1 效果
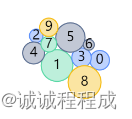
初始化时节点向中间聚拢
拖动后,随引力作用缓缓向中间聚拢
点击节点,节点放大,并展示标签文字
2 代码分析
2.1 数据
2.1.1 节点数据
nodes: [
{
id: '0',
label: '0',
value: 10,
cluster: 'a',
description: 'this is node 0, \nand the value of it is 10',
},
{
id: '1',
label: '1',
value: 20,
cluster: 'b',
description: 'this is node 1, \nand the value of it is 20',
},
value: 决定节点大小
cluster: a b c d 对应不同的样式 cluster值决定拿到colors、strokes数组中的某一项
label: 默认节点文本(默认配置项属性)
description: 点击节点放大后 该该数据赋值给label 展示文本
2.1.2 节点样式
样式并不是按照顺序固定给某节点的的,而是通过cluster拿到对应数组的某一项,赋予节点
// 节点填充颜色
const colors = [
'#BDD2FD',
'#BDEFDB',
'#C2C8D5',
'#FBE5A2',
'#F6C3B7',
'#B6E3F5',
'#D3C6EA',
'#FFD8B8',
'#AAD8D8',
'#FFD6E7',
];
// 节点边颜色
const strokes = [
'#5B8FF9',
'#5AD8A6',
'#5D7092',
'#F6BD16',
'#E8684A',
'#6DC8EC',
'#9270CA',
'#FF9D4D',
'#269A99',
'#FF99C3',
];
2.2 图配置
Graph 的初始化通过 new 进行实例化,实例化时需要传入需要的参数。
<div id="container"></div>
const graph = new G6.Graph({
container: 'container',
width,
height,
layout: {
type: 'force', // 力导向布局
nodeStrength: 30, // 节点作用力,正数代表节点之间的引力作用,负数代表节点之间的斥力作用
collideStrength: 0.7, // 防止重叠的力强度,范围 [0, 1]
alphaDecay: 0.01, // 迭代阈值的衰减率 ?啥玩意
preventOverlap: true, // 是否防止重叠 必须在数据中设置了 size 或在该布局中配置了与当前图节点大小相同的 nodeSize 值
},
modes: {
default: ['collapse-expand-combo'], // combo类型 之前采用drag-node 不太丝滑
},
defaultNode: {
size: [10, 10],
},
});
2.3 定义节点样式
// 遍历nodes 根据cluster属性 给节点添加对应style属性
nodes.forEach((node) => {
nodeMap.set(node.id, node);
// cluster
if (node.cluster && clusterMap.get(node.cluster) === undefined) {
clusterMap.set(node.cluster, clusterId);
clusterId++;
}
const cid = clusterMap.get(node.cluster);
if (!node.style) node.style = {
};
node.style.fill = colors[cid % colors.length]; //节点颜色
node.style.stroke = strokes[cid % strokes.length]; //节点边颜色
node.x = width / 2 + 200 * (Math.random() - 0.5);
node.y = height / 2 + 200 * (Math.random() - 0.5);
});
2.4 节点大小设置
// 调用scaleNodeProp
scaleNodeProp(nodes, 'size', 'value', nodeSizeDataRange, nodeSizeRange);
// 添加size属性
function scaleNodeProp (elements, propName, refPropName, dataRange, outRange) {
const outLength = outRange[1] - outRange[0];
const dataLength = dataRange[1] - dataRange[0];
elements.forEach(function (n) {
if (propName.split('.')[0] === 'style') {
if (n.style) {
n.style[propName.split('.')[1]] =
((n[refPropName] - dataRange[0]) * outLength) / dataLength + outRange[0];
} else {
n.style = _defineProperty(
{
},
propName.split('.')[1],
((n[refPropName] - dataRange[0]) * outLength) / dataLength + outRange[0],
);
}
} else {
n[propName] = ((n[refPropName] - dataRange[0]) * outLength) / dataLength + outRange[0];
}
});
}
2.5 节点交互事件
// 方法:跟随拖动的位置 节点位置移动
// 参数e:鼠标拖动信息
function refreshDragedNodePosition (e) {
const model = e.item.get('model');
model.fx = e.x;
model.fy = e.y;
}
2.5.1 节点开始被拖拽
// 事件绑定 graph.on()
// Node 交互事件: node:dragstart 当节点开始被拖拽的时候触发的事件
graph.on('node:dragstart', function (e) {
graph.layout(); // graph.layout()重新以当前配置的属性进行一次布局
refreshDragedNodePosition(e);
});
2.5.2 开始拖拽过程
// node:drag 当节点在拖动过程中时触发的事件
graph.on('node:drag', function (e) {
refreshDragedNodePosition(e);
});
2.5.3 拖拽完成后
// node:dragend 当拖拽完成后触发的事件
graph.on('node:dragend', function (e) {
e.item.get('model').fx = null;
e.item.get('model').fy = null;
});
2.5.4 点击事件
// node:click 鼠标左键单击节点时触发
graph.on('node:click', function (e) {
// debugger;
const node = e.item; //那到当前点击的节点
const states = node.getStates(); //返回当前元素的所有状态 啥也没有
let clicked = false;
const model = node.getModel(); // 获得节点位置
let size = 200; // 变大
let labelText = 'NODE: ' + model.id + '\n' + model.description; // 拼接: "NODE: this is node 8, and the value of it is 21"
states.forEach(function (state) {
if (state === 'click') {
clicked = true;
size = model.oriSize;
labelText = model.oriLabel;
}
});
graph.setItemState(node, 'click', !clicked); //设置元素状态(元素实例,状态值,是否启用状态)
// 更新元素,包括更新数据、样式等
graph.updateItem(node, {
size,
label: labelText,
});
graph.layout(); // graph.layout()重新以当前配置的属性进行一次布局
});
2.6 初始化图数据
graph.data(data); // 初始化图数据,data是一个包括 节点 数组和 边 数组的对象
graph.render();
2.7 mounted() 调用
上述代码包裹在 getInit() 方法中
在组件挂载后调用 getInit()