注意:文中彩色代码均在Visual Studio 2022编译器中编写,本文为C语言数据结构手抄版,文中有部分改动,非原创。
目录
学习目标
- 熟悉树的定义、表示方法、有关术语和基本概念。
- 熟练掌握二叉树的递归定义、二叉树的性质, 了解相应的证明方法。
- 熟练掌握二叉树的两种存储方法、特点及适用范围。
- 熟练掌握二叉树的各种次序的遍历算法,灵活运用三种遍历算法实现二叉树的其他运算,并能解决简单的应用问题。
- 了解二叉树的线索化及其实质,掌握在中序线索树中查找给定结点的中序前驱和中序后继的方法。
- 掌握树、森林与二叉树之间的转换方法以及树和森林的遍历方法。
- 了解最优二叉树的特性,熟练掌握构造哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码的方法。
5.1.树的基本概念和术语
树形结构是一类重要的非线性数据结构,树中结点之间具有明确的层次关系,并且结点之间有分支,非常类似于真正的树。树形结构在客观世界中大量存在,如行政组织机构和人类社会的家谱等都可用树形结构形象地表示。在计算机应用领域中,树形结构也被广泛地应用,例如在编译程序中,用树结构来表示源程序的语法结构;在数据库系统中,用树结构来组织信息;在计算机图形学中,用树结构来表示图像关系等。
在现实生活中,存在许多可以用树形结构描述的实际问题。例如,某大学的行政组织机构就是一种树形结构:大学领导各部处或学院(系),部处领导各科室,院系领导各教研室。这个行政组织机构关系可用图5.1所示的树形图来描述,它就像一棵倒画的树,其中大学是“树根”,部处、学院是“分支",科、室、教研室是“树叶”。以大学为根的树是一棵大树,它可分成部处、学院为根的小树(子树),每棵子树又可分为若干棵子树。可见,树形结构是一个递归结构。

1.树的定义
树(Tree)是n (n≥0)个结点的有限集T。它或是空集(空树即n=0),或者是非空集。对于任意一棵非空树:
1.有且仅有一个特定的称为根(Root)的结点;
2.当n>1时,其余的结点可分为m (m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1, T2,...,Tm,其中每个集合本身又是一棵树,并称为根的子树。例如,图5.2 (a)表示的是一个有11个结点的树,其中A是根结点,其余的结点分成三棵互不相交的子集: T1={B, E,F, J, K}, T2={C, G}, T3={D, H, I); T1、T2和T3都是根A的子树,且本身也是一棵子树。
2.树的表示法
树的表示法有多种,但最常用的是树形图表示法。在树形图表示中,结点通常用圆圈表示,结点名一般写在圆圈内或写在圆圈旁,如图5.2 (a)所示。这种表示法非常直观,因此在书中多数情况下,都是用它来表示树结构的。
在不同的应用场合,树的表示方法也不尽相同。除了树形表示法外,通常还有三种表示方法,如图5.2 (a)中所示的树可以用图(b)、(c)和(d)来表示,其中图5.2 (b)是以嵌套集合的形式表示的;图5.2 (c)用的是凹形表示法;图5.2 (d)是以广义表的形式表示的,树根作为由子树森林组成的表的名字写在表的左边。

3.基本术语
为了更好地理解和掌握树结构的相关知识,首先要熟悉树结构中的基本术语。
树的结点包含一个数据元素及若干个指向其子树的分支。一个结点拥有的子树数称为该结点的度(Degree)。例如,图5.2 (a)中根结点A有三棵子树,因此它的度为3,C的度为1, E的度为0。一棵树中结点的最大度数称为该树的度,如图5.2 (a)中树的度为3。度数为零的结点称为叶子(Leaf)结点或终端结点,图5.2 (a)中的结点E、J、K、G、 H、I都是树的叶子结点。度数不为零的结点称为非终端结点或分支结点。除根结点之外,分支结点也称为内部结点,而根结点又称为开始结点。
树中某个结点子树的根称为该结点的孩子(Child),相应地,该结点称为孩子结点的双亲(Parent)或父结点。例如,在图5.2 (a)所示的树中, B是子树T1的根,则B是A的孩子,而A则是B的双亲,同一个双亲的孩子之间互为兄弟。又如,结点B.C.D之间互为兄弟。若将上述这种双亲关系进一步推广,可以认为结点B是结点K的祖父。
若在一棵树中存在着一个结点序列k1,K2,...,Kj使得ki是ki+1的父结点(1≤i≤j),则称该结点序列是从k1到kj的一条路径。例如,在图5.2(a)中,结点A到K有一条路径ABFK,它的路径长度是3。显然,从树根到树中其余结点均存在唯一的一条路径。
若树中结点ki到kj存在一条路径,则称结点ki是kj的祖先,结点kj是ki的子孙。例如,在图5.2 (a)所示的树中,结点J祖先是A,B和F,结点B的子孙有E、F、J和K。
树中结点的层次(Level)是从根开始算起,根为第一层,其余结点的层次等于其双亲结点的层数加1,树中结点的最大层次称为树的深度(Depth)或高度。如图5.2 (a)表示的树,其结点F的层次为3,而该树的高度是4。
如果将树中结点的各子树看成是从左至右依次有序且不能交换,则称该树为有序树,否则称为无序树
森林(Forest)是m (m≥0)棵互不相交的树的集合。若将一棵树的根结点删除,就得到该树的子树所构成的森林;如果将森林中所有树作为子树,用一个根结点把子树都连起来,森林就变成一棵树。
5.2.二叉树
二叉树是树形结构的一种重要类型,在实际应用中具有十分重要的意义。从许多实际问题中抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树的形式,即使是一般的树也能够简单地转换为二叉树形式,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都比较简单,因此,我们将详细地讨论关于二叉树的存储、运算及应用。
5.2.1.二叉树的定义和性质
1.二叉树定义
二叉树(Binary Tree)是n (n≥0)个结点的有限集合,它的每个结点至多只有两棵子树。它或者是空集,或者是由一个根结点及两棵互不相交的分别称作这个根的左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
从上面的二叉树定义可以看出它是递归的,根据这个定义可以导出二叉树如图5.3所示的物种基本形态。其中, 图5.3 (a)为空二叉树,图5.3 (b)为只有单个跟结点的二叉树,图5.3 (c)为只有根结点及左子树的二叉树,图5.3 (d)为只有根结点及右子树的二叉树,图5.3 (e)为有根及左、右子树的二叉树。

2.二叉树的性质
二叉树具有几个非常重要的性质,如下所述。
性质1在二叉树的第i层上至多有2i-1个结点(i≥1)
利用数学归纳法证明如下:
- 当i=1时,只有一个根结点,即2i-1=20=1,命题成立。
- 假设对所有的j (1≤j≤i),命题成立,即第j层上最多有2i-1个结点。
- 由归纳假设,第i-1层上至多有2i-2个结点。由于二叉树的每个结点的度至多为2,因此,在第i层上的结点数至多是第i-1层上最大结点数的2倍,即2×2i-2=2i-1个结点,所以命题成立
性质2深度为k的二叉树至多有2k-1个结点(k≥1)
证明: 一棵深度为k的二叉树最多含有的结点数,应该是该二叉树中每一层上最多含有结点数的总和。由性质1可知,深度为k的二叉树的最大结点数为

因此,命题成立。
性质3对任何一棵二叉树T,若其终端结点数为n0,度数为2的结点数为n2,则no=n2+1
证明:设n1为二叉树T中度为1的结点数。因为二叉树中所有结点的度均不大于2,所以二叉树T上的结点总数为:
n=n0+n1+n2 (5-1)
另一方面,度数为1的结点表示它有一个孩子结点,度数为2的结点有两个孩子结点,所以树中孩子结点总数应该是n1+2n2。而树中只有根结点不是任何结点的孩子结点,因此二叉树中的结点总数又可表示为:
n=n1+2n2 +1 (5-2)
由式(5-1)和式(5-2)解得: n0=n2+1,所以命题成立。
满二叉树和完全二叉树是两种特殊情形的二叉树。
- 满二叉树:一棵深度为k且有2k-1个结点的二叉树称为满二叉树。如图5.4 (a)所示的二叉树是一棵深度为4的满二叉树,这种树的特点是每一层上的结点数都达到最大值,因此不存在度数为1的结点,且所有叶子结点都在第k层上。
- 完全二叉树:若一棵深度为k的二叉树,其前k-1层是一棵满二叉树,而最下面一层(即第k层)上的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置上,则称此二叉树为完全二叉树。如图5.4 (b)所示的二叉树就是一棵完全二叉树,而图5.4(c)所示就不是一棵完全二叉树,因为最下面一层上的结点L不是在最左边的若干位置上。
显然,满二叉树一定是完全二叉树,但完全二叉树则不一定是满二叉树。

性质4 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为⌊logn⌋+1或(⌈log(n+1)⌉)。
证明:假设二叉树的深度为k,则根据完全二叉树的定义得知,它的前k-1层是深度为k-1的满二叉树,共有2k-1-1个结点。由于二叉树深度为k,所以第k层上还有结点,因此该二叉树的结点数n>2k-1-1。再由性质2可知n≤2k-1,所以有:
2k-1-1<n≤2k-1
由此可推出2k-1<n≤2k,三项取对数后有k-1≤logn<k,因为k为整数,所以有:⌊logn⌋+1。
5.2.2.二叉树的存储结构
1.顺序存储结构
在顺序存储一棵具有n结点的完全二叉树时,只要从树根开始自上到下,每层从左至右地给该树中每个结点进行编号(假定编号从0开始),就能够得到一个反映整个二叉树结构的线性序列,如图5.5 (a)所示。然后以各结点的编号为下标,把每个结点的值应存储到一个一维数组bt中,如图5.5 (b)所示

由完全二叉树定义可知,在完全二叉树中除最下面一层外,各层结点都达最大值,每一层上结点个数恰好是上一层结点个数的2倍。因此,从一个结点的编号就可以推得其双亲及左、右孩子等结点的编号。
例如,假设编号为i的结点qi (0≤i<n),那么,
①若i=0,则qi为根结点,无双亲;否则, qi的双亲结点编号为⌊(i-1)/2⌋。
②若2i+1<n,则qi的左孩子结点编号为2i+1;否则, qi无左孩子,即qi必定是叶子结点。
③若2i+2<n,则qi的右孩子结点编号为2i+2;否则, qi无右孩子。
显然,对于完全二叉树而言,使用顺序存储结构既简单又节省存储空间。但对于一般的二叉树来说,采用顺序存储时,为了使用结点在数组中的相对位置来表示结点之间的逻辑关系,就必须增加一些虚结点使其成为完全二叉树的形式。这样存储二叉树中的结点会造成存储空间上的浪费,在最坏的情况下,一棵深度为k且只有k个结点的单支二叉树却需要2k-1个结点的存储空间。例如,只有4个结点的二叉树,将其添加一些实际上不存在的虚结点“@",使之成为如图5.6 (a)所示的完全二叉树,其相应的顺序存储结构如图5.6 (b)所示。
2.链式存储结构
从上面介绍的二叉树顺序存储结构来看,它仅适用于完全二叉树,但对于一般的二叉树来说,不但会浪费存储空间,而且当经常在二叉树中进行插入或删除结点操作时,需要移动大量的结点。因此,在一般情况下,多采用链式存储方式来存储二叉树。设计不同的(结点)结构可构成不同形式的链式存储结构。在二又树的链式存储表示中,通常采用的方法是:每个结点设置三个域,即值域、左指针域和右指针域,用data表示值域, Ichild和rightChild分别表示指向左右子树(孩子)的指针域,如图5.7 (a)所示。

相应的类型说明为如下:
二叉链:
| struct BinaryNode { char data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }binaryNode, binaryTree; |
三叉链:
| struct TriadicNode { char data; struct TriadicNode* left; struct TriadicNode* right; struct TriadicNode* parent; }triadicNode, triadicTree; |
在一棵二叉树中,设有一个指向其根结点(即开始结点)的BinaryTree型头指针及所有类型为BinaryNode的结点,就构成了二叉树的链式存储结构,并称其为二叉链表。例如,图5.8 (a)所示二叉树的二叉链表如图5.8 (b)所示。

二叉链表是一种常用的二叉树存储结构,在二叉树上的有关运算一般都是采用这种链式存储结构,但有时为了便于查找结点的双亲,还可以在结点结构中增加一个指向其双亲的指针parent,其结点结构如图5.7 (b)所示。
5.3.二叉树的运算
5.3.1.二叉树的生成
所谓生成,实际上就是要建立二叉树的存储结构。
由于建立二叉树的顺序存储结构比较简单,在这里就不作讨论,下面着重讨论如何建立二叉树的链式存储结构,即二叉链表。根据输入二叉树结点形式的不同,建立二叉链表的方法也不同。下面介绍两种建立二叉链表的方法。
1.广义表--链表算法
该算法相对简单一些,但要求对用广义表表示二叉树的理解要深刻。它与普通的表示树的广义表形式有所不同,因为它有左右子树之分。例如,如图5.9所示的二叉树的广义表表示形式为:
(A(B(,D(E,F)),C))
靠近左括号的结点是在左子树上,而逗号右边的结点是在右子树上。

实现建立二叉链表的算法如下,算法中用了栈(3.1.2小节顺序栈封装)存储结点的双亲指针,根据读入广义表中的字符分四种不同的情况进行处理:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <Windows.h> #include "serialStack.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" #define PRINT 1 #define EMPTY_NODE '*' struct BinaryNode { char* data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }; struct BinaryTree { struct BinaryNode* root; int depth; }; struct TreeArray { int seat; struct BinaryNode* node; }; struct TreeList { int size; struct TreeArray* treeArray; }; void linkChangeArray(struct BinaryNode* node, struct TreeArray* treeArray, int index) { if (node == NULL) { return; } treeArray[index].node = node; linkChangeArray(node->left, treeArray, index * 2 + 1); linkChangeArray(node->right, treeArray, index * 2 + 2); } int leftGetParent(int index) { return (index - 1) >> 1; } int rightGetParent(int index) { return (index - 2) >> 1; } int getLeftTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 1; } int getRightTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 2; } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markParentIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0) { if (treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markRightIndex(treeList, getRightTree(index), ++counter); } else { markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), counter); } } } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, rightGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markTreeIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index) { int counter = 1; treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } void printBinaryTree(struct TreeList* treeList) { int seat, size = treeList->size, front = 0, jump = 1, add = 2; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { seat = treeList->treeArray[i].seat - front; for (int j = 0; j < seat; j++) { printf(" "); front++; } if (treeList->treeArray[i].node == NULL) { printf("%c", EMPTY_NODE); } else { printf("%s", treeList->treeArray[i].node->data); } CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\\"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X - 2; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("/"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); front++; if ((i + 1) % jump == 0) { CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\n"); jump = jump + add; add = add * 2; front = 0; } } } void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { double size = floor(pow(2, binaryTree->depth)) - 1; struct TreeArray* treeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeArray) * size); struct TreeList* treeList = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeList)); if (treeArray == NULL || treeList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("绘制二叉树时。内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { treeArray[i].seat = -1; treeArray[i].node = NULL; } treeList->size = size; treeList->treeArray = treeArray; linkChangeArray(binaryTree->root, treeArray, 0); markTreeIndex(treeList, (int)size >> 1); printBinaryTree(treeList); } void stockpileBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { currentNode->data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; } } int setBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; return 1; } return 0; } struct BinaryTree* createListBinaryTree(char* list) { int index = 0, left = 1, probe = 0, depth = probe; char pointer = list[index]; struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); struct BinaryNode* currentNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* stackTopNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* treeRoot = NULL; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; while (pointer != '\0') { if (pointer == ' ') { index++; pointer = list[index]; continue; } switch (pointer) { case '(': left = 1; probe++; stack->push(currentNode, stack); stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; break; case ',': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); left = 0; break; case ')': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); stack->pop(stack); if (depth < probe)depth = probe; probe--; break; default: if (setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer)) break; currentNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (currentNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } currentNode->data = NULL; currentNode->left = NULL; currentNode->right = NULL; setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList = initArrayList(5), pointer); if (treeRoot == NULL) { treeRoot = currentNode; } else { stackTopNode = (struct SequenceStack*)stack->top(stack); switch (left) { case 1: stackTopNode->left = currentNode; break; case 0: stackTopNode->right = currentNode; break; } } break; } index++; pointer = list[index]; } struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = treeRoot; binaryTree->depth = depth; return binaryTree; } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = createListBinaryTree(list); drawBinaryTree(listBinaryTree); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ * D G H / \ / \ / \ / \ * * E F * * * I / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ * * * * J * * * * * * * * * K * / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / \ |
2.完全二叉树--链表的算法
该算法的基本思想是:首先对一般的二叉树添加若干个虚结点,使其成为完全二叉树,第一个结点,则令其为根结点,然后依次设置结点信息,若设置的结点不是虚结点"*",则建立一个新结点,将新结点作为左孩子或右孩子链接到它的双亲结点上,如此重复下去,直到没有结点为止。
为了使新结点能正确地链接到其双亲结点上,使用为队列(3.3小节顺序队列)保存已记录的结点地址,使用数组(2.2小节动态数组)遍历索引指向当前访问结点。利用队列的队头指针front指向当前结点的双亲结点,利用数组索引指向当前结点。若数组索引为奇数,则说明当前结点应作为左孩子链接到font所指向的左结点上;否则,当前结点应作为右孩子链接到front所指向的右结点上;若当前结点为虚结点,则不需链接。每当数组索引遇到偶数索引,移除队头指针front指向的双亲结点。具体实现算法如下:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <Windows.h> #include "serialStack.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" #define PRINT 1 #define EMPTY_NODE '*' struct BinaryNode { char* data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }; struct BinaryTree { struct BinaryNode* root; int depth; }; struct TreeArray { int seat; struct BinaryNode* node; }; struct TreeList { int size; struct TreeArray* treeArray; }; void linkChangeArray(struct BinaryNode* node, struct TreeArray* treeArray, int index) { if (node == NULL) { return; } treeArray[index].node = node; linkChangeArray(node->left, treeArray, index * 2 + 1); linkChangeArray(node->right, treeArray, index * 2 + 2); } int leftGetParent(int index) { return (index - 1) >> 1; } int rightGetParent(int index) { return (index - 2) >> 1; } int getLeftTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 1; } int getRightTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 2; } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markParentIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0) { if (treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markRightIndex(treeList, getRightTree(index), ++counter); } else { markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), counter); } } } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, rightGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markTreeIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index) { int counter = 1; treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } void printBinaryTree(struct TreeList* treeList) { int seat, size = treeList->size, front = 0, jump = 1, add = 2; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { seat = treeList->treeArray[i].seat - front; for (int j = 0; j < seat; j++) { printf(" "); front++; } if (treeList->treeArray[i].node == NULL) { printf("%c", EMPTY_NODE); } else { printf("%s", treeList->treeArray[i].node->data); } CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\\"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X - 2; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("/"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); front++; if ((i + 1) % jump == 0) { CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\n"); jump = jump + add; add = add * 2; front = 0; } } } void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { double size = floor(pow(2, binaryTree->depth)) - 1; struct TreeArray* treeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeArray) * size); struct TreeList* treeList = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeList)); if (treeArray == NULL || treeList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("绘制二叉树时。内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { treeArray[i].seat = -1; treeArray[i].node = NULL; } treeList->size = size; treeList->treeArray = treeArray; linkChangeArray(binaryTree->root, treeArray, 0); markTreeIndex(treeList, (int)size >> 1); printBinaryTree(treeList); } struct ArrayList* createArrayByBinaryTree(char* array) { int index = 0; char pointer = array[index]; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; struct ArrayList* dataList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != '\0') { arrayList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != ' ' && pointer != '\0') { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; index++; pointer = array[index]; } char* data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList = NULL; dataList->insert(dataList->size(dataList), data, dataList); index++; pointer = array[index]; } return dataList; } struct BinaryTree* createBinaryTreeUseQueue(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array); struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); struct BinaryNode* rootNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (rootNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树根结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } rootNode->data = dataList->get(0, dataList); rootNode->left = NULL; rootNode->right = NULL; queue->push(rootNode, queue); int size = dataList->size(dataList); for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { char* data = dataList->get(i, dataList); char* emptyNode = malloc(sizeof(char) * 2); if (emptyNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树空结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } emptyNode[0] = EMPTY_NODE; emptyNode[1] = '\0'; if (strcmp(data, emptyNode) != 0) { struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryNode->data = data; binaryNode->left = NULL; binaryNode->right = NULL; queue->push(binaryNode, queue); struct BinaryNode* front = queue->front(queue); if (i % 2 == 0) { front->right = binaryNode; } else { front->left = binaryNode; } free(emptyNode); emptyNode == NULL; } else { queue->push(emptyNode, queue); } if (i % 2 == 0) { queue->pop(queue); } } struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = rootNode; binaryTree->depth = log2(size + 1); return binaryTree; } int main() { char* array = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* arrayBinaryTree = createBinaryTreeUseQueue(array); drawBinaryTree(arrayBinaryTree); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ |
还有一种算法,直接通过计算,计算二叉树双亲节点与孩子结点在数组(2.2小节动态数组)中的索引位置,然后利用数组的索引访问并创建二叉树链表结构。
双亲结点与孩子结点在数组中的位置计算方式为:双亲结点索引值的两倍加一的索引位置为其左孩子,双亲结点索引值的两倍加二的索引位置为其右孩子。
算法实现:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <Windows.h> #include "serialStack.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" #define PRINT 1 #define EMPTY_NODE '*' struct BinaryNode { char* data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }; struct BinaryTree { struct BinaryNode* root; int depth; }; struct TreeArray { int seat; struct BinaryNode* node; }; struct TreeList { int size; struct TreeArray* treeArray; }; void linkChangeArray(struct BinaryNode* node, struct TreeArray* treeArray, int index) { if (node == NULL) { return; } treeArray[index].node = node; linkChangeArray(node->left, treeArray, index * 2 + 1); linkChangeArray(node->right, treeArray, index * 2 + 2); } int leftGetParent(int index) { return (index - 1) >> 1; } int rightGetParent(int index) { return (index - 2) >> 1; } int getLeftTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 1; } int getRightTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 2; } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markParentIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0) { if (treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markRightIndex(treeList, getRightTree(index), ++counter); } else { markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), counter); } } } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, rightGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markTreeIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index) { int counter = 1; treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } void printBinaryTree(struct TreeList* treeList) { int seat, size = treeList->size, front = 0, jump = 1, add = 2; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { seat = treeList->treeArray[i].seat - front; for (int j = 0; j < seat; j++) { printf(" "); front++; } if (treeList->treeArray[i].node == NULL) { printf("%c", EMPTY_NODE); } else { printf("%s", treeList->treeArray[i].node->data); } CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\\"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X - 2; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("/"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); front++; if ((i + 1) % jump == 0) { CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\n"); jump = jump + add; add = add * 2; front = 0; } } } void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { double size = floor(pow(2, binaryTree->depth)) - 1; struct TreeArray* treeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeArray) * size); struct TreeList* treeList = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeList)); if (treeArray == NULL || treeList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("绘制二叉树时。内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { treeArray[i].seat = -1; treeArray[i].node = NULL; } treeList->size = size; treeList->treeArray = treeArray; linkChangeArray(binaryTree->root, treeArray, 0); markTreeIndex(treeList, (int)size >> 1); printBinaryTree(treeList); } struct ArrayList* createArrayByBinaryTree(char* array) { int index = 0; char pointer = array[index]; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; struct ArrayList* dataList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != '\0') { arrayList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != ' ' && pointer != '\0') { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; index++; pointer = array[index]; } char* data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList = NULL; dataList->insert(dataList->size(dataList), data, dataList); index++; pointer = array[index]; } return dataList; } struct BinaryNode* createBinaryNodeByArray(struct ArrayList* dataList, int size, int index, struct BinaryNode** binaryNode) { if (index < size && index >= 0 && *binaryNode == NULL) { *binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (*binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } (*binaryNode)->data = dataList->get(index, dataList); (*binaryNode)->left = NULL; (*binaryNode)->right = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getLeftTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->left); createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getRightTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->right); } } struct BinaryTree* createArrayBinaryTree(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, dataList->size(dataList), 0, &binaryTree->root); binaryTree->depth = log2(dataList->size(dataList) + 1); return binaryTree; } int main() { char* array = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* arrayBinaryTree = createArrayBinaryTree(array); drawBinaryTree(arrayBinaryTree); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ |
3.封装二叉树生成算法
将上述构建二叉树的算法封装起来以便日后复用,创建binaryTree.h头文件:
| #pragma once #ifndef BINARY_TREE_H #define BINARY_TREE_H struct BinaryTree { struct BinaryNode* root; int depth; void (*draw)(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); }; struct BinaryNode { char* data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }; struct BinaryTree* initBinaryTree(char* arrayOrList, int listOrArray); #endif |
实现头文件逻辑binaryTree.c:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <Windows.h> #include "binaryTree.h" #include "serialStack.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" #define PRINT 1 #define EMPTY_NODE '*' void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); struct BinaryTree* createListBinaryTree(char* list); struct BinaryTree* createArrayBinaryTree(char* array); struct BinaryTree* createBinaryTreeUseQueue(char* array); struct BinaryTree* initBinaryTree(char* arrayOrList, int listOrArray) { struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = NULL; if (listOrArray == 2) { binaryTree = createBinaryTreeUseQueue(arrayOrList); } else if (listOrArray) { binaryTree = createListBinaryTree(arrayOrList); } else { binaryTree = createArrayBinaryTree(arrayOrList); } binaryTree->draw = drawBinaryTree; return binaryTree; } struct TreeArray { int seat; struct BinaryNode* node; }; struct TreeList { int size; struct TreeArray* treeArray; }; void linkChangeArray(struct BinaryNode* node, struct TreeArray* treeArray, int index) { if (node == NULL) { return; } treeArray[index].node = node; linkChangeArray(node->left, treeArray, index * 2 + 1); linkChangeArray(node->right, treeArray, index * 2 + 2); } int leftGetParent(int index) { return (index - 1) >> 1; } int rightGetParent(int index) { return (index - 2) >> 1; } int getLeftTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 1; } int getRightTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 2; } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markParentIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0) { if (treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markRightIndex(treeList, getRightTree(index), ++counter); } else { markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), counter); } } } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, rightGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markTreeIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index) { int counter = 1; treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } void printBinaryTree(struct TreeList* treeList) { int seat, size = treeList->size, front = 0, jump = 1, add = 2; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { seat = treeList->treeArray[i].seat - front; for (int j = 0; j < seat; j++) { printf(" "); front++; } if (treeList->treeArray[i].node == NULL) { printf("%c", EMPTY_NODE); } else { printf("%s", treeList->treeArray[i].node->data); } CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\\"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X - 2; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("/"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); front++; if ((i + 1) % jump == 0) { CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\n"); jump = jump + add; add = add * 2; front = 0; } } } void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { double size = floor(pow(2, binaryTree->depth)) - 1; struct TreeArray* treeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeArray) * size); struct TreeList* treeList = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeList)); if (treeArray == NULL || treeList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("绘制二叉树时。内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { treeArray[i].seat = -1; treeArray[i].node = NULL; } treeList->size = size; treeList->treeArray = treeArray; linkChangeArray(binaryTree->root, treeArray, 0); markTreeIndex(treeList, (int)size >> 1); printBinaryTree(treeList); } void stockpileBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { currentNode->data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; } } int setBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; return 1; } return 0; } struct BinaryTree* createListBinaryTree(char* list) { int index = 0, left = 1, probe = 0, depth = probe; char pointer = list[index]; struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); struct BinaryNode* currentNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* stackTopNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* treeRoot = NULL; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; while (pointer != '\0') { if (pointer == ' ') { index++; pointer = list[index]; continue; } switch (pointer) { case '(': left = 1; probe++; stack->push(currentNode, stack); stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; break; case ',': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); left = 0; break; case ')': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); stack->pop(stack); if (depth < probe)depth = probe; probe--; break; default: if (setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer)) break; currentNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (currentNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } currentNode->data = NULL; currentNode->left = NULL; currentNode->right = NULL; setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList = initArrayList(5), pointer); if (treeRoot == NULL) { treeRoot = currentNode; } else { stackTopNode = (struct SequenceStack*)stack->top(stack); switch (left) { case 1: stackTopNode->left = currentNode; break; case 0: stackTopNode->right = currentNode; break; } } break; } index++; pointer = list[index]; } struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = treeRoot; binaryTree->depth = depth; return binaryTree; } struct ArrayList* createArrayByBinaryTree(char* array) { int index = 0; char pointer = array[index]; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; struct ArrayList* dataList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != '\0') { arrayList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != ' ' && pointer != '\0') { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; index++; pointer = array[index]; } char* data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList = NULL; dataList->insert(dataList->size(dataList), data, dataList); index++; pointer = array[index]; } return dataList; } struct BinaryNode* createBinaryNodeByArray(struct ArrayList* dataList, int size, int index, struct BinaryNode** binaryNode) { if (index < size && index >= 0 && *binaryNode == NULL) { *binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (*binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } (*binaryNode)->data = dataList->get(index, dataList); (*binaryNode)->left = NULL; (*binaryNode)->right = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getLeftTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->left); createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getRightTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->right); } } struct BinaryTree* createArrayBinaryTree(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, dataList->size(dataList), 0, &binaryTree->root); binaryTree->depth = log2(dataList->size(dataList) + 1); return binaryTree; } struct BinaryTree* createBinaryTreeUseQueue(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array); struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); struct BinaryNode* rootNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (rootNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树根结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } rootNode->data = dataList->get(0, dataList); rootNode->left = NULL; rootNode->right = NULL; queue->push(rootNode, queue); int size = dataList->size(dataList); for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { char* data = dataList->get(i, dataList); char* emptyNode = malloc(sizeof(char) * 2); if (emptyNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树空结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } emptyNode[0] = EMPTY_NODE; emptyNode[1] = '\0'; if (strcmp(data, emptyNode) != 0) { struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryNode->data = data; binaryNode->left = NULL; binaryNode->right = NULL; queue->push(binaryNode, queue); struct BinaryNode* front = queue->front(queue); if (i % 2 == 0) { front->right = binaryNode; } else { front->left = binaryNode; } free(emptyNode); emptyNode == NULL; } else { queue->push(emptyNode, queue); } if (i % 2 == 0) { queue->pop(queue); } } struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = rootNode; binaryTree->depth = log2(size + 1); return binaryTree; } |
测试:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); listBinaryTree->draw(listBinaryTree); char* array = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* arrayBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(array, 0); arrayBinaryTree->draw(arrayBinaryTree); char* queue = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* queueBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(queue, 2); queueBinaryTree->draw(queueBinaryTree); return 0; } |
测试结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ * D G H / \ / \ / \ / \ * * E F * * * I / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ * * * * J * * * * * * * * * K * / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ |
5.3.2.二叉树遍历
在二叉树的应用中,遍历二叉树是一种最重要的运算,是二叉树中所有其他运算的基础。所谓遍历,是指沿着某条搜索路径(线)周游二叉树,依次对树中每个结点访问且仅访问一次。遍历对于一般的线性结构来说是一个很容易解决的问题,只需要从开始结点出发,依次访问当前结点的直接后继,直到终端结点为止。然而,对于二又树而言,树中每个结点都可能有两个后继结点,这将导致存在多条遍历路线。因此,需要寻找一种规律,以便系统地访问树中各个结点。
1.递归遍历
根据二叉树的递归定义,遍历一棵非空二叉树的问题可分解为三个子问题:访问根结点、遍历左子树和遍历右子树。若分别用D、L和R表示以上三个问题,则有DLR、LDR、LRD和DRL、RDL、RLD六种次序遍历方案。其中,前三种方案是按先左后右的次序遍历根的两棵子树,而后三种则是按先右后左的次序遍历两棵子树。由于两者对称,因此这里仅讨论前三种次序的遍历方案。
在遍历方案DLR中,因为访问根结点的操作在遍历左、右子树之前,故称之为前序(Preorder)遍历或先根遍历;类似地,在方案LDR中,访问根结点的操作在遍历左子树之后和遍历右子树之前,故称之为中序(Inorder)遍历或中根遍历;在方案LRD中,因为访问根结点的操作在遍历左、右子树之后,故称之为后序(Postorder)遍历或后根遍历。显然,遍历左、右子树的问题仍然是遍历二叉树的问题,当二叉树为空时递归遍历结束,所以很容易给出以上三种遍历的递归算法定义。
(1)前序遍历二叉树的递归定义
若二叉树非空,则依次进行操作: ①访问根结点; ②前序遍历左子树; ③前序遍历右子树。
(2)中序遍历三叉树的递归定义
若二叉树非空,则依次进行操作: ①中序遍历左子树; ②访问根结点; ③中序遍历右子树。
(3)后序遍历二叉树的递归定义
若二叉树非空,则依次进行操作: ①后序遍历左子树; ②后序遍历右子树; ③访问根结点。
在有了上述遍历二叉树的递归定义描述之后,三种遍历的算法就很容易实现。遍历算法中的递归终止条件是二叉树为空。用C语言描述的前序遍历的递归算法如下:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" void preorderTraversal(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return; } printf("%s ", node->data); preorderTraversal(node->left); preorderTraversal(node->right); } void inorderTraversal(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return; } inorderTraversal(node->left); printf("%s ", node->data); inorderTraversal(node->right); } void subsequentTraversal(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return; } subsequentTraversal(node->left); subsequentTraversal(node->right); printf("%s ", node->data); } void recursionTree(struct BinaryNode* node) { printf("先序:"); preorderTraversal(node); printf("\n中序:"); inorderTraversal(node); printf("\n后序:"); subsequentTraversal(node); printf("\n"); } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); recursionTree(listBinaryTree->root); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| 先序:A B D E J F C G H I K 中序:B J E D F A G C H K I 后序:J E F D B G K I H C A |
为了便于理解递归算法,现以图5.10所示的二叉树以及该二叉树对应的二叉链表为上述算法遍历二叉树的执行过程。

| void preorderTraversal(struct BinaryNode* node) ① { if (node == NULL) ⑤ { return; } printf("%s ", node->data); ② preorderTraversal(node->left); ③ preorderTraversal(node->right); ④ } |
为了叙述方便,在二叉链表的每个结点左边标上一个序号,假设为该结点的存储地址。
当一个函数调用前序遍历算法时,先将指向二叉树根结点的地址实参1,传递给算法中的形参node,然后执行算法:
1. 执行算法,②先打印出node结点存储的数据;
2. 然后③遍历左字树,将的左子树地址2递归传递给算法形参node,回到第1步执行算法;
3. 此时的右子树并没有得到及时的遍历,所以系统要记住此时右子树的访问地址④,等左子树遍历结束后再回来遍历右子树④。遍历右子树,将右子树地址3递归传递给算法形参node,回到第1步执行算法;
4. 当接收的参数node为空时,⑤结束执行函数,递归回到上一步的函数调用者(可能是③、④或者是根结点A),继续执行函数逻辑。
2.非递归遍历
依照递归算法执行过程中递归工作栈的状态变化,很容易写出相应的非递归算法。
利用栈容器可以实现二叉树的非递归遍历,首先将每个节点都设置一个标志,默认标志为假,根据节点的的状态进行如下流程。
1.将根结点压入栈中。
2.进入循环:只要栈中元素个数大于0,进行循环操作。
• 弹出栈顶元素;
• 如果这个栈顶元素标志为真,输出这个元素,并且执行下一次循环;
• 如果栈顶元素标志为假,将结点的标志设置为真;
• ❌将该结点的右子树、左子树、以及该结点压入栈中;
• 执行下一次循环。
执行上述流程,可以得到前序遍历的结果,如果想得到其他二叉树遍历结果,修改❌号步骤即可。
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" #include "serialStack.h" struct BinaryNodeStack { char* data; struct BinaryNodeStack* left; struct BinaryNodeStack* right; int flag; }; void foreachBinaryTree(struct BinaryNodeStack* node) { struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); stack->push(node, stack); while (stack->size(stack) > 0) { struct BinaryNodeStack* currentNode = stack->top(stack); stack->pop(stack); if (currentNode->flag == 0) { currentNode->flag = 1; if (currentNode->right != NULL) { stack->push(currentNode->right, stack); } if (currentNode->left != NULL) { stack->push(currentNode->left, stack); } stack->push(currentNode, stack); continue; } printf("%s ", currentNode->data); } stack->destroy(stack); } struct BinaryNodeStack* copyTree(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return NULL; } struct BinaryNode* left = copyTree(node->left); struct BinaryNode* right = copyTree(node->right); struct BinaryNodeStack* treeNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNodeStack)); if (treeNode == NULL) { return NULL; } treeNode->data = node->data; treeNode->left = left; treeNode->right = right; treeNode->flag = 0; return treeNode; } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); struct BinaryNodeStack* node = copyTree(listBinaryTree->root); foreachBinaryTree(node); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A B D E J F C G H I K |
3.层序遍历
非递归的按层遍历二叉链表树。其算法思想是:采用一队列Q,若树不空,先将二叉树根结点输出,并将根结点指针入队,然后出队。若根结点有左子树,则将左子树的根结点输出并将其指针入队;若其有右子树,则将其右子树的根结点输出并将其指针入队,再出队,如此下去,直至队列空为止。因此,实现要求的算法如下:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" void foreachTier(struct BinaryNode* node) { struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); queue->push(node, queue); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct BinaryNode* currentNode = queue->front(queue); printf("%s ", currentNode->data); if (currentNode->left != NULL) queue->push(currentNode->left, queue); if (currentNode->right != NULL) queue->push(currentNode->right, queue); queue->pop(queue); } } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); listBinaryTree->draw(listBinaryTree); foreachTier(listBinaryTree->root); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ * D G H / \ / \ / \ / \ * * E F * * * I / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ * * * * J * * * * * * * * * K * / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / \ A B C D G H E F I J K |
【例5.1】分别写出如图5.12所示的二叉树的前、中、后序遍历序列。
解:按照前面介绍的三种递归或非递归的遍历二叉树算法,很容易给出遍历序列。其中,前序序列为ABDHEICFG,中序序列为DHBEIAFCG,后序序列为HDIEBFGCA

5.3.3.二叉树应用
【例5.2】已知二叉树的前序和中序遍历序列或中序和后序遍历序列,求其二叉树。
分析:根据二叉树的三种遍历算法可以得出这样一个结论:已知一棵三叉树的前序和中序遍历序列或中序和后序遍历序列,可唯一地确定一棵二叉树。具体方法如下:
(1)根据前序或后序遍历序列确定二叉树的各子树的根;
(2)根据中序遍历序列确定各子树根的左、右子树。
例如,一棵二叉树的前序和中序遍历序列分别为ABDEGHCFI和DBGEHACIF,要求出其后序遍历序列,就必须求出其二叉树。
求解过程如下:
(1)由前序遍历序列确定二叉树的根为A,再由中序遍历序列确定A的左、右子树。
A BDEGH CFI //前序遍历序列的根、左子树个右子树
DBGEH A CIF //中序遍历序列的左子树、根和右子树
(2)确定A的左子树
B D EGH //前序遍历左子树的根、左子树和右子树
D B GEH //中序遍历左子树的左子树、根和右子树
- 再确定B的右子树:由前序序列EGH和中序序列GEH唯一确定E为根,G、H分为左子树和右子树。
- 确定A的右子树。
C FI //前序遍历A右子树的根和右子树
C IF //中序遍历A右子树的根和右子树
- 再确定C的右子树。由前序FI和中序IF确定F为根,I为左子树。
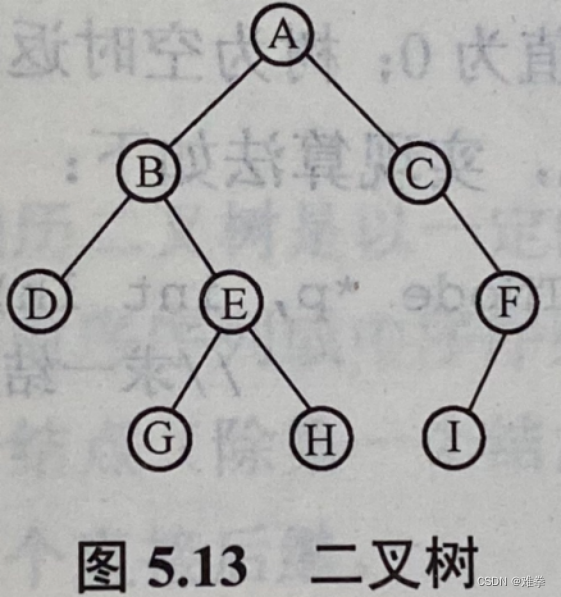
由此可得所求二叉树如图5.13所示。因此,该二叉树的后序遍历序列为:DGHEBIFCA。
算法实现:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" struct ArrayList* createArrayByBinary(char* array) { int index = 0; char pointer = array[index]; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; struct ArrayList* dataList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != '\0') { arrayList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != ' ' && pointer != '\0') { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) return; arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; index++; pointer = array[index]; } char* data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList = NULL; dataList->insert(dataList->size(dataList), data, dataList); index++; pointer = array[index]; } return dataList; } static struct SortArray { char* data; int index; }; void sortPreorderArray(struct SortArray* array, int inorderSize) { int flag = 0; struct SortArray* temp = malloc(sizeof(struct SortArray)); for (int i = 0; i < inorderSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < inorderSize - 1 - i; j++) { if (array[j].index > array[j + 1].index) { flag = 0; temp->data = array[j].data; temp->index = array[j].index; array[j].data = array[j + 1].data; array[j].index = array[j + 1].index; array[j + 1].data = temp->data; array[j + 1].index = temp->index; } else { flag++; } } if (flag == (inorderSize - 1 - i)) { break; } flag = 0; } free(temp); temp = NULL; } struct ArrayList* convertPreorder(struct ArrayList* preorder, struct ArrayList* referTo) { int preorderSize = preorder->size(preorder); int referToSize = referTo->size(referTo); struct SortArray* array = malloc(sizeof(struct SortArray) * referToSize); if (array == NULL) { return NULL; } for (int i = 0; i < referToSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < preorderSize; j++) { if (strcmp(referTo->get(i, referTo), preorder->get(j, preorder)) == 0) { array[i].data = preorder->get(j, preorder); array[i].index = j; continue; } } } sortPreorderArray(array, referToSize); struct ArrayList* preorderList = initArrayList(5); for (int i = 0; i < referToSize; i++) { preorderList->insert(i, array[i].data, preorderList); } free(array); array = NULL; return preorderList; } struct BinaryNode* createNodeByPreorderAndInorder(struct ArrayList* preorder, struct ArrayList* inorder, int* depth, int probe) { if (preorder->size(preorder) <= 0 || inorder->size(inorder) <= 0) { return NULL; } char* parentData = preorder->get(0, preorder); struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (binaryNode == NULL) { return; } binaryNode->data = parentData; binaryNode->left = NULL; binaryNode->right = NULL; if (preorder->size(preorder) == 1 || inorder->size(inorder) == 1) { if (*depth < probe) *depth = probe; return binaryNode; } // find parent node index by inorder. int size = inorder->size(inorder), index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (strcmp(inorder->get(i, inorder), parentData) == 0) { index = i; break; } } struct ArrayList* leftInorder = initArrayList(5); inorder->copy(inorder, leftInorder, 0, index); binaryNode->left = createNodeByPreorderAndInorder(convertPreorder(preorder, leftInorder), leftInorder, depth, ++probe); leftInorder->destroy(leftInorder); probe--; struct ArrayList* rightInorder = initArrayList(5); inorder->copy(inorder, rightInorder, index + 1, -1); binaryNode->right = createNodeByPreorderAndInorder(convertPreorder(preorder, rightInorder), rightInorder, depth, ++probe); rightInorder->destroy(rightInorder); return binaryNode; } struct BinaryTree* createTreeByPreorderAndInorder(char* preorderArray, char* inorderArray) { struct ArrayList* preorder = createArrayByBinary(preorderArray); struct ArrayList* inorder = createArrayByBinary(inorderArray); int* depth = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (depth == NULL) { return NULL; } *depth = 0; struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = createNodeByPreorderAndInorder(preorder, inorder, depth, 1); preorder->destroy(preorder); inorder->destroy(inorder); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { return NULL; } binaryTree->root = binaryNode; binaryTree->depth = *depth; free(depth); depth = NULL; return binaryTree; } int main() { char preorder[19] = "A B D E G H C F I"; char inorder[19] = "D B G E H A C I F"; struct BinaryTree* tree = createTreeByPreorderAndInorder(preorder, inorder); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = initBinaryTree("", 2); binaryTree->root = tree->root; binaryTree->depth = tree->depth; binaryTree->draw(binaryTree); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ D E * F / \ / \ / \ / \ * * G H * * I * / / / / / / / / \ |
【例5.3】已知二叉树的链式存储结构,求二叉树的深度。
分析:若一棵二叉树为空,则它的深度为0,否则它的深度等于其左右子树中的最大深度加1。设depl和depr分别表示左右子树的深度,则二叉树的深度为:
max(dep1,depr)+1
因此,求二叉树深度的递归算法如下:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" int depth(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return 0; } int left = depth(node->left); int right = depth(node->right); return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1; } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1);
printf("深度:%d", depth(listBinaryTree->root)); return 0; } |
【例5.4】 以二叉链表为存储结构,试编写在二叉树中查找值为x的结点及求x所在结点在树中层数的算法。
分析: (1)按值查找。该算法是比较简单的,无论是利用三种遍历算法的哪一种,都很容易实现,不妨用前序遍历算法。
(2)求结点的层次。依照题意,仍然采用递归算法。从根节点开始递归遍历,每递归一层加一,回退一层减一,匹配到数值则打印出来。因此,实现算法如下:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" int getBinaryNode(struct BinaryNode* binaryNode, char* data, int tier) { if (binaryNode != NULL && tier > 0) { if (strcmp(binaryNode->data, data) == 0) { printf("%s %d\n", binaryNode->data, tier); tier = 0; } else { tier = getBinaryNode(binaryNode->left, data, ++tier); --tier; tier = getBinaryNode(binaryNode->right, data, ++tier); } } return tier; } int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); getBinaryNode(binaryTree->root, "C", 1); getBinaryNode(binaryTree->root, "J", 1); getBinaryNode(binaryTree->root, "H", 1); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| C 2 J 5 H 3 |
5.3.4.二叉树生成算法与应用
binaryTree.h头文件:
| #pragma once #ifndef BINARY_TREE_H #define BINARY_TREE_H #include "serialStack.h" #include "dynamicArray.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" enum Sequence { preorder = 1, inorder = 2, subsequent = 3 }; struct BinaryTree { struct BinaryNode* root; int depth; void (*draw)(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); void (*foreachUseRecursion)(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence); void (*foreachUseStack)(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence); void (*foreachTier)(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); }; struct BinaryNode { char* data; struct BinaryNode* left; struct BinaryNode* right; }; struct BinaryTree* initBinaryTree(char* arrayOrList, int listOrArray); struct BinaryTree* initTreeBySequenceAndInorder(char* sequenceArray, char* inorderArray, int foreOrHind); #endif |
实现头文件逻辑binaryTree.c:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> #include <Windows.h> #include "binaryTree.h" #define PRINT 1 #define EMPTY_NODE '*' void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); struct BinaryTree* createListBinaryTree(char* list); struct BinaryTree* createArrayBinaryTree(char* array); struct BinaryTree* createBinaryTreeUseQueue(char* array); void foreachRecursionBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence); void foreachStackBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence); void foreachBinaryTreeTier(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree); void setBinaryTreeFunction(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { binaryTree->draw = drawBinaryTree; binaryTree->foreachUseRecursion = foreachRecursionBinaryTree; binaryTree->foreachUseStack = foreachStackBinaryTree; binaryTree->foreachTier = foreachBinaryTreeTier; } struct BinaryTree* initBinaryTree(char* arrayOrList, int listOrArray) { struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = NULL; if (listOrArray == 2) { binaryTree = createBinaryTreeUseQueue(arrayOrList); } else if (listOrArray) { binaryTree = createListBinaryTree(arrayOrList); } else { binaryTree = createArrayBinaryTree(arrayOrList); } setBinaryTreeFunction(binaryTree); return binaryTree; } struct TreeArray { int seat; struct BinaryNode* node; }; struct TreeList { int size; struct TreeArray* treeArray; }; void linkChangeArray(struct BinaryNode* binaryNode, struct TreeArray* treeArray, int index) { if (binaryNode == NULL) { return; } treeArray[index].node = binaryNode; linkChangeArray(binaryNode->left, treeArray, index * 2 + 1); linkChangeArray(binaryNode->right, treeArray, index * 2 + 2); } int leftGetParent(int index) { return (index - 1) >> 1; } int rightGetParent(int index) { return (index - 2) >> 1; } int getLeftTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 1; } int getRightTree(int index) { return (index << 1) + 2; } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter); void markParentIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0) { if (treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markRightIndex(treeList, getRightTree(index), ++counter); } else { markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), counter); } } } void markLeftIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markRightIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index, int counter) { if (index < treeList->size && index >= 0 && treeList->treeArray[index].seat == -1) { if (getLeftTree(index) <= treeList->size) { markLeftIndex(treeList, getLeftTree(index), counter); return; } treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, rightGetParent(index), ++counter); } } void markTreeIndex(struct TreeList* treeList, int index) { int counter = 1; treeList->treeArray[index].seat = counter; markParentIndex(treeList, leftGetParent(index), ++counter); } void printBinaryTree(struct TreeList* treeList) { int seat, size = treeList->size, front = 0, jump = 1, add = 2; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { seat = treeList->treeArray[i].seat - front; for (int j = 0; j < seat; j++) { printf(" "); front++; } if (treeList->treeArray[i].node == NULL) { printf("%c", EMPTY_NODE); } else { printf("%s", treeList->treeArray[i].node->data); } CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\\"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X - 2; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("/"); coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); front++; if ((i + 1) % jump == 0) { CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO ipBuffer; GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), &ipBuffer); COORD coord = { 0 }; coord.X = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.X; coord.Y = ipBuffer.dwCursorPosition.Y + 1; SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), coord); printf("\n"); jump = jump + add; add = add * 2; front = 0; } } } void drawBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { int depth = binaryTree->depth; if (depth <= 0) { #if PRINT printf("空二叉树无法绘制!\n"); #endif return; } double size = floor(pow(2, depth)) - 1; struct TreeArray* treeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeArray) * size); struct TreeList* treeList = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeList)); if (treeArray == NULL || treeList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("绘制二叉树时。内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { treeArray[i].seat = -1; treeArray[i].node = NULL; } treeList->size = size; treeList->treeArray = treeArray; linkChangeArray(binaryTree->root, treeArray, 0); markTreeIndex(treeList, (int)size >> 1); printBinaryTree(treeList); free(treeArray); treeArray = NULL; free(treeList); treeList = NULL; } void stockpileBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { currentNode->data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; } } int setBinaryNodeData(struct BinaryNode* currentNode, struct ArrayList* arrayList, char pointer) { if (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->data == NULL && arrayList != NULL) { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; return 1; } return 0; } struct BinaryTree* createListBinaryTree(char* list) { int index = 0, left = 1, probe = 0, depth = probe; char pointer = list[index]; struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); struct BinaryNode* currentNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* stackTopNode = NULL; struct BinaryNode* treeRoot = NULL; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; while (pointer != '\0') { if (pointer == ' ') { index++; pointer = list[index]; continue; } switch (pointer) { case '(': left = 1; probe++; stack->push(currentNode, stack); stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); arrayList == NULL; currentNode == NULL; break; case ',': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); left = 0; break; case ')': stockpileBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer); stack->pop(stack); if (depth < probe)depth = probe; probe--; break; default: if (setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList, pointer)) break; currentNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (currentNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } currentNode->data = NULL; currentNode->left = NULL; currentNode->right = NULL; setBinaryNodeData(currentNode, arrayList = initArrayList(5), pointer); if (treeRoot == NULL) { treeRoot = currentNode; } else { stackTopNode = (struct SequenceStack*)stack->top(stack); switch (left) { case 1: stackTopNode->left = currentNode; break; case 0: stackTopNode->right = currentNode; break; } } break; } index++; pointer = list[index]; } stack->destroy(stack); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = treeRoot; binaryTree->depth = depth; return binaryTree; } struct ArrayList* createArrayByBinaryTree(char* array) { int index = 0; char pointer = array[index]; struct ArrayList* arrayList = NULL; struct ArrayList* dataList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != '\0') { arrayList = initArrayList(5); while (pointer != ' ' && pointer != '\0') { char* data = malloc(sizeof(char)); if (data == NULL || arrayList == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点赋值失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } arrayList->insert(arrayList->size(arrayList), data, arrayList); *data = pointer; index++; pointer = array[index]; } char* data = arrayList->toString(arrayList); arrayList->ruin(arrayList); arrayList = NULL; dataList->insert(dataList->size(dataList), data, dataList); index++; pointer = array[index]; } return dataList; } struct BinaryNode* createBinaryNodeByArray(struct ArrayList* dataList, int size, int index, struct BinaryNode** binaryNode) { if (index < size && index >= 0 && *binaryNode == NULL) { *binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (*binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } (*binaryNode)->data = dataList->get(index, dataList); (*binaryNode)->left = NULL; (*binaryNode)->right = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getLeftTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->left); createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, size, getRightTree(index), &(*binaryNode)->right); } } struct BinaryTree* createArrayBinaryTree(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = NULL; createBinaryNodeByArray(dataList, dataList->size(dataList), 0, &binaryTree->root); binaryTree->depth = log2(dataList->size(dataList) + 1); dataList->destroy(dataList); return binaryTree; } struct BinaryTree* createBinaryTreeUseQueue(char* array) { struct ArrayList* dataList = createArrayByBinaryTree(array);
struct BinaryNode* rootNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (rootNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树根结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } rootNode->data = NULL; rootNode->left = NULL; rootNode->right = NULL; int size = dataList->size(dataList); if (size > 0) { struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); rootNode->data = dataList->get(0, dataList); queue->push(rootNode, queue); char* emptyNode = malloc(sizeof(char) * 2); if (emptyNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树空结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } emptyNode[0] = EMPTY_NODE; emptyNode[1] = '\0'; for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { char* data = dataList->get(i, dataList); if (strcmp(data, emptyNode) != 0) { struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryNode->data = data; binaryNode->left = NULL; binaryNode->right = NULL; queue->push(binaryNode, queue); struct BinaryNode* front = queue->front(queue); if (i % 2 == 0) { front->right = binaryNode; } else { front->left = binaryNode; } } else { queue->push(emptyNode, queue); } if (i % 2 == 0) { queue->pop(queue); } } free(emptyNode); emptyNode == NULL; queue->destroy(queue); } struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryTree->root = rootNode; binaryTree->depth = log2(size + 1); return binaryTree; } void recursionPreorderTraversal(struct BinaryNode* binaryNode) { if (binaryNode == NULL) { return; } printf("%s ", binaryNode->data); recursionPreorderTraversal(binaryNode->left); recursionPreorderTraversal(binaryNode->right); } void recursionInorderTraversal(struct BinaryNode* binaryNode) { if (binaryNode == NULL) { return; } recursionInorderTraversal(binaryNode->left); printf("%s ", binaryNode->data); recursionInorderTraversal(binaryNode->right); } void recursionSubsequentTraversal(struct BinaryNode* binaryNode) { if (binaryNode == NULL) { return; } recursionSubsequentTraversal(binaryNode->left); recursionSubsequentTraversal(binaryNode->right); printf("%s ", binaryNode->data); } void foreachRecursionBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence) { if (binaryTree == NULL || binaryTree->root == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("二叉树不存在!\n"); #endif return; } struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = binaryTree->root; if (sequence == 1) { printf("先序:"); recursionPreorderTraversal(binaryNode); printf("\n"); } else if (sequence == 2) { printf("中序:"); recursionInorderTraversal(binaryNode); printf("\n"); } else if (sequence == 3) { printf("后序:"); recursionSubsequentTraversal(binaryNode); printf("\n"); } else { printf("未知遍历顺序!\n"); } } struct BinaryNodeStack { char* data; struct BinaryNodeStack* left; struct BinaryNodeStack* right; int flag; }; struct BinaryNodeStack* convertBinaryNode(struct BinaryNode* node) { if (node == NULL) { return NULL; } struct BinaryNode* left = convertBinaryNode(node->left); struct BinaryNode* right = convertBinaryNode(node->right); struct BinaryNodeStack* treeNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNodeStack)); if (treeNode == NULL) { return NULL; } treeNode->data = node->data; treeNode->left = left; treeNode->right = right; treeNode->flag = 0; return treeNode; } void preorderTraversal(struct BinaryNodeStack* binaryNode, struct SequenceStack* stack) { if (binaryNode->right != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->right, stack); } if (binaryNode->left != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->left, stack); } stack->push(binaryNode, stack); } void inorderTraversal(struct BinaryNodeStack* binaryNode, struct SequenceStack* stack) { if (binaryNode->right != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->right, stack); } stack->push(binaryNode, stack); if (binaryNode->left != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->left, stack); } } void subsequentTraversal(struct BinaryNodeStack* binaryNode, struct SequenceStack* stack) { stack->push(binaryNode, stack); if (binaryNode->right != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->right, stack); } if (binaryNode->left != NULL) { stack->push(binaryNode->left, stack); } } void recursionStackBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, int sequence) { if (binaryTree == NULL || binaryTree->root == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("二叉树不存在!\n"); #endif return; } struct BinaryNodeStack* binaryNode = convertBinaryNode(binaryTree->root); struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); stack->push(binaryNode, stack); while (stack->size(stack) > 0) { struct BinaryNodeStack* currentNode = stack->top(stack); stack->pop(stack); if (currentNode->flag == 0) { currentNode->flag = 1; if (sequence == 1) { preorderTraversal(currentNode, stack); } else if (sequence == 2) { inorderTraversal(currentNode, stack); } else if (sequence == 3) { subsequentTraversal(currentNode, stack); } continue; } printf("%s ", currentNode->data); } stack->destroy(stack); } void foreachStackBinaryTree(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree, enum Sequence sequence) { if (sequence == 1) { printf("先序:"); recursionStackBinaryTree(binaryTree, sequence); printf("\n"); } else if (sequence == 2) { printf("中序:"); recursionStackBinaryTree(binaryTree, sequence); printf("\n"); } else if (sequence == 3) { printf("后序:"); recursionStackBinaryTree(binaryTree, sequence); printf("\n"); } else { printf("未知遍历顺序!\n"); } } void foreachBinaryTreeTier(struct BinaryTree* binaryTree) { if (binaryTree == NULL || binaryTree->root == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("二叉树不存在!\n"); #endif return; } struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = binaryTree->root; printf("层序遍历:"); struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); queue->push(binaryNode, queue); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct BinaryNode* currentNode = queue->front(queue); printf("%s ", currentNode->data); if (currentNode->left != NULL) queue->push(currentNode->left, queue); if (currentNode->right != NULL) queue->push(currentNode->right, queue); queue->pop(queue); } queue->destroy(queue); printf("\n"); } static struct SortArray { char* data; int index; }; void sortPreorderOrSubsequentArray(struct SortArray* array, int size) { int flag = 0; struct SortArray* temp = malloc(sizeof(struct SortArray)); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) { if (array[j].index > array[j + 1].index) { flag = 0; temp->data = array[j].data; temp->index = array[j].index; array[j].data = array[j + 1].data; array[j].index = array[j + 1].index; array[j + 1].data = temp->data; array[j + 1].index = temp->index; } else { flag++; } } if (flag == (size - 1 - i)) { break; } flag = 0; } free(temp); temp = NULL; } // Use Preorder And Inorder create BinaryTree. struct ArrayList* convertPreorderOrSubsequent(struct ArrayList* preorderOrSubsequent, struct ArrayList* referTo) { int preorderOrSubsequentSize = preorderOrSubsequent->size(preorderOrSubsequent); int referToSize = referTo->size(referTo); struct SortArray* array = malloc(sizeof(struct SortArray) * referToSize); if (array == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树获取子树前序遍历顺序失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } for (int i = 0; i < referToSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < preorderOrSubsequentSize; j++) { if (strcmp(referTo->get(i, referTo), preorderOrSubsequent->get(j, preorderOrSubsequent)) == 0) { array[i].data = preorderOrSubsequent->get(j, preorderOrSubsequent); array[i].index = j; continue; } } } sortPreorderOrSubsequentArray(array, referToSize); struct ArrayList* resultList = initArrayList(5); for (int i = 0; i < referToSize; i++) { resultList->insert(i, array[i].data, resultList); } free(array); array = NULL; return resultList; } struct BinaryNode* createNodeBySequenceAndInorder(struct ArrayList* sequence, struct ArrayList* inorder, int foreOrHind, int* depth, int probe) { if (sequence->size(sequence) <= 0 || inorder->size(inorder) <= 0) { return NULL; } char* parentData = NULL; if (foreOrHind == 0) { parentData = sequence->get(0, sequence); } else { parentData = sequence->get(sequence->size(sequence) - 1, sequence); } struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryNode)); if (binaryNode == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树结点失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return; } binaryNode->data = parentData; binaryNode->left = NULL; binaryNode->right = NULL; if (sequence->size(sequence) == 1 || inorder->size(inorder) == 1) { if (*depth < probe) *depth = probe; return binaryNode; } // find parent node index by inorder. int size = inorder->size(inorder), index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (strcmp(inorder->get(i, inorder), parentData) == 0) { index = i; break; } } struct ArrayList* leftInorder = initArrayList(5); inorder->copy(inorder, leftInorder, 0, index); binaryNode->left = createNodeBySequenceAndInorder(convertPreorderOrSubsequent(sequence, leftInorder), leftInorder, foreOrHind, depth, ++probe); leftInorder->destroy(leftInorder); probe--; struct ArrayList* rightInorder = initArrayList(5); inorder->copy(inorder, rightInorder, index + 1, -1); binaryNode->right = createNodeBySequenceAndInorder(convertPreorderOrSubsequent(sequence, rightInorder), rightInorder, foreOrHind, depth, ++probe); rightInorder->destroy(rightInorder); return binaryNode; } struct BinaryTree* initTreeBySequenceAndInorder(char* sequenceArray, char* inorderArray, int foreOrHind) { struct ArrayList* sequence = createArrayByBinaryTree(sequenceArray); struct ArrayList* inorder = createArrayByBinaryTree(inorderArray); int* depth = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (depth == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树计算深度失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } *depth = 0; struct BinaryNode* binaryNode = createNodeBySequenceAndInorder(sequence, inorder, foreOrHind, depth, 1); sequence->destroy(sequence); inorder->destroy(inorder); struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree)); if (binaryTree == NULL) { #if PRINT printf("创建二叉树失败,内存空间不足!\n"); #endif return NULL; } binaryTree->root = binaryNode; binaryTree->depth = *depth; if (*depth == 0) { #if PRINT printf("空二叉树!\n"); #endif } free(depth); depth = NULL; setBinaryTreeFunction(binaryTree); return binaryTree; } |
测试:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "binaryTree.h" int main() { char* list = "(A (B(,D(E(J),F)),C(G,H(,I(K)))))"; struct BinaryTree* listBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(list, 1); listBinaryTree->draw(listBinaryTree); char* array = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* arrayBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(array, 0); arrayBinaryTree->draw(arrayBinaryTree); char* queue = "A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O"; struct BinaryTree* queueBinaryTree = initBinaryTree(queue, 2); queueBinaryTree->draw(queueBinaryTree); char preorder[19] = "A B D E G H C F I"; char inorder[19] = "D B G E H A C I F"; struct BinaryTree* binaryTree = initTreeBySequenceAndInorder(preorder, inorder, 0); binaryTree->draw(binaryTree); char subsequent[19] = "D G H E B I F C A"; struct BinaryTree* tree = initTreeBySequenceAndInorder(subsequent, inorder, 1); tree->draw(tree); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A / \ B C / \ / \ * D G H / \ / \ / \ / \ * * E F * * * I / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ * * * * J * * * * * * * * * K * / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E F G / \ / \ / \ / \ H I J K L M N O / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E * F / \ / \ / \ / \ * * G H * * I * / / / / / / / / \ A / \ B C / \ / \ D E * F / \ / \ / \ / \ * * G H * * I * / / / / / / / / \ |