相机坐标和世界坐标变换原理就是在4个坐标系直接转换, 如果考虑GIS系统那么还需要考虑空间参考坐标, 空间参考坐标系又需要考虑地理和投影坐标系, 加起来就是6个坐标系. 示例图如下
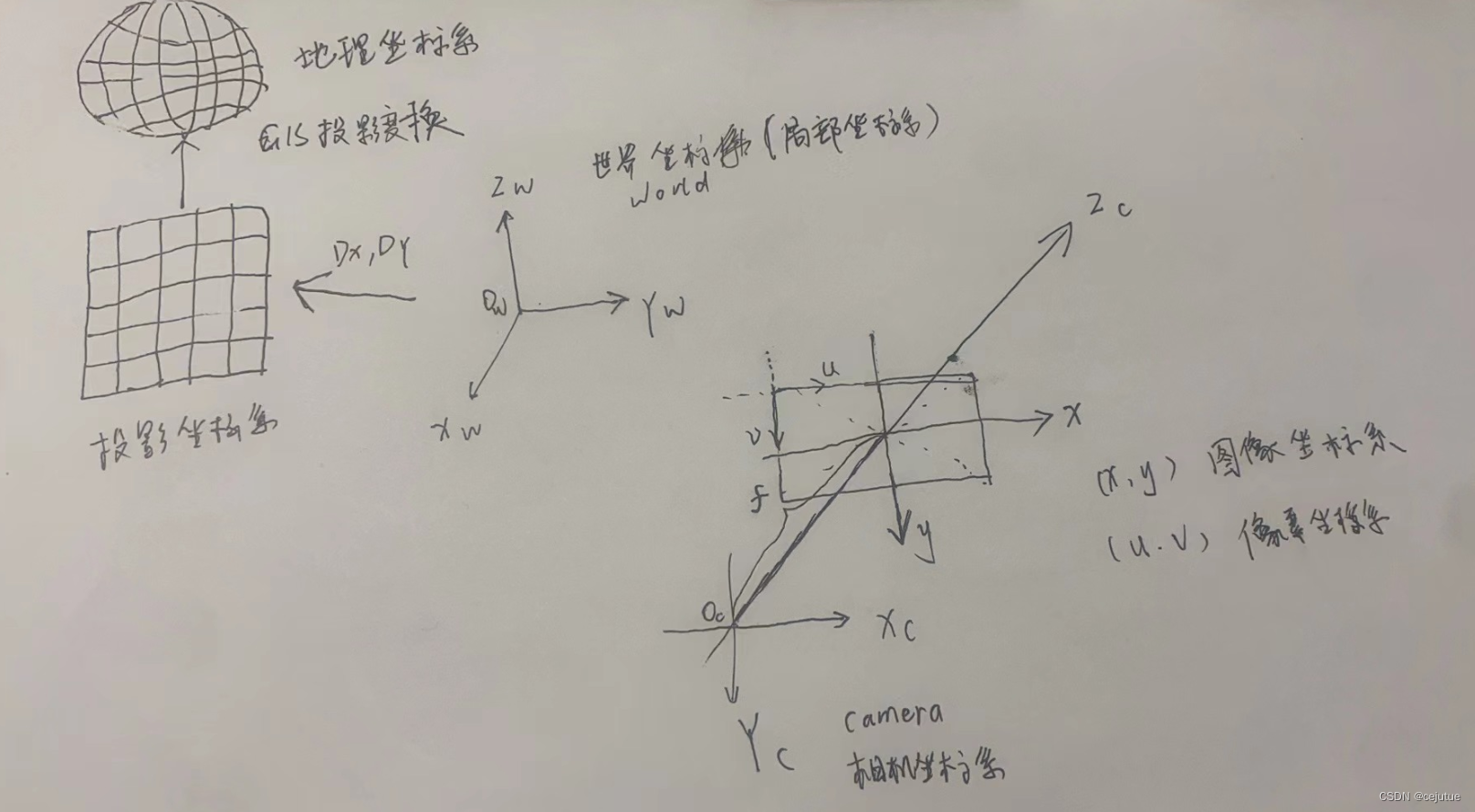
此段代码基于opencv, 畸变参数未考虑, 采用pnp求解内外参数,封装相机坐标和世界坐标转换方法, GIS系统的坐标系都是一种世界坐标, 一般标定都是局部世界坐标系和GIS中投影空间参考坐标有一个x,y方向的平移参数即可完成转换, 投影转地理这直接GDAL中转换即可搞定. 具体代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctype.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
#ifdef _DEBUG
#pragma comment(lib,"opencv_world460d.lib")
#else
#pragma comment(lib,"opencv_world460.lib")
#endif // _DEBUG
void CameraToWorld(InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray rV, InputArray tV, Point2d& imgPoints, Point3d& worldPoints)
{
cv::Mat cameraMatrix1 = cameraMatrix.getMat();
///根据公式求Zc,即s
cv::Mat imagePoint = cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type);
cv::Mat tempMat, tempMat2;
//输入一个2D坐标点,便可以求出相应的s
imagePoint.at<double>(0, 0) = imgPoints.x;
imagePoint.at<double>(1, 0) = imgPoints.y;
imagePoint.at<double>(2, 0) = 1;
double zConst = 0;//实际坐标系的距离
//计算参数s
double s;
tempMat = rV.getMat().inv() * cameraMatrix1.inv() * imagePoint;
tempMat2 = rV.getMat().inv() * tV.getMat();
s = zConst + tempMat2.at<double>(2, 0);
s /= tempMat.at<double>(2, 0);
cv::Mat imagePoint_your_know = cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //u,v,1
imagePoint_your_know.at<double>(0, 0) = imgPoints.x;
imagePoint_your_know.at<double>(1, 0) = imgPoints.y;
imagePoint_your_know.at<double>(2, 0) = 1;
Mat wcPoint = rV.getMat().inv() * (cameraMatrix1.inv() * s * imagePoint_your_know - tV.getMat());
worldPoints.x = wcPoint.at<double>(0, 0);
worldPoints.y = wcPoint.at<double>(1, 0);
worldPoints.z = wcPoint.at<double>(2, 0);
cout << "CameraToWorld 2D to 3D: " << worldPoints << endl;
}
void WorldToCamera(InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray rV, InputArray tV, Point3d& worldPoint, Point2d& imgPoint)
{
cv::Mat cameraMatrix1 = cameraMatrix.getMat();
cv::Mat worldPoints = Mat::ones(4, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type);
worldPoints.at<double>(0, 0) = worldPoint.x;
worldPoints.at<double>(1, 0) = worldPoint.y;
worldPoints.at<double>(2, 0) = worldPoint.z;
cout << "world Points : " << worldPoints << endl;
Mat image_points = Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type);
//setIdentity(image_points);
Mat RT_;
hconcat(rV, tV, RT_);
cout << "RT_" << RT_ << endl;
cout << "cameraMatrix1_" << cameraMatrix1 << endl;
image_points = cameraMatrix1 * RT_ * worldPoints;
Mat D_Points = Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type);
D_Points.at<double>(0, 0) = image_points.at<double>(0, 0) / image_points.at<double>(2, 0);
D_Points.at<double>(1, 0) = image_points.at<double>(1, 0) / image_points.at<double>(2, 0);
//cv::projectPoints(worldPoints, rV, tV, cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, imagePoints);
cout << "WorldToCamera 3D to 2D: " << D_Points << endl;
}
int main()
{
// 求内外参数通过PnP求解相机的R&T//
Point2f point;
vector<Point2f> boxPoints; //存入像素坐标
// Loading image
Mat sourceImage = imread("D:/source/kernel/example/opencv_uvxyztest/x64/Debug/a.bmp");
namedWindow("Source", 1);
// Setting box corners in image
//one Point
point = Point2f((float)558, (float)259); //640X480
boxPoints.push_back(point);
circle(sourceImage, boxPoints[0], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8);
//two Point
point = Point2f((float)629, (float)212); //640X480
boxPoints.push_back(point);
circle(sourceImage, boxPoints[1], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8);
//three Point
point = Point2f((float)744, (float)260); //640X480
boxPoints.push_back(point);
circle(sourceImage, boxPoints[2], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8);
//four Point
point = Point2f((float)693, (float)209); //640X480
boxPoints.push_back(point);
circle(sourceImage, boxPoints[3], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8);
//Setting box corners in real world
vector<Point3f> worldBoxPoints; //存入世界坐标
Point3f tmpPoint;
tmpPoint = Point3f((float)2750, (float)890, (float)0);
worldBoxPoints.push_back(tmpPoint);
tmpPoint = Point3f((float)3500, (float)450, (float)0);
worldBoxPoints.push_back(tmpPoint);
tmpPoint = Point3f((float)2790, (float)-240, (float)0);
worldBoxPoints.push_back(tmpPoint);
tmpPoint = Point3f((float)3620, (float)-50, (float)0);
worldBoxPoints.push_back(tmpPoint);
//camera intristic///
cv::Mat cameraMatrix1 = Mat::eye(3, 3, cv::DataType<double>::type); //相机内参矩阵
cv::Mat distCoeffs1(5, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //畸变参数
distCoeffs1.at<double>(0, 0) = 0.061439051;
distCoeffs1.at<double>(1, 0) = 0.03187556;
distCoeffs1.at<double>(2, 0) = -0.00726151;
distCoeffs1.at<double>(3, 0) = -0.00111799;
distCoeffs1.at<double>(4, 0) = -0.00678974;
//Taken from Mastring OpenCV d 相机固定参数
double fx = 328.61652824;
double fy = 328.56512516;
double cx = 629.80551148;
double cy = 340.5442837;
cameraMatrix1.at<double>(0, 0) = fx;
cameraMatrix1.at<double>(1, 1) = fy;
cameraMatrix1.at<double>(0, 2) = cx;
cameraMatrix1.at<double>(1, 2) = cy;
//PnP solve R&T///
cv::Mat rvec1(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //旋转向量
cv::Mat tvec1(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //平移向量
cv::solvePnP(worldBoxPoints, boxPoints, cameraMatrix1, distCoeffs1, rvec1, tvec1, false, 0);
cv::Mat rvecM1(3, 3, cv::DataType<double>::type); //旋转矩阵
cv::Rodrigues(rvec1, rvecM1);
//此处用于求相机位于坐标系内的旋转角度, 2D - 3D的转换并不用求
const double PI = 3.1415926;
double thetaZ = atan2(rvecM1.at<double>(1, 0), rvecM1.at<double>(0, 0)) / PI * 180;
double thetaY = atan2(-1 * rvecM1.at<double>(2, 0), sqrt(rvecM1.at<double>(2, 1)*rvecM1.at<double>(2, 1)
+ rvecM1.at<double>(2, 2)*rvecM1.at<double>(2, 2))) / PI * 180;
double thetaX = atan2(rvecM1.at<double>(2, 1), rvecM1.at<double>(2, 2)) / PI * 180;
cout << "theta x " << thetaX << endl << "theta Y: " << thetaY << endl << "theta Z: " << thetaZ << endl;
///World To Camera
Point2d d2p;
Point3d wd(3620, -590, 345);
cout << "world Points : " << wd << endl;
WorldToCamera(cameraMatrix1, rvecM1, tvec1, wd, d2p);
// Camera To World
Point2d d2pcw(757.0414822810177, 213.3698894820287);
Point3d wdcw;
cout << "camera Points : " << d2pcw << endl;
CameraToWorld(cameraMatrix1, rvecM1, tvec1, d2pcw, wdcw);
return 0;
}