SparkSQL数据源:从各种数据源创建DataFrame
因为 spark sql,dataframe,datasets 都是共用 spark sql 这个库的,三者共享同样的代码优化,生成以及执行流程,所以 sql,dataframe,datasets 的入口都是 sqlContext。
可用于创建 spark dataframe 的数据源有很多:

SparkSQL数据源:RDD
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// this is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.
import sqlContext.implicits._
// Define the schema using a case class.
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
// Create an RDD of Person objects and register it as a table.
val people = sc.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt))
.toDF()
val people = sc
.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt))
sqlContext.createDataFrame(people)
SparkSQL数据源:Hive
当从Hive 中读取数据时,Spark SQL 支持任何Hive 支持的存储格式(SerDe),包括文件、RCFiles、ORC、Parquet、Avro,以及Protocol Buffer(当然Spark SQL也可以直接读取这些文件)。
要连接已部署好的Hive,需要拷贝hive-site.xml、core-site.xml、hdfs-site.xml到Spark 的./conf/ 目录下即可
如果不想连接到已有的hive,可以什么都不做直接使用HiveContext:
Spark SQL 会在当前的工作目录中创建出自己的Hive 元数据仓库,叫作metastore_db
如果你尝试使用HiveQL 中的CREATE TABLE(并非CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE)语句来创建表,这些表会被放在你默认的文件系统中的/user/hive/warehouse 目录中(如果你的classpath 中有配好的hdfs-site.xml,默认的文件系统就是HDFS,否则就是本地文件系统)。
SparkSQL数据源:Hive读写
// sc is an existing SparkContext.
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveContext(sc)
sqlContext.sql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS src (key INT, value STRING)")
sqlContext.sql("LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH 'examples/src/main/resources/kv1.txt' INTO TABLE src")
// Queries are expressed in HiveQL
sqlContext.sql("FROM src SELECT key, value").collect().foreach(println)
SparkSQL数据源:访问不同版本的metastore
从Spark1.4开始,Spark SQL可以通过修改配置去查询不同版本的?Hive metastores(不用重新编译)

SparkSQL数据源:Parquet
Parquet(http://parquet.apache.org/)是一种流行的列式存储格式,可以高效地存储具有嵌套字段的记录。
Parquet 格式经常在Hadoop 生态圈中被使用,它也支持Spark SQL 的全部数据类型。Spark SQL 提供了直接读取和存储Parquet 格式文件的方法。
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// this is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a DataFrame.
import sqlContext.implicits._
// Define the schema using a case class.
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
// Create an RDD of Person objects and register it as a table.
val people = sc
.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt))
.toDF()
people.write.parquet("xxxx")
val parquetFile = sqlContext.read.parquet("people.parquet")
//Parquet files can also be registered as tables and then used in SQL statements.
parquetFile.registerTempTable("parquetFile")
val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM parquetFile WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")
teenagers.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)
SparkSQL数据源:Parquet -- Partition Discovery
在Hive中通常会用分区表来优化性能,比如:
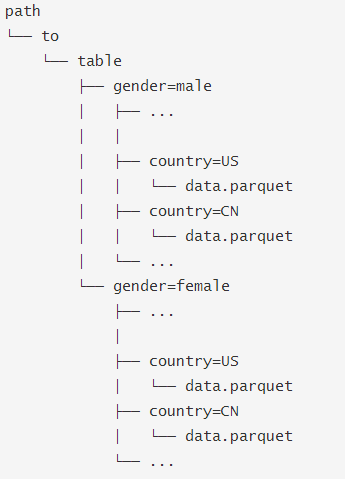
SQLContext.read.parquet或者SQLContext.read.load只需要指定path/to/table,SparkSQL会自动从路径中提取分区信息,返回的DataFrame 的schema 将是:

当然你可以使用Hive读取方式:
hiveContext.sql("FROM src SELECT key, value").
SparkSQL数据源:Json
SparkSQL支持从Json文件或者Json格式的RDD读取数据
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// 可以是目录或者文件夹
val path = "examples/src/main/resources/people.json"
val people = sqlContext.read.json(path)
// The inferred schema can be visualized using the printSchema() method.
people.printSchema()
// Register this DataFrame as a table.
people.registerTempTable("people")
// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.
val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")
// Alternatively, a DataFrame can be created for a JSON dataset represented by
// an RDD[String] storing one JSON object per string.
val anotherPeopleRDD = sc.parallelize("""{"name":"Yin","address":{"city":"Columbus","state":"Ohio"}}""" :: Nil)
val anotherPeople = sqlContext.read.json(anotherPeopleRDD)
SparkSQL数据源:JDBC
val jdbcDF = sqlContext.read.format("jdbc")
.options(Map("url" -> "jdbc:postgresql:dbserver","dbtable" -> "schema.tablename"))
.load()
支持的参数:
