本文介绍一些注意力机制的实现,包括EMHSA/SA/SGE/AFT/Outlook Attention。
【深度学习】注意力机制(五)
目录
一、EMHSA(Efficient Multi-Head Self-Attention)
三、SGE(Spatial Group-wise Enhance)
四、AFT(Attention Free Transformer)
一、EMHSA(Efficient Multi-Head Self-Attention)
论文:论文地址
如下图:

代码(代码连接):
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
class EMSA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, d_k, d_v, h,dropout=.1,H=7,W=7,ratio=3,apply_transform=True):
super(EMSA, self).__init__()
self.H=H
self.W=W
self.fc_q = nn.Linear(d_model, h * d_k)
self.fc_k = nn.Linear(d_model, h * d_k)
self.fc_v = nn.Linear(d_model, h * d_v)
self.fc_o = nn.Linear(h * d_v, d_model)
self.dropout=nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.ratio=ratio
if(self.ratio>1):
self.sr=nn.Sequential()
self.sr_conv=nn.Conv2d(d_model,d_model,kernel_size=ratio+1,stride=ratio,padding=ratio//2,groups=d_model)
self.sr_ln=nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.apply_transform=apply_transform and h>1
if(self.apply_transform):
self.transform=nn.Sequential()
self.transform.add_module('conv',nn.Conv2d(h,h,kernel_size=1,stride=1))
self.transform.add_module('softmax',nn.Softmax(-1))
self.transform.add_module('in',nn.InstanceNorm2d(h))
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_k = d_k
self.d_v = d_v
self.h = h
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, queries, keys, values, attention_mask=None, attention_weights=None):
b_s, nq ,c = queries.shape
nk = keys.shape[1]
q = self.fc_q(queries).view(b_s, nq, self.h, self.d_k).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # (b_s, h, nq, d_k)
if(self.ratio>1):
x=queries.permute(0,2,1).view(b_s,c,self.H,self.W) #bs,c,H,W
x=self.sr_conv(x) #bs,c,h,w
x=x.contiguous().view(b_s,c,-1).permute(0,2,1) #bs,n',c
x=self.sr_ln(x)
k = self.fc_k(x).view(b_s, -1, self.h, self.d_k).permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # (b_s, h, d_k, n')
v = self.fc_v(x).view(b_s, -1, self.h, self.d_v).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # (b_s, h, n', d_v)
else:
k = self.fc_k(keys).view(b_s, nk, self.h, self.d_k).permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # (b_s, h, d_k, nk)
v = self.fc_v(values).view(b_s, nk, self.h, self.d_v).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # (b_s, h, nk, d_v)
if(self.apply_transform):
att = torch.matmul(q, k) / np.sqrt(self.d_k) # (b_s, h, nq, n')
att = self.transform(att) # (b_s, h, nq, n')
else:
att = torch.matmul(q, k) / np.sqrt(self.d_k) # (b_s, h, nq, n')
att = torch.softmax(att, -1) # (b_s, h, nq, n')
if attention_weights is not None:
att = att * attention_weights
if attention_mask is not None:
att = att.masked_fill(attention_mask, -np.inf)
att=self.dropout(att)
out = torch.matmul(att, v).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous().view(b_s, nq, self.h * self.d_v) # (b_s, nq, h*d_v)
out = self.fc_o(out) # (b_s, nq, d_model)
return out
二、SA(SHUFFLE ATTENTION)
论文:论文地址
如下图:

代码如下(代码连接):
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class ShuffleAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512,reduction=16,G=8):
super().__init__()
self.G=G
self.channel=channel
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channel // (2 * G), channel // (2 * G))
self.cweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.cbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
@staticmethod
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = x.reshape(b, groups, -1, h, w)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
# flatten
x = x.reshape(b, -1, h, w)
return x
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
#group into subfeatures
x=x.view(b*self.G,-1,h,w) #bs*G,c//G,h,w
#channel_split
x_0,x_1=x.chunk(2,dim=1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
#channel attention
x_channel=self.avg_pool(x_0) #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel=self.cweight*x_channel+self.cbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel=x_0*self.sigmoid(x_channel)
#spatial attention
x_spatial=self.gn(x_1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial=self.sweight*x_spatial+self.sbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial=x_1*self.sigmoid(x_spatial) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
# concatenate along channel axis
out=torch.cat([x_channel,x_spatial],dim=1) #bs*G,c//G,h,w
out=out.contiguous().view(b,-1,h,w)
# channel shuffle
out = self.channel_shuffle(out, 2)
return out三、SGE(Spatial Group-wise Enhance)
论文:Spatial Group-wise Enhance: Improving Semanti
如下图:

代码如下(代码连接):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SpatialGroupEnhance(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, groups = 64):
super(SpatialGroupEnhance, self).__init__()
self.groups = groups
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.weight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, groups, 1, 1))
self.bias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, groups, 1, 1))
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x): # (b, c, h, w)
b, c, h, w = x.size()
x = x.view(b * self.groups, -1, h, w)
xn = x * self.avg_pool(x)
xn = xn.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)
t = xn.view(b * self.groups, -1)
t = t - t.mean(dim=1, keepdim=True)
std = t.std(dim=1, keepdim=True) + 1e-5
t = t / std
t = t.view(b, self.groups, h, w)
t = t * self.weight + self.bias
t = t.view(b * self.groups, 1, h, w)
x = x * self.sig(t)
x = x.view(b, c, h, w)
return x四、AFT(Attention Free Transformer)
论文:An Attention Free Transformer
如下图:
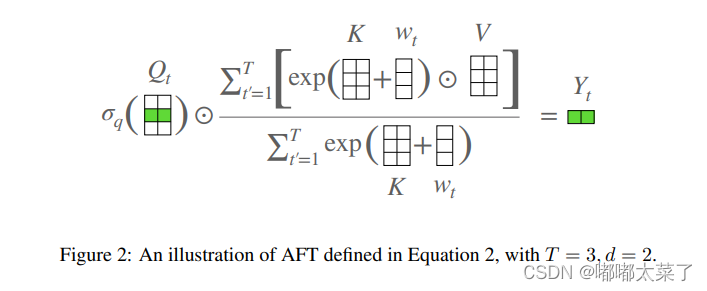
代码如下(代码连接):
import torch, math
from torch import nn, einsum
import torch.nn.functional as F
class AFTFull(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, max_seqlen, dim, hidden_dim=64):
super().__init__()
'''
max_seqlen: the maximum number of timesteps (sequence length) to be fed in
dim: the embedding dimension of the tokens
hidden_dim: the hidden dimension used inside AFT Full
Number of heads is 1 as done in the paper
'''
self.dim = dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.to_q = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.project = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim)
self.wbias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(max_seqlen, max_seqlen))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.wbias)
def forward(self, x):
B, T, _ = x.shape
Q = self.to_q(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
K = self.to_k(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
V = self.to_v(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
temp_wbias = self.wbias[:T, :T].unsqueeze(0) # sequences can still be variable length
'''
From the paper
'''
Q_sig = torch.sigmoid(Q)
temp = torch.exp(temp_wbias) @ torch.mul(torch.exp(K), V)
weighted = temp / (torch.exp(temp_wbias) @ torch.exp(K))
Yt = torch.mul(Q_sig, weighted)
Yt = Yt.view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
Yt = self.project(Yt)
return Yt
class AFTSimple(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, max_seqlen, dim, hidden_dim=64):
super().__init__()
'''
max_seqlen: the maximum number of timesteps (sequence length) to be fed in
dim: the embedding dimension of the tokens
hidden_dim: the hidden dimension used inside AFT Full
Number of Heads is 1 as done in the paper.
'''
self.dim = dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.to_q = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.project = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim)
def forward(self, x):
B, T, _ = x.shape
Q = self.to_q(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
K = self.to_k(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
V = self.to_v(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
'''
From the paper
'''
weights = torch.mul(torch.softmax(K, 1), V).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)
Q_sig = torch.sigmoid(Q)
Yt = torch.mul(Q_sig, weights)
Yt = Yt.view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
Yt = self.project(Yt)
return Yt
class AFTLocal(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, max_seqlen, dim, hidden_dim=64, s=256):
super().__init__()
'''
max_seqlen: the maximum number of timesteps (sequence length) to be fed in
dim: the embedding dimension of the tokens
hidden_dim: the hidden dimension used inside AFT Full
s: the window size used for AFT-Local in the paper
Number of heads is 1 as done in the paper
'''
self.dim = dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.to_q = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_dim)
self.project = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, dim)
self.wbias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(max_seqlen, max_seqlen))
self.max_seqlen = max_seqlen
self.s = s
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.wbias)
def forward(self, x):
B, T, _ = x.shape
Q = self.to_q(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
K = self.to_k(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
V = self.to_v(x).view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
self.wbias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor([
[self.wbias[i][j] if math.fabs(i-j) < self.s else 0 for j in range(self.max_seqlen)]
for i in range(self.max_seqlen)
]))
temp_wbias = self.wbias[:T, :T].unsqueeze(0) # sequences can still be variable length
'''
From the paper
'''
Q_sig = torch.sigmoid(Q)
temp = torch.exp(temp_wbias) @ torch.mul(torch.exp(K), V)
weighted = temp / (torch.exp(temp_wbias) @ torch.exp(K))
Yt = torch.mul(Q_sig, weighted)
Yt = Yt.view(B, T, self.hidden_dim)
Yt = self.project(Yt)
return Yt
五、Outlook Attention
论文:VOLO: Vision Outlooker for Visual Recognition
如下图:
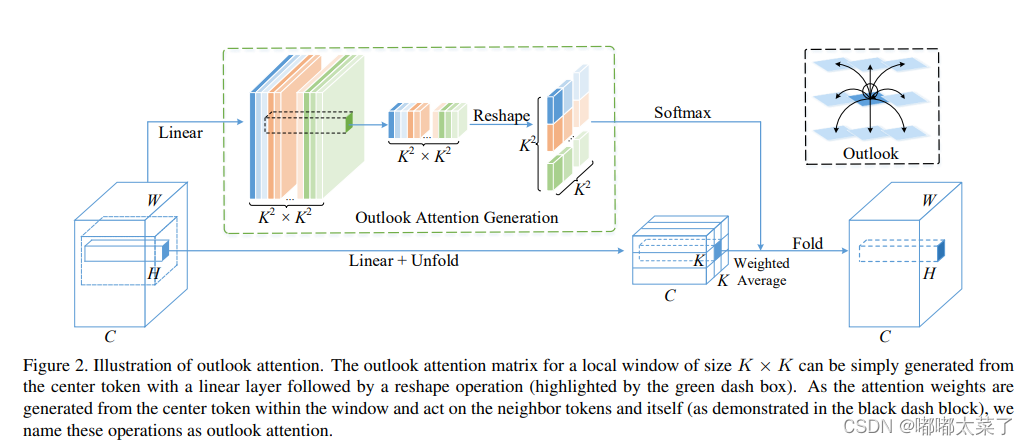
代码如下(代码连接):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class OutlookAttention(nn.Module):
"""
Implementation of outlook attention
--dim: hidden dim
--num_heads: number of heads
--kernel_size: kernel size in each window for outlook attention
return: token features after outlook attention
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1,
qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.padding = padding
self.stride = stride
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim**-0.5
self.v = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn = nn.Linear(dim, kernel_size**4 * num_heads)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
self.unfold = nn.Unfold(kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding, stride=stride)
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=stride, stride=stride, ceil_mode=True)
def forward(self, x):
B, H, W, C = x.shape
v = self.v(x).permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # B, C, H, W
h, w = math.ceil(H / self.stride), math.ceil(W / self.stride)
v = self.unfold(v).reshape(B, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads,
self.kernel_size * self.kernel_size,
h * w).permute(0, 1, 4, 3, 2) # B,H,N,kxk,C/H
attn = self.pool(x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)).permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
attn = self.attn(attn).reshape(
B, h * w, self.num_heads, self.kernel_size * self.kernel_size,
self.kernel_size * self.kernel_size).permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4) # B,H,N,kxk,kxk
attn = attn * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).permute(0, 1, 4, 3, 2).reshape(
B, C * self.kernel_size * self.kernel_size, h * w)
x = F.fold(x, output_size=(H, W), kernel_size=self.kernel_size,
padding=self.padding, stride=self.stride)
x = self.proj(x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1))
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x