题目:打开命令行输入参数所要求打开的文件(如果不存在则创建,并开放所有权限),然后清空文件内容,向文件内写入hello world之后,从当前位置开一个大小为10000的洞,最后输出文件内的前五个字符。
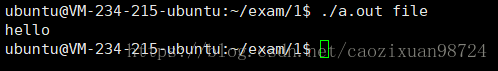
实例: ./a.out file
考点:open,write,read,lseek的使用。
注意点:
1.返回值异常要及时报错。
2.产生的空洞要再次写入才能显示出来。也就是说lseek之后还要再write。
3.最后不要忘记关闭文件。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
char buf[5];
int fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0777);
if(fd<0){
printf("file open error!\n");
return 1;
}
char *s = "hello,world";
write(fd,s,strlen(s));
if(lseek(fd,10000,SEEK_CUR)==-1)
{
printf("seek error!\n");
}
write(fd,s,strlen(s));
if(lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET)==-1)
{
printf("seek error");
}
read(fd,buf,5);
printf("%s",buf);
printf("\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
1738217 查看本文章


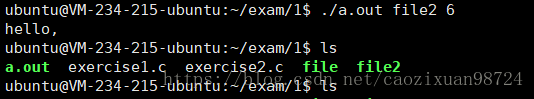
改进:再增加一个参数,使得用户可以选择返回的字符数(0-9)
注意:需要用到malloc和free函数。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
int num = argv[2][0]-'0';
char *buf = (char*)malloc(num);
int fd = open(argv[1],O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0777);
if(fd<0){
printf("file open error!\n");
return 1;
}
char *s = "hello,world";
write(fd,s,strlen(s));
if(lseek(fd,10000,SEEK_CUR)==-1)
{
printf("seek error!\n");
}
write(fd,s,strlen(s));
if(lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET)==-1)
{
printf("seek error");
}
read(fd,buf,num);
printf("%s",buf);
printf("\n");
free(buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
输出结果: