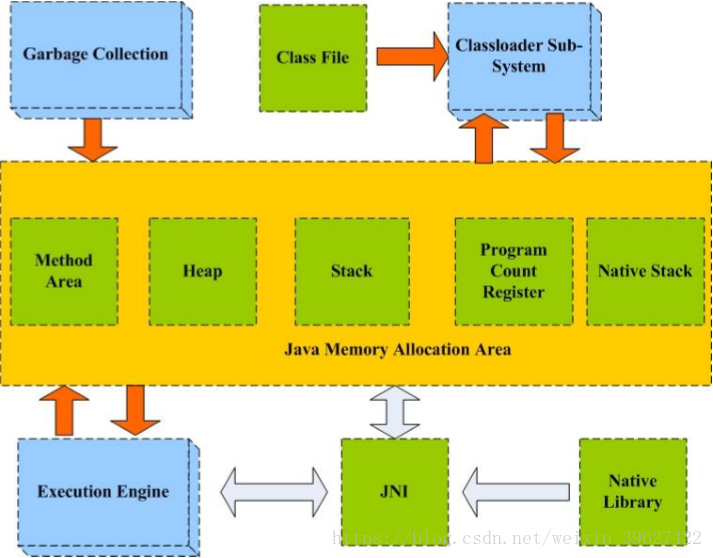
内存管理模型:堆、栈
所有局部的基本类型都在栈上创建,所有对象都在堆上创建
多线程之间传递数据,是通过复制而非引用
即使是局部变量的object,也是在堆上创建
堆上创建的对象可被所有线程共享引用,可访问对象,就可以访问对象内的成员变量
JVM模型:
栈的用途:
1.用于传参
2.方法的返回值
3.在计算表达式时存储中间结果
4.存储局部变量
堆的用途:
1.对象
2.Array
3.通过使用“new”操作符
Garbage Collection
三种模式下的空间回收:
1.在静态内存分配模式下,无需进行内存回收,所有都是已确定的(对于每一个对象,都有一个附加的实体;只要实体是活动的,执行就需要保留对象的空间。因此在适当的意义上不可能进行回收。)
2。在栈上进行内存空间回收:按block (某个方法)整体进行
3.在heap 上进行内存空间回收,最复杂—— 无法 提前预知某个object 是否已经变得无用。
Reachable and Unreachable Objects:
在系统执行的任何时候,origins/roots的集合都由根对象组成
只要对象仍然可以从程序计算的某些部分获得,它就可以存活。这些origins/roots的任何相关的、直接的或间接的都是可到达的,而任何其他的对象都是不可达的
In common language implementations roots include
– Words in the static area 静态区域的数据
– Registers 寄存器
– Words on the execution stack that point into the heap. 目前的执行栈中的数据所指向的内存对象
活对象:从root 可达的对象
死对象:从root
垃圾回收器根据对象的“活性”( 从root 的可达性) 来决定是否回收该对象的内存
GC的成本指标:执行时间、延迟时间、内存使用情况、其他重要指标
可靠性:收集到的每个对象都是不可达的。
完整性:所有不可达的对象都会被收集。
GC的四种基本算法
Reference counting 引用计数在你的车库里对每一个对象都做一个记录,表明对该对象的引用次数。如果一个对象的引用计数变为0,则将该对象抛出(它已死)。
为每个object 存储一 个计数RC ,当有其他reference 指向它时,RC++ ;当其他reference 与其断开时,RC-- ;如果RC==0 ,则回收它。
引用计数方法的优点:简单、计算代价分散 ,“幽灵时间”短 ->0
引用计数方法 的缺点:不全面(容易漏掉循环引用的对象)、并发支持较弱、占用额外内存空间等。
Mark-Sweep 标记- 清除
-在你需要的对象(根)上做个说明。
-然后递归地在一个活动对象需要的任何东西上放一个注释。
-检查所有对象,剔除无注释的对象。
为每个object 设定状态位(live/dead) 并记录,即mark 阶段;将标记为dead 的对象进行清理,即sweep 可阶段。
Advantages of mark-sweep
Comprehensive: cyclic garbage collected naturally
No run-time overhead on pointer manipulations
Loosely coupled to mutator
Does not move objects
– Does not break any mutator invariants
– Optimizer-friendly
– Requires only one reference to each live object to be discovered
(rather than having to find every reference)
Disadvantages of mark-sweep
Stop/start nature leads to disruptive pauses and long zombie time.
Every location in memory must be examined during the sweep
stage of this algorithm - this can be time-consuming and the
complexity is O(heap) rather than O(live)
– Every live object is visited in mark phase
– Every object, alive or dead, is visited in sweep phase
Degrades with residency (heap occupancy)
– The collector needs headroom in the heap to avoid thrashing
– Example: lots of marking to do if heap is full
Fragmentation: Can leave several gaps in used memory when
objects are swept out. This fragmentation cause serious performance
problems for applications which make heavy memory demands.
Tracing collectors must be able to find roots.
Mark-Compact 标记- 整理
-在你需要的物品上做笔记。
-把任何有纸条的东西搬到车库里。
-把车库前的东西都烧掉(都死了)。
Copying 复制
-把你需要的东西搬到新的车库。
-然后递归地移动新车库中对象需要的任何东西。
-然后,烧掉旧车库(里面的任何东西都是死的)!
CopyGC的优点
压实免费
对于所有对象大小,分配非常便宜。
外置检查是指针比较。
只需增加要分配的自由指针
只处理活动数据(通常是堆的一小部分)
固定的空间开销
自由和扫描的指针
可以在用户数据上写入转发地址
综合:自然回收循环垃圾
实现合理有效的复制GC非常简单
CopyGC的缺点
停止与复制可能是破坏性的
降解与居住
需要其他简单收集器的两倍地址空间
触摸两倍的页面
权衡反对分裂
复制大型对象的成本。
长寿命数据可能被反复复制。
所有引用必须更新
移动的物体可能会破坏可变子不变量
宽度优先的复制可能会干扰本地模式
JVM的内存管理模型
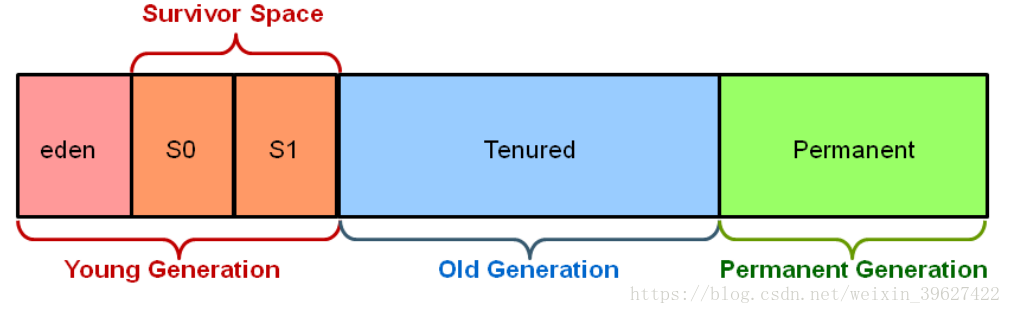
Java GC 将堆分为不同的区域,各区域采用不同的GC 策略,以提高GC 的效率
针对年轻代: 只 有 一小部分对象可较长时间存活,故采用copy 算法减少GC代价
针对年老代:这里的对象有很高的幸存度,使用Mark-Sweep 或Mark-Compact
只有当某个区域不能再为对象分配内存时(满),才启动GC
针对young generation , 使用minor GC,Minor GC所需时间较短,如果历经多次minor GC仍存活下来,将其copy到old generation,如果old generation 满了,则启动full GC, 当perm generation 满了之后,无法存储更多的元数据,也启动full GC
JVM中的垃圾收集调优:
尽可能减少GC 时间,一般不超过程序执行时间的5%
一旦初始分配给程序的内存满了,就抛出内存溢出异常
在启动程序时,可为其配置内存分配的具体大小
堆的大小决定着VM 将会以何种频度进行GC 、每次GC的时间多长
较大的heap会导致较少发生GC,但每次GC时间很长
通过 以下 参数 设置young generation 的 尺寸
– -XX: NewSize=<n>[g|m|k] The initial and minimum size of the
young generation space. <n> is the size. [g|m|k] indicates whether the
size should be interpreted as gigabytes, megabytes, or kilobytes.
– -XX: MaxNewSize=<n>[g|m|k] The maximum size of the young
generation space.
– -Xmn<n>[g|m|k] Sets the initial, minimum, and maximum size of the
young generation space.
– -XX:NewRatio=<n> The ratio between the young and old generation is
1:n. In other words, the combined size of the eden and survivor spaces
will be 1/(1+n) of the total heap size.
– -XX:SurvivorRatio=<n> The ratio between eden and a survivor space
to n:1, i.e., each survivor space will be 1/n the size of eden, and thus
1/(2+n) the size of the young.
old generation 的尺寸不需设置,根据其他各参数的取值可计算得到
– The initial old generation space size is the value of -Xms minus -
XX:NewSize.
– The maximum old generation space size is the value of -Xmx minus -
XX:MaxNewSize.
– If -Xms and -Xmx are set to the same value and -Xmn is used, or -
XX:NewSize is the same value as -XX:MaxNewSize, then the old
generation size is -Xmx (or -Xms) minus -Xmn.