一、UDF说明
array_struct_sort(array(struct1,struct2,...), string sortField):Returns the passed array struct, ordered by the given field. 对所给的Array<Struct>按sortField字段进行排序并返回。
二、代码
package com.scb.dss.udf;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentTypeException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.metadata.HiveException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.udf.generic.GenericUDF;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde.Constants;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.util.*;
import static org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.ObjectInspector.Category.LIST;
@Description(name = "array_struct_sort",
value = "_FUNC_(array(struct1,struct2,...), string sortField) - "
+ "Returns the passed array struct, ordered by the given field",
extended = "Example:\n"
+ " > SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age') as struct_array\n" +
" FROM (\n" +
" SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t\n" +
" union all \n" +
" SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t\n" +
" union all \n" +
" SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t\n" +
" union all\n" +
" SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t\n" +
" ) as test_data\n" +
" group by class;\n")
public class UDFArrayStructSort extends GenericUDF {
protected ObjectInspector[] argumentOIs;
ListObjectInspector loi;
StructObjectInspector elOi;
// cache comparators for performance
Map<String, Comparator> comparatorCache = new HashMap<String, Comparator>();
@Override
public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] ois) throws UDFArgumentException {
// all common initialization
argumentOIs = ois;
// clear comparator cache from previous invokations
comparatorCache.clear();
return checkAndReadObjectInspectors(ois);
}
/**
* Utility method to check that an object inspector is of the correct type,
* and returns its element object inspector
*
* @param ois
* @return
* @throws UDFArgumentTypeException
*/
protected ListObjectInspector checkAndReadObjectInspectors(ObjectInspector[] ois)
throws UDFArgumentTypeException, UDFArgumentException {
// check number of arguments. We only accept two,
// the list of struct to sort and the name of the struct field
// to sort by
if (ois.length != 2) {
throw new UDFArgumentException("2 arguments needed, found " + ois.length);
}
// first argument must be a list/array
if (!ois[0].getCategory().equals(LIST)) {
throw new UDFArgumentTypeException(0, "Argument 1"
+ " of function " + this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " must be " + Constants.LIST_TYPE_NAME
+ ", but " + ois[0].getTypeName()
+ " was found.");
}
// a list/array is read by a LIST object inspector
loi = (ListObjectInspector) ois[0];
// a list has an element type associated to it
// elements must be structs for this UDF
if (loi.getListElementObjectInspector().getCategory() != ObjectInspector.Category.STRUCT) {
throw new UDFArgumentTypeException(0, "Argument 1"
+ " of function " + this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " must be an array of structs " +
" but is an array of " + loi.getListElementObjectInspector().getCategory().name());
}
// store the object inspector for the elements
elOi = (StructObjectInspector) loi.getListElementObjectInspector();
// returns the same object inspector
return loi;
}
// factory method for cached comparators
Comparator getComparator(Text field) {
if (!comparatorCache.containsKey(field.toString())) {
comparatorCache.put(field.toString(), new StructFieldComparator(field.toString()));
}
return comparatorCache.get(field.toString());
}
@Override
public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] dos) throws HiveException {
// get list
if (dos == null || dos.length != 2) {
throw new HiveException("received " + (dos == null ? "null" :
Integer.toString(dos.length) + " elements instead of 2"));
}
// each object is supposed to be a struct
// we make a shallow copy of the list. We don't want to sort
// the list in place since the object could be used elsewhere in the
// hive query
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(loi.getList(dos[0].get()));
// sort with our comparator, then return
// note that we could get a different field to sort by for every
// invocation
Collections.sort(al, getComparator((Text) dos[1].get()));
return al;
}
@Override
public String getDisplayString(String[] children) {
return (children == null ? null : this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "(" + children[0] + "," + children[1] + ")");
}
// to sort a list , we must supply our comparator
public class StructFieldComparator implements Comparator {
StructField field;
public StructFieldComparator(String fieldName) {
field = elOi.getStructFieldRef(fieldName);
}
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// ok..so both not null
Object f1 = elOi.getStructFieldData(o1, field);
Object f2 = elOi.getStructFieldData(o2, field);
// compare using hive's utility functions
return ObjectInspectorUtils.compare(f1, field.getFieldObjectInspector(),
f2, field.getFieldObjectInspector());
}
}
}三、测试
测试数据如下:
| class | struct |
| 1 | {"name":"N003","age":"20"} |
| 2 | {"name":"N001","age":"18"} |
| 1 | {"name":"N002","age":"19"} |
| 2 | {"name":"N000","age":"17"} |
测试代码:
SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age') as struct_array
FROM (
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t
) as test_data
group by class;测试结果如下:
![]()
在结合上节的Hive UDAF collect_map我们就可以对MAP<STRING, ARRAY<STRUCT<x,x>>>进行聚合排序操作了。
SELECT class, collect_map(class, struct_array) as res
FROM (
SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age') as struct_array
FROM (
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t
) as test_data
group by class
) as tmp
group by class
; ![]()
跟上节的结果相比,这次出来的struct可以按照age进行排序了。
res字段类型为MAP<STRING, ARRAY<STRUCT<field1,field2,field3>>>,如果要取一班年纪最新的学生名字,代码如下:
select res['1'][0].name
from (
SELECT class, collect_map(class, struct_array) as res
FROM (
SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age') as struct_array
FROM (
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t
) as test_data
group by class
) as tmp
group by class
) as t
;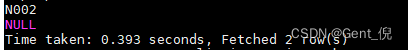
可以在加个where条件去过滤NULL
四、改进
上面的代码只支持升序排序,那么如果需要降序呢?我们可以使用Collections.reverseOrder()方法来实现降序。完整代码如下:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
15833005 查看本文章


package com.scb.dss.udf;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.Description;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentTypeException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.metadata.HiveException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.udf.generic.GenericUDF;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde.Constants;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.BooleanWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.util.*;
import static org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.objectinspector.ObjectInspector.Category.LIST;
@Description(name = "array_struct_sort",
value = "_FUNC_(array(struct1,struct2,...), string sortField, bool asc) - "
+ "Returns the passed array struct, ordered by the given field. The default sorting method is ascending",
extended = "Example:\n"
+ " > SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age', true) as struct_array\n" +
" FROM (\n" +
" SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t\n" +
" union all \n" +
" SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t\n" +
" union all \n" +
" SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t\n" +
" union all\n" +
" SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t\n" +
" ) as test_data\n" +
" group by class;\n")
public class UDFArrayStructSort extends GenericUDF {
protected ObjectInspector[] argumentOIs;
ListObjectInspector loi;
StructObjectInspector elOi;
// cache comparators for performance
Map<String, Comparator> comparatorCache = new HashMap<String, Comparator>();
@Override
public ObjectInspector initialize(ObjectInspector[] ois) throws UDFArgumentException {
// all common initialization
argumentOIs = ois;
// clear comparator cache from previous invokations
comparatorCache.clear();
return checkAndReadObjectInspectors(ois);
}
/**
* Utility method to check that an object inspector is of the correct type,
* and returns its element object inspector
*
* @param ois
* @return
* @throws UDFArgumentTypeException
*/
protected ListObjectInspector checkAndReadObjectInspectors(ObjectInspector[] ois)
throws UDFArgumentTypeException, UDFArgumentException {
// check number of arguments. We only accept two,
// the list of struct to sort and the name of the struct field
// to sort by
if (ois.length != 3) {
throw new UDFArgumentException("3 arguments needed, found " + ois.length);
}
// first argument must be a list/array
if (!ois[0].getCategory().equals(LIST)) {
throw new UDFArgumentTypeException(0, "Argument 1"
+ " of function " + this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " must be " + Constants.LIST_TYPE_NAME
+ ", but " + ois[0].getTypeName()
+ " was found.");
}
// a list/array is read by a LIST object inspector
loi = (ListObjectInspector) ois[0];
// a list has an element type associated to it
// elements must be structs for this UDF
if (loi.getListElementObjectInspector().getCategory() != ObjectInspector.Category.STRUCT) {
throw new UDFArgumentTypeException(0, "Argument 1"
+ " of function " + this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " must be an array of structs " +
" but is an array of " + loi.getListElementObjectInspector().getCategory().name());
}
// store the object inspector for the elements
elOi = (StructObjectInspector) loi.getListElementObjectInspector();
// returns the same object inspector
return loi;
}
// factory method for cached comparators
Comparator getComparator(Text field) {
if (!comparatorCache.containsKey(field.toString())) {
comparatorCache.put(field.toString(), new StructFieldComparator(field.toString()));
}
return comparatorCache.get(field.toString());
}
@Override
public Object evaluate(DeferredObject[] dos) throws HiveException {
// get list
if (dos == null || dos.length != 3) {
throw new HiveException("received " + (dos == null ? "null" :
Integer.toString(dos.length) + " elements instead of 3"));
}
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(loi.getList(dos[0].get()));
if (((BooleanWritable) dos[2].get()).get()) {
Collections.sort(al, getComparator((Text) dos[1].get()));
} else {
Collections.sort(al, Collections.reverseOrder(getComparator((Text) dos[1].get())));
}
return al;
}
@Override
public String getDisplayString(String[] children) {
return (children == null ? null : this.getClass().getCanonicalName() + "(" + children[0] + "," + children[1] + ")");
}
public class StructFieldComparator implements Comparator {
StructField field;
public StructFieldComparator(String fieldName) {
field = elOi.getStructFieldRef(fieldName);
}
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Object f1 = elOi.getStructFieldData(o1, field);
Object f2 = elOi.getStructFieldData(o2, field);
// compare using hive's utility functions
return ObjectInspectorUtils.compare(f1, field.getFieldObjectInspector(),
f2, field.getFieldObjectInspector());
}
}
}测试代码:
SELECT class, collect_map(class, struct_array) as res
FROM (
SELECT class, array_struct_sort(collect_list(struct_t), 'age', false) as struct_array
FROM (
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N003', 'age', '20') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N001', 'age', '18') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '1' as class, named_struct('name', 'N002', 'age', '19') as struct_t
union all
SELECT '2' as class, named_struct('name', 'N000', 'age', '17') as struct_t
) as test_data
group by class
) as tmp
group by class
;测试截图:

五、参考文档
» Structured data in Hive: a generic UDF to sort arrays of structs Roberto Congiu's blog