mIsolatedAppBindArgs = new HashMap<>();
mIsolatedAppBindArgs.put("package", ServiceManager.getService("package"));
}
return mIsolatedAppBindArgs;
}
if (mAppBindArgs == null) {
mAppBindArgs = new HashMap<>();
// Setup the application init args
mAppBindArgs.put("package", ServiceManager.getService("package"));
mAppBindArgs.put("window", ServiceManager.getService("window"));
mAppBindArgs.put(Context.ALARM_SERVICE,
ServiceManager.getService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE));
}
return mAppBindArgs;
}这里少了wifi相关的Service,所以还是走的
getIServiceManager().getService(name) private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}“从最表层的API过度到JNI层,然后与Lib层通讯”什么鬼,我只是个java工程师=-=
先给个结论,wifiManager调用接口是调用到WifiServiceImpl那边去了。
-------------------------------2018/6/19日更新,native层的正推没办法了,从倒推开始吧----------------------------------------
之前讲过WifiService是在SystemServer启动起来的,流程如下:
SystemServer.java:
// Wifi Service must be started first for wifi-related services.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWifi");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS);
traceEnd();SystemServiceManager:
简单来说就是调用下WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS("com.android.server.wifi.WifiService")的构造器和onStart方法
/**
* Starts a service by class name.
*
* @return The service instance.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public SystemService startService(String className) {
final Class<SystemService> serviceClass;
try {
serviceClass = (Class<SystemService>)Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + className);
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + className
+ ": service class not found, usually indicates that the caller should "
+ "have called PackageManager.hasSystemFeature() to check whether the "
+ "feature is available on this device before trying to start the "
+ "services that implement it", ex);
}
return startService(serviceClass);
}
/**
* Creates and starts a system service. The class must be a subclass of
* {@link com.android.server.SystemService}.
*
* @param serviceClass A Java class that implements the SystemService interface.
* @return The service instance, never null.
* @throws RuntimeException if the service fails to start.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}WifiService:
public final class WifiService extends SystemService {
private static final String TAG = "WifiService";
final WifiServiceImpl mImpl;
public WifiService(Context context) {
super(context);
mImpl = new WifiServiceImpl(context, new WifiInjector(context), new WifiAsyncChannel(TAG));
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
Log.i(TAG, "Registering " + Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
publishBinderService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE, mImpl);
}SystemService:
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service) {
publishBinderService(name, service, false);
}
/**
* Publish the service so it is accessible to other services and apps.
*/
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated) {
ServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
}这边的addService方法和getService方法是对应起来的,一个get,一个add。
所以之前的getService方法就是WifiServiceImpl。
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);2.2.2 Service的WiFi启动流程
先看下WifiServiceImpl流程:
public class WifiServiceImpl extends IWifiManager.Stub {
/**
* see {@link android.net.wifi.WifiManager#setWifiEnabled(boolean)}
* @param enable {@code true} to enable, {@code false} to disable.
* @return {@code true} if the enable/disable operation was
* started or is already in the queue.
*/
@Override
public synchronized boolean setWifiEnabled(String packageName, boolean enable)
throws RemoteException {
enforceChangePermission();
Slog.d(TAG, "setWifiEnabled: " + enable + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()
+ ", uid=" + Binder.getCallingUid() + ", package=" + packageName);
mLog.info("setWifiEnabled package=% uid=% enable=%").c(packageName)
.c(Binder.getCallingUid()).c(enable).flush();
boolean isFromSettings = checkNetworkSettingsPermission(
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid());
// If Airplane mode is enabled, only Settings is allowed to toggle Wifi
if (mSettingsStore.isAirplaneModeOn() && !isFromSettings) {
mLog.info("setWifiEnabled in Airplane mode: only Settings can enable wifi").flush();
return false;
}
// If SoftAp is enabled, only Settings is allowed to toggle wifi
boolean apEnabled =
mWifiStateMachine.syncGetWifiApState() != WifiManager.WIFI_AP_STATE_DISABLED;
if (apEnabled && !isFromSettings) {
mLog.info("setWifiEnabled SoftAp not disabled: only Settings can enable wifi").flush();
return false;
}
/*
* Caller might not have WRITE_SECURE_SETTINGS,
* only CHANGE_WIFI_STATE is enforced
*/
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (! mSettingsStore.handleWifiToggled(enable)) {
// Nothing to do if wifi cannot be toggled
return true;
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
if (mPermissionReviewRequired) {
final int wiFiEnabledState = getWifiEnabledState();
if (enable) {
if (wiFiEnabledState == WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLING
|| wiFiEnabledState == WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLED) {
if (startConsentUi(packageName, Binder.getCallingUid(),
WifiManager.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE)) {
return true;
}
}
} else if (wiFiEnabledState == WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLING
|| wiFiEnabledState == WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLED) {
if (startConsentUi(packageName, Binder.getCallingUid(),
WifiManager.ACTION_REQUEST_DISABLE)) {
return true;
}
}
}
mWifiController.sendMessage(CMD_WIFI_TOGGLED);
return true;
}mSettingsStore.handleWifiToggled(enable)设置一下SettingsProvider中存储的WIFI_ON的值
private void persistWifiState(int state) {
final ContentResolver cr = mContext.getContentResolver();
mPersistWifiState = state;
Settings.Global.putInt(cr, Settings.Global.WIFI_ON, state);
} /* Values tracked in Settings.Global.WIFI_ON */
static final int WIFI_DISABLED = 0;
static final int WIFI_ENABLED = 1;
/* Wifi enabled while in airplane mode */
private static final int WIFI_ENABLED_AIRPLANE_OVERRIDE = 2;
/* Wifi disabled due to airplane mode on */
private static final int WIFI_DISABLED_AIRPLANE_ON = 3;
public synchronized boolean handleWifiToggled(boolean wifiEnabled) {
// Can Wi-Fi be toggled in airplane mode ?
if (mAirplaneModeOn && !isAirplaneToggleable()) {
return false;
}
if (wifiEnabled) {
if (mAirplaneModeOn) {
persistWifiState(WIFI_ENABLED_AIRPLANE_OVERRIDE);
} else {
persistWifiState(WIFI_ENABLED);
}
} else {
// When wifi state is disabled, we do not care
// if airplane mode is on or not. The scenario of
// wifi being disabled due to airplane mode being turned on
// is handled handleAirplaneModeToggled()
persistWifiState(WIFI_DISABLED);
}
return true;
}这里接着会调用到WifiController,WifiController是个状态机设计模式,也就是说会根据WiFi的不同状态决定处理WiFi消息的不同逻辑。
初始化逻辑如下:
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mApStaDisabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mStaEnabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mDeviceActiveState, mStaEnabledState);
addState(mDeviceInactiveState, mStaEnabledState);
addState(mScanOnlyLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mFullLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mFullHighPerfLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mNoLockHeldState, mDeviceInactiveState);
addState(mStaDisabledWithScanState, mDefaultState);
addState(mApEnabledState, mDefaultState);
addState(mEcmState, mDefaultState);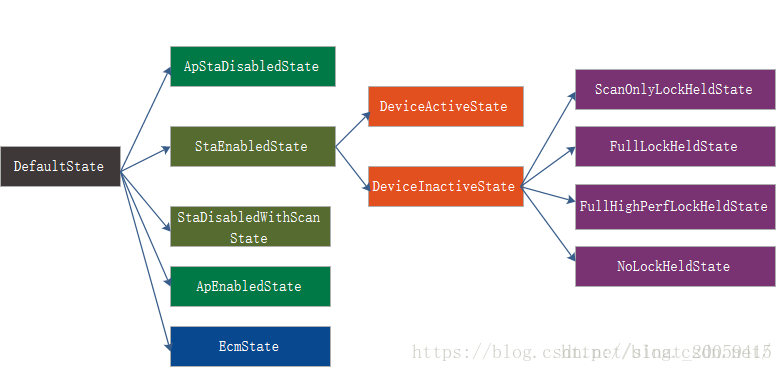
2.2.3 WifiController
WifiController的状态比较多,而我比较关注从关闭到打开的状态变化,即:
class ApStaDisabledState extends State {
private int mDeferredEnableSerialNumber = 0;
private boolean mHaveDeferredEnable = false;
private long mDisabledTimestamp;
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateMachine.setSupplicantRunning(false);
// Supplicant can't restart right away, so not the time we switched off
mDisabledTimestamp = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
mDeferredEnableSerialNumber++;
mHaveDeferredEnable = false;
mWifiStateMachine.clearANQPCache();
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case CMD_WIFI_TOGGLED:
case CMD_AIRPLANE_TOGGLED:
if (mSettingsStore.isWifiToggleEnabled()) {
if (doDeferEnable(msg)) {
if (mHaveDeferredEnable) {
// have 2 toggles now, inc serial number an ignore both
mDeferredEnableSerialNumber++;
}
mHaveDeferredEnable = !mHaveDeferredEnable;
break;
}
if (mDeviceIdle == false) {
// wifi is toggled, we need to explicitly tell WifiStateMachine that we
// are headed to connect mode before going to the DeviceActiveState
// since that will start supplicant and WifiStateMachine may not know
// what state to head to (it might go to scan mode).
mWifiStateMachine.setOperationalMode(WifiStateMachine.CONNECT_MODE);
transitionTo(mDeviceActiveState);
} else {
checkLocksAndTransitionWhenDeviceIdle();
}
} else if (mSettingsStore.isScanAlwaysAvailable()) {
transitionTo(mStaDisabledWithScanState);
}
break;现在就上面一串代码挨个解析。
WifiServiceImpl在走到WifiController之前有提及修改了一下SettingsProvider,其实也顺带改了一下WifiSettingsStore的mPersistWifiState值,用来标记wifi状态。
persistWifiState(WIFI_ENABLED); public synchronized boolean isWifiToggleEnabled() {
if (!mCheckSavedStateAtBoot) {
mCheckSavedStateAtBoot = true;
if (testAndClearWifiSavedState()) return true;
}
if (mAirplaneModeOn) {
return mPersistWifiState == WIFI_ENABLED_AIRPLANE_OVERRIDE;
} else {
return mPersistWifiState != WIFI_DISABLED;
}
}收到消息也不是立刻处理的:
private boolean doDeferEnable(Message msg) {
long delaySoFar = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - mDisabledTimestamp;
if (delaySoFar >= mReEnableDelayMillis) {
return false;
}
log("WifiController msg " + msg + " deferred for " +
(mReEnableDelayMillis - delaySoFar) + "ms");
// need to defer this action.
Message deferredMsg = obtainMessage(CMD_DEFERRED_TOGGLE);
deferredMsg.obj = Message.obtain(msg);
deferredMsg.arg1 = ++mDeferredEnableSerialNumber;
sendMessageDelayed(deferredMsg, mReEnableDelayMillis - delaySoFar + DEFER_MARGIN_MS);
return true;
}
...
mReEnableDelayMillis = mFacade.getLongSetting(mContext,
Settings.Global.WIFI_REENABLE_DELAY_MS, DEFAULT_REENABLE_DELAY_MS);
/**
* See {@link Settings.Global#WIFI_REENABLE_DELAY_MS}. This is the default value if a
* Settings.Global value is not present. This is the minimum time after wifi is disabled
* we'll act on an enable. Enable requests received before this delay will be deferred.
*/
private static final long DEFAULT_REENABLE_DELAY_MS = 500;wifi关闭后立刻打开有可能流程还没走完导致问题(压力测试会频繁开关WiFi),所以这边Google应该考虑到这点加了个最短时限500ms,如果短于这时间,就强迫补个差来个500+5ms的延时。
以小于500ms的间隔发送消息会由于mDeferredEnableSerialNumber值自增导致前一个消息失效。
case CMD_DEFERRED_TOGGLE:
if (msg.arg1 != mDeferredEnableSerialNumber) {
log("DEFERRED_TOGGLE ignored due to serial mismatch");
break;
}
log("DEFERRED_TOGGLE handled");
sendMessage((Message)(msg.obj));
break; // wifi is toggled, we need to explicitly tell WifiStateMachine that we
// are headed to connect mode before going to the DeviceActiveState
// since that will start supplicant and WifiStateMachine may not know
// what state to head to (it might go to scan mode).
mWifiStateMachine.setOperationalMode(WifiStateMachine.CONNECT_MODE);
transitionTo(mDeviceActiveState);由于是一个类,看下StaEnabledState(DeviceActiveState的父状态)和DeviceActiveState,状态机设计模式状态改变会先走进父状态的enter中。
class StaEnabledState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateMachine.setSupplicantRunning(true);
} /* Parent: StaEnabledState */
class DeviceActiveState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateMachine.setOperationalMode(WifiStateMachine.CONNECT_MODE);
mWifiStateMachine.setHighPerfModeEnabled(false);
}可以看到其实是调用顺序
mWifiStateMachine.setOperationalMode(WifiStateMachine.CONNECT_MODE);mWifiStateMachine.setSupplicantRunning(true);mWifiStateMachine.setOperationalMode(WifiStateMachine.CONNECT_MODE);mWifiStateMachine.setHighPerfModeEnabled(false);
2.2.4 WifiStateMachine
wifiStateMachine也是一个状态机:
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF IndentationCheck
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mScanModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mRoamingState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApState, mDefaultState);
// CHECKSTYLE:ON IndentationCheck这里看下WifiController下发的4个操作
1、3)setOperationalMode:
/**
* Track the state of Wifi connectivity. All event handling is done here,
* and all changes in connectivity state are initiated here.
*
* Wi-Fi now supports three modes of operation: Client, SoftAp and p2p
* In the current implementation, we support concurrent wifi p2p and wifi operation.
* The WifiStateMachine handles SoftAp and Client operations while WifiP2pService
* handles p2p operation.
*
* @hide
*/
public class WifiStateMachine extends StateMachine implements WifiNative.WifiRssiEventHandler,
WifiMulticastLockManager.FilterController { /**
* TODO: doc
*/
public void setOperationalMode(int mode) {
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) log("setting operational mode to " + String.valueOf(mode));
sendMessage(CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE, mode, 0);
})2)setSupplicantRunning
/** * TODO: doc
*/
public void setSupplicantRunning(boolean enable) {
if (enable) {
sendMessage(CMD_START_SUPPLICANT);
} else {
sendMessage(CMD_STOP_SUPPLICANT);
}
} /**
* Set high performance mode of operation.
* Enabling would set active power mode and disable suspend optimizations;
* disabling would set auto power mode and enable suspend optimizations
*
* @param enable true if enable, false otherwise
*/
public void setHighPerfModeEnabled(boolean enable) {
sendMessage(CMD_SET_HIGH_PERF_MODE, enable ? 1 : 0, 0);
}来看下初始状态对消息的处理
class InitialState extends State {
private void cleanup() {
// Tearing down the client interfaces below is going to stop our supplicant.
mWifiMonitor.stopAllMonitoring();
mDeathRecipient.unlinkToDeath();
mWifiNative.tearDown();
}
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateTracker.updateState(WifiStateTracker.INVALID);
cleanup();
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch (message.what) {
case CMD_START_SUPPLICANT:
Pair<Integer, IClientInterface> statusAndInterface =
mWifiNative.setupForClientMode();
if (statusAndInterface.first == WifiNative.SETUP_SUCCESS) {
mClientInterface = statusAndInterface.second;
} else {
incrementMetricsForSetupFailure(statusAndInterface.first);
}
if (mClientInterface == null
|| !mDeathRecipient.linkToDeath(mClientInterface.asBinder())) {
setWifiState(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_UNKNOWN);
cleanup();
break;
}
try {
// A runtime crash or shutting down AP mode can leave
// IP addresses configured, and this affects
// connectivity when supplicant starts up.
// Ensure we have no IP addresses before a supplicant start.
mNwService.clearInterfaceAddresses(mInterfaceName);
// Set privacy extensions
mNwService.setInterfaceIpv6PrivacyExtensions(mInterfaceName, true);
// IPv6 is enabled only as long as access point is connected since:
// - IPv6 addresses and routes stick around after disconnection
// - kernel is unaware when connected and fails to start IPv6 negotiation
// - kernel can start autoconfiguration when 802.1x is not complete
mNwService.disableIpv6(mInterfaceName);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
loge("Unable to change interface settings: " + re);
} catch (IllegalStateException ie) {
loge("Unable to change interface settings: " + ie);
}
if (!mWifiNative.enableSupplicant()) {
loge("Failed to start supplicant!");
setWifiState(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_UNKNOWN);
cleanup();
break;
}
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) log("Supplicant start successful");
mWifiMonitor.startMonitoring(mInterfaceName, true);
mWifiInjector.getWifiLastResortWatchdog().clearAllFailureCounts();
setSupplicantLogLevel();
transitionTo(mSupplicantStartingState);
break;
case CMD_START_AP:
transitionTo(mSoftApState);
break;
case CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE:
mOperationalMode = message.arg1;
if (mOperationalMode != DISABLED_MODE) {
sendMessage(CMD_START_SUPPLICANT);
}
break;
default:
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
return HANDLED;
}
}在InitialState 中 1、 3 步最后走的逻辑和第2步是一样的,都是发出了一个CMD_START_SUPPLICANT消息,不是很懂这块处理逻辑=-=搜了下真正对CONNECT_MODE有处理的是以下状态,应该是第3步发出的消息会得到ScanModeState的处理:
class ScanModeState extends State {
private int mLastOperationMode;
@Override
public void enter() {
mLastOperationMode = mOperationalMode;
mWifiStateTracker.updateState(WifiStateTracker.SCAN_MODE);
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch(message.what) {
case CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE:
if (message.arg1 == CONNECT_MODE) {
mOperationalMode = CONNECT_MODE;
setWifiState(WIFI_STATE_ENABLING);
transitionTo(mDisconnectedState);
} else if (message.arg1 == DISABLED_MODE) {
transitionTo(mSupplicantStoppingState);
}
// Nothing to do
break;
// Handle scan. All the connection related commands are
// handled only in ConnectModeState
case CMD_START_SCAN:
handleScanRequest(message);
break;
default:
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
return HANDLED;
}
}先看下接收到该消息进行的关键操作:
- mWifiNative.enableSupplicant()
- mWifiMonitor.startMonitoring(mInterfaceName, true);
- 切换到SupplicantStartingState状态
PS:
/**
* Enable wpa_supplicant via wificond.
* @return Returns true on success.
*/
public boolean enableSupplicant() {
return mWificondControl.enableSupplicant();
} /**
* Start Monitoring for wpa_supplicant events.
*
* @param iface Name of iface.
* TODO: Add unit tests for these once we remove the legacy code.
*/
public synchronized void startMonitoring(String iface, boolean isStaIface) {
if (ensureConnectedLocked()) {
setMonitoring(iface, true);
broadcastSupplicantConnectionEvent(iface);
} else {
boolean originalMonitoring = isMonitoring(iface);
setMonitoring(iface, true);
broadcastSupplicantDisconnectionEvent(iface);
setMonitoring(iface, originalMonitoring);
Log.e(TAG, "startMonitoring(" + iface + ") failed!");
}
}看切换完了再收到这个消息后就是延迟发送了,后面估计是轮到哪个状态就是不同的处理逻辑的,但就我看来这个消息主要就是start supplicant的,start完了应该完成任务了。
case CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE:
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_DEFERRED;
deferMessage(message);
break;至于第4步
SupplicantStartedState状态会处理:
case CMD_SET_HIGH_PERF_MODE:
if (message.arg1 == 1) {
setSuspendOptimizations(SUSPEND_DUE_TO_HIGH_PERF, false);
} else {
setSuspendOptimizations(SUSPEND_DUE_TO_HIGH_PERF, true);
}
break;都是WifiNative的代码,溜了溜了。
private void setSuspendOptimizationsNative(int reason, boolean enabled) {
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) {
log("setSuspendOptimizationsNative: " + reason + " " + enabled
+ " -want " + mUserWantsSuspendOpt.get()
+ " stack:" + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[2].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[3].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[4].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[5].getMethodName());
}
//mWifiNative.setSuspendOptimizations(enabled);
if (enabled) {
mSuspendOptNeedsDisabled &= ~reason;
/* None of dhcp, screen or highperf need it disabled and user wants it enabled */
if (mSuspendOptNeedsDisabled == 0 && mUserWantsSuspendOpt.get()) {
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) {
log("setSuspendOptimizationsNative do it " + reason + " " + enabled
+ " stack:" + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[2].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[3].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[4].getMethodName()
+ " - " + Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[5].getMethodName());
}
mWifiNative.setSuspendOptimizations(true);
}
} else {
mSuspendOptNeedsDisabled |= reason;
mWifiNative.setSuspendOptimizations(false);
}
}