丑数定义:“丑数”(ugly number)是正数,且质数因子只包含2、3、5。例如6,8是丑数,但14不是丑数,因为它包含因子7,规定整数1为第一个丑数。
问题分析:丑数一定是有限个2、3、5的乘积,因为所有的正整数都能分解成1与一个或多个素数的乘积。如果一个数是丑数,那么反复除以2、3、5后,一定会是1;如果一个数不是丑数,那么反复除以2、3、5后,一定还会剩下了一个质数无法被2、3、5整除。
编程内容(python代码 & C++代码):
1、判断一个整数是否是丑数?
2、给定区间,输出丑数的个数或丑数。
3、求第N个丑数
##############################################################################################
寻找丑数算法1:
(1)设置一个计数器用来统计出现的丑数的个数
(2)从1开始遍历每一个整数,判断是否是丑数,如果是丑数则计数器加1,否则遍历下一个整数。
(3)当计数器的值=N时,停止遍历,输出丑数。
##########################################################################################################
寻找丑数算法2:
从上一个丑数推断出下一个丑数,而不需要从1开始遍历再判断。从1开始的10个丑数分别为1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,12。可以发现除了1以外,丑数都是由某个丑数*2或者*3或者*5得到的。如2是丑数1*2得到的,3是丑数1*3得到的,4是丑数1*4得到的,5是丑数1*5得到的,6是丑数2*3得到的……
具体算法步骤:
(1)从第一个丑数1开始,求出1*2=2 ,1*3=3 ,1*5 = 5;
(2)取上面乘积中大于1的最小值2,作为第二个丑数(丑数是个递增序列,所以第i+1个丑数一定比第i个丑数大)
(3)求丑数2之前的丑数与2、3、5的乘积:1*2=2 ,1*3=3 ,1*5 = 5; 2*2 = 4; 2*3 = 6; 2*5 =10;
(4)取上面乘积中大于2的最小值3,作为第三个丑数
……
(i)取出丑数i之前的丑数分别与2、3、5的乘积
(i+1)取乘积中大于i的最小值作为丑数
(i+2)重复(i)(i+1)的步骤直到计数器等于N
##########################################################################################################
问题一:判断一个数是否为丑数
python代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
# 判断一个数是否为丑数
def isUglyNumber(num):
if num<=0:
return False
elif num>=1:
for i in [2,3,5]:
while num%i==0:
num = num / i
if num == 1:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
arr = int(input())
print(isUglyNumber(arr))
except:
pass
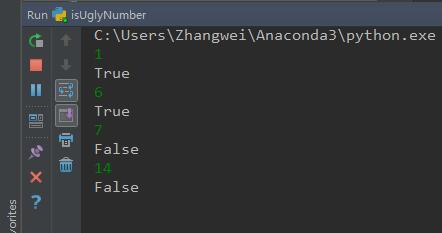
运行结果:
C++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//判断一个数是否为丑数
bool isUglyNumber(int num){
vector<int> index = { 2, 3, 5 };
if (num <= 0) return false;
else if (num >= 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
while (num%index[i] == 0)
{
num /= index[i];
}
}
if (num == 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
int main(){
int num;
while (1){
cin >> num;
bool index = isUglyNumber(num);
if (index == true)
cout << "True" << endl;
else
cout << "False" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
问题二:给定区间,输出丑数的个数或丑数
python 代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
# 判断一个数是否为丑数
def isUglyNumber(num):
if num<=0:
return False
elif num>=1:
for i in [2,3,5]:
while num%i==0:
num = num / i
if num == 1:
return True
else:
return False
def getUglyNumber(lowIndex,highIndex):
res = []
if highIndex<=0: #如果区间右端点小于或等于0,则返回空列表
return res
elif lowIndex>=highIndex: #如果区间左端点大于或等于右端点,则返回空列表
return res
elif lowIndex<=0 and highIndex>0: #如果区间左端点小于或等于0,右端点大于0
for i in range(1,highIndex+1):
if isUglyNumber(i)==True:
res.append(i)
return res
elif lowIndex>0 and highIndex>0: #如果区间左端点大于0,右端点大于0,且右端点大于左端点
for i in range(lowIndex,highIndex+1):
if isUglyNumber(i)==True:
res.append(i)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
arr = [int(t) for t in sys.stdin.readline().split()]
# 等价于 arr = [int(t) for t in input("").split()]
res = getUglyNumber(arr[0],arr[1])
# print(res) 输出格式为:如[1,2,3,4,5,6]
if len(res)>=1:
print(" ".join(str(i) for i in res)) # 输出列表元素,以空格为分隔符,且最后一个无空格
else:
print('no')
except:
pass
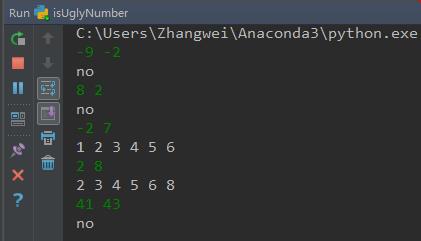
运行结果:
C++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//判断一个数是否为丑数
bool isUglyNumber(int num){
vector<int> index = { 2, 3, 5 };
if (num <= 0) return false;
else if (num >= 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
while (num%index[i] == 0)
{
num /= index[i];
}
}
if (num == 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
// 获取第N个丑数
vector<int> getUglyNumber(int lowIndex, int highIndex){
vector<int> res;
// 如果区间右端点小于或等于0,则返回空向量
if (highIndex <= 0) return res;
// 如果区间左端点大于或等于右端点,则返回空列表
else if (lowIndex >= highIndex) return res;
// 如果区间左端点小于或等于0,右端点大于0
else if (lowIndex <= 0 && highIndex > 0){
for (int i = 1; i < highIndex + 1; i++){
if (isUglyNumber(i) == true){
res.push_back(i);
}
}
}
// 如果区间左端点大于0,右端点大于0
else if (lowIndex > 0 && highIndex > 0){
for (int i = lowIndex; i < highIndex + 1; i++){
if (isUglyNumber(i) == true){
res.push_back(i);
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main(){
vector<int> index(2),myRes;
while (1){
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
cin >> index[i];
}
myRes = getUglyNumber(index[0],index[1]);
int len = myRes.size();// 求myRes长度
if (len >= 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++){
cout << myRes[j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
else{
cout << "no" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
问题三:求第N个丑数
python代码1:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
# 判断一个数是否为丑数
def isUglyNumber(num):
if num<=0:
return False
elif num>=1:
for i in [2,3,5]:
while num%i==0:
num = num / i
if num == 1:
return True
else:
return False
# 获取第N个丑数
def getUglyNumber(N):
count = 0 #用于计数
if N<=0:
return 0
else:
num = 1
while (count<N):
if isUglyNumber(num) == True:
count = count + 1
num = num + 1
return num-1
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
arr = int(input())
print(getUglyNumber(arr))
except:
pass
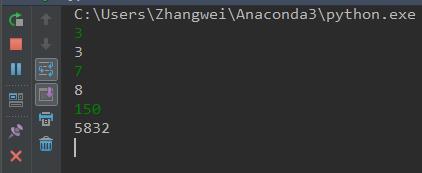
运行结果:
C++代码1:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//判断一个数是否为丑数
bool isUglyNumber(int num){
vector<int> index = { 2, 3, 5 };
if (num <= 0) return false;
else if (num >= 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
while (num%index[i] == 0)
{
num /= index[i];
}
}
if (num == 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
//获取第N个丑数
int getUglyNumber(int N){
int count = 0;
if (N <= 0) return 0;
else{
int num = 1;
while (count < N){
if (isUglyNumber(num) == true){
count += 1;
}
num += 1;
}
return num - 1;
}
}
int main(){
int num;
while (1){
cin >> num;
cout << getUglyNumber(num) << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
python代码2:
import sys
def getUglyNumber(N):
if N < 1:
return 0
res = [1]
t2 = t3 = t5 = 0
next = 1
while next < N:
min_num = min(res[t2] * 2, res[t3] * 3, res[t5] * 5)
res.append(min_num)
if res[t2] * 2 <= min_num:
t2 += 1
if res[t3] * 3 <= min_num:
t3 += 1
if res[t5] * 5 <= min_num:
t5 += 1
next += 1
return res[N - 1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
arr = int(input())
print(getUglyNumber(arr))
except:
pass
运行结果如上,该方法在优于方法1。因此,在剑指offer上的剑指offer——丑数的提交python代码应为方法2,方法1不通过。
即:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def GetUglyNumber_Solution(self, index):
# write code here
if index < 1:
return 0
res = [1]
t2 = t3 = t5 = 0
next = 1
while next < index:
min_num = min(res[t2]*2, res[t3]*3, res[t5]*5)
res.append(min_num)
if res[t2]*2 <= min_num:
t2 += 1
if res[t3]*3 <= min_num:
t3 += 1
if res[t5]*5 <= min_num:
t5 += 1
next += 1
return res[index-1]
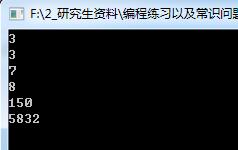
提交结果:
C++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//返回三个数字里面的最小值
int min(int num1, int num2, int num3)
{
int min = num1 < num2 ? num1 : num2;
min = min < num3 ? min : num3;
return min;
}
//获取第N个丑数
int getUglyNumber(int N){
if (N < 1) return 0;
vector<int> res = { 1 };
int t2 = 0;
int t3 = 0;
int t5 = 0;
int next = 1;
while (next < N){
int min_num = min(res[t2] * 2, res[t3] * 3, res[t5] * 5);
res.push_back(min_num);
if (res[t2] * 2 <= min_num) t2 += 1;
if (res[t3] * 3 <= min_num) t3 += 1;
if (res[t5] * 5 <= min_num) t5 += 1;
next += 1;
}
return res[N - 1];
}
int main(){
int num;
while (1){
cin >> num;
int res = getUglyNumber(num);
cout << res << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
同理,在剑指offer上的剑指offer——丑数的提交C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
int min(int num1, int num2, int num3){
int min = num1 < num2 ? num1 : num2;
min = min < num3 ? min : num3;
return min;
}
int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if (index < 1) return 0;
vector<int> res = { 1 };
int t2 = 0;
int t3 = 0;
int t5 = 0;
int next = 1;
while (next < index){
int min_num = min(res[t2] * 2, res[t3] * 3, res[t5] * 5);
res.push_back(min_num);
if (res[t2] * 2 <= min_num) t2 += 1;
if (res[t3] * 3 <= min_num) t3 += 1;
if (res[t5] * 5 <= min_num) t5 += 1;
next += 1;
}
return res[index - 1];
}
};
提交结果:
参考网址:
1、https://blog.csdn.net/u013632190/article/details/52036119
2、https://blog.csdn.net/lzuacm/article/details/51336420
3、https://blog.csdn.net/my_mao/article/details/24366291