目录
案例的代码已经放入百度网盘,有需要可自行提取。
http://链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Vcqn7-A5YWOMqhBLpr3I0A?pwd=759w 提取码: 759w
一、MapReduce概述
1、MapReduce核心思想
MapReduce的核心思想“分而治之”,即将一个任务分解成多个子任务,这些子任务之间没有必然的相互依赖,都可以单独执行,最后再将这些子任务的结果,进行汇总合并。
2、MapReduce编程模型
MapReduce作为一种编程模型,专门处理大规模数据的并行运算,该模型借鉴了函数式程序设计的思想,程序实现过程是通过map()函数和reduce()函数实现的。使用MapReduce处理计算任务的时候,每个任务都会分成两个阶段,Map阶段和Reduce阶段。
(1)Map阶段:对于原始数据的预处理。
(2)Reduce阶段:将Map阶段的处理结果进行汇总,最后得到最终结果。
流程说明:第一步,将原始的数据转换成键值对<k1,v1>的形式;第二步,转换后的键值对<k1,v1>导入到map()函数,map()函数根据映射规则,将键值对<k1,v1>映射为一系列中间结果形式的键值对<k2,v2>;第三步,将中间形式的键值对<k2,v2>形成<k2,{v2......}>形式传给reduce()函数处理,把具有相同结果的key的value合并在一起,产生新的键值对<k3,v3>,此时键值对<k3,v3>就是最终的结果。
二、MapReduce工作原理
1、分片、格式化数据源
输入Map阶段的数据源,需要经过分片和格式操作。
(1)分片操作:将源文件划分为大小相等的小数据块,然后hadoop会为每一个分片构建一个Map任务,由该任务运行自定义的map()函数,从而处理分片里的每一条记录。
(2)格式化操作:将划分好的分片格式化为键值对<key,value>形式的数据,其中key代表偏移量,value代表一行内容。
2、执行 MapTask
(1)Read阶段:Map Task通过用户编写的RecordReader,从输入的InputSplit中解析一个个键值对<k,v>。
(2)Map阶段:将解析出的<k,v>交给用户编写的map函数处理,产生新的键值对<k,v>。
(3)Collect阶段:在用户编写的map函数中,数据处理完后,一般会调用outputCollector.collect()输出结果,在该函数内部生成键值对<k,v>分片,并写如环形内存缓冲区。
(4)Spill阶段:如果环形缓冲区满后,MapReduce会将数据写入到本地磁盘中,生成一个临时文件。这里需要注意,数据写入本地磁盘前,需要对数据进行一次排序,必要时需要对数据进行合并、压缩等操作。
(5)Combine阶段:当所有数据处理完后,Map Task会对所有的临时文件进行一次合并,以却确保最终只会生成一个数据文件。
3、执行Shuffle过程
Shuffle会将Map Task输出的处理结果数据分发给RecudeTask,并在分发的过程中,对数据按key进行分区和排序。
4、执行RecudeTack
(1)Copy阶段:Recude会从各个MapTask上远程复制一份数据,并针对某一数据,如果其大小超过一定值,则写到磁盘中,否则存放到内存中。
(2)Merge阶段:在远程复制数据的同时,RecudeTack会启动两个后台线程,分别对内存和磁盘上的文件进行合并,防止内存使用过多或磁盘文件过多。
(3)Sort阶段:用户编写reduce()方法输入数据是按 key进行聚集的一组数据。为了 I key 相同的数据聚在一起.Hadoop 采用了基于排序的策略。由于各个 MapTask 已经实现对自己的处理结果进行了局部排序,因此,ReduceTask 只需对所有数据进行一次归井排序即可。
(4)Reduce阶段:对排序后的键值对调用reduce()方法,键相等的键值对调用一次reduce()方法,每次调用会产生零个或多个键值对,最后把这些键值对写入到HDFS中。
(5)Write阶段:reduce()函数将计算结果写入到HDFS中。
5、写入文件
MapReduce框架会自动把RecudeTack生成的<key,value>传入OutputFormat的write方法,实现文件的写入操作。
三、案例
1、词频统计
这里通过词频统计这个案例来简单的了解一下MapReduce的相关组件。
(1)InputFormat组件
该组件主要用于描述输入数据的格式,它提供以下两个功能。
a、数据切分:按照策略将输入的数据切分成诺干个分片,以便确定MapTask的个数以及对应的分片。
b、为Mapper提供输入数据源:给定某个分片,将其解析成一个个键值对<k,v>。
Hadoop自带一个InputFormat接口,该接口定义代码如下。
public abstract class InputFormat <K, V> {
public abstract List<InputFormat>getSplits(JobContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
public abstract RecordReader <K, V> createRecordReader (InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
}InputFormat接口定义了getSplits()和createRecordReader()两个方法,getSplits()方法负责将文件切分成为多个分片,createRecordReader()方法负责创建RecordReader对象,用来从分片中获取数据。
(2)Mapper组件
MapReduce程序会根据输入的文件产生多个map任务,Mapper类实现Map任务的一个抽象类,该类提供一个map()方法,默认情况下,该方法是没有任何处理,这时我们可以自定义map()方法,继承Mapper类并重写map()方法。
接下来我们以词频统计为例,自定义map()方法,代码如下。
package cn.itcast.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//接收传入进来的一行文本,并转换成String类型
String line = value.toString();
//将这行内容按分隔符空格切割成单词,保存在String数组中
String[] words = line.split(" ");
//遍历数组,产生<K2,V2>键值对,形式为<单词,1>
for (String word : words
) {
//使用context,把map阶段处理的数据发送给reduce阶段作为输入数据
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}(3)Reducer组件
Map过程输出的键值对,将由Reducer组件进行合并处理。这里以词频统计为例,自定义reduce()方法。
package cn.itcast.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//定义一个计数器
int count = 0;
//遍历一组迭代器,把每一个数量1累加起来构成了单词出现的总次数
for (IntWritable iw : values
) {
count +=iw.get();
}
//向上下文context写入<k3,v3>
context.write(key, new IntWritable(count));
}
}(4)Combiner组件
该组件的作用是对Map阶段的输出重复数据先做一次合并计算,然后把新的键值对作为Reduce阶段的输入。如果想要自定义Combiner类,需要继承Reducer类,并重写reduce()方法,具体代码如下。
package cn.itcast.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountCombiner extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//局部汇总
//定义一个计数器
int count = 0;
//遍历一组迭代器,把每一个数量1累加起来构成了单词出现的总次数
for (IntWritable v : values
) {
count += v.get();
}
//向上下文context写入<k3,v3>
context.write(key, new IntWritable(count));
}
}(5)MapReduce的运行模式
MapReduce的运行模式分为两种,本地运行模式和集群运行模式两种。
a、本地运行模式:在当前开发环境模拟MapReduce的运行环境,处理数据的输出结果都在本地。
b、集群运行模式:把MapReduce程序打成jar包,上传到Yarn集群运行,处理的数据和结果都在HDFS上。
这里我们主要讲本地运行模式,要实现本地的运行,我们还需要一个Driver类,代码如下。
package cn.itcast.mr.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
//通过 Job 来封装本次 MR 的相关信息
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//配置MR运行模式,使用 local 表示本地模式,可以省略
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name","local");
//获取 Job 运行实例
Job wcjob = Job.getInstance(conf);
//指定 MR Job jar运行主类
wcjob.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
//指定本次 MR 所有的 Mapper Combiner Reducer类
wcjob.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
wcjob.setCombinerClass(WordCountCombiner.class); //不指定Combiner的话也不影响结果
wcjob.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
//设置业务逻辑 Mapper 类的输出 key 和 value 的数据类型
wcjob.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
wcjob.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//设置业务逻辑 Reducer 类的输出 key 和 value 的数据类型
wcjob.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
wcjob.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//使用本地模式指定要处理的数据所在的位置
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(wcjob,"/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/WordCount/input");
//使用本地模式指定处理完成后的结果所保持的位置
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(wcjob,new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/WordCount/output"));
//提交程序并且监控打印程序执行情况
boolean res = wcjob.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(res ? 0:1);
}
}当我们运行完后,会在本地生成一个结果文件。

2、倒排索引
(1)介绍
倒排索引是文档检索系统的中常用数据格式结构,被广泛应用于全文搜索引擎。可以简单的理解为根据内容来查找文档,而不是根据文档来查找内容。
(2)Map阶段的实现
package cn.itcast.mr.invertedIndex;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
//存储单词和文档名称
private static Text keyInfo = new Text();
// 存储词频,初始化为1
private static final Text valueInfo = new Text("1");
/*
* 在该方法中将K1、V1转换为K2、V2
* key: K1行偏移量
* value: V1行文本数据
* context: 上下文对象
* 输出: <MapReduce:file3 "1">
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
// 得到单词数组
String[] fields = line.split(" ");
//得到这行数据所在的文件切片
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
//根据文件切片得到文件名
String filename = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
for (String field : fields
) {
// key值由单词和文件名组成,如“MapReduce:file1”
keyInfo.set(field + ":" + filename);
context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo);
}
}
}(3)Combine阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.invertedIndex;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
private static Text info = new Text();
// 输入: <MapReduce:file3 {1,1,...}>
// 输出:<MapReduce file3:2>
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0; //统计词频
//遍历一组迭代器,把每一个数量1累加起来构成了单词出现的总次数
for (Text value : values) {
sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString());
}
int splitIndex = key.toString().indexOf(":");
// 重新设置 value 值由文件名和词频组成
info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum);
// 重新设置 key 值为单词
key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex));
//向上下文context写入<k3,v3>
context.write(key, info);
}
}
(4)Reduce阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.invertedIndex;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
private static Text result = new Text();
// 输入:<MapReduce, file3:2>
// 输出:<MapReduce, file1:1;file2:1;file3:2;>
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 生成文档列表
StringBuffer fileList = new StringBuffer();
for (Text value : values) {
fileList.append(value.toString() + ";");
}
result.set(fileList.toString());
context.write(key, result);
}
}
(5)Driver程序主类实现
package cn.itcast.mr.invertedIndex;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InvertedIndexDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
//通过 Job 来封装本次 MR 的相关信息
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//获取 Job 运行实例
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
//指定 MR Job jar运行主类
job.setJarByClass(InvertedIndexDriver.class);
//指定本次 MR 所有的 Mapper Combiner Reducer类
job.setMapperClass(InvertedIndexMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(InvertedIndexCombiner.class);
job.setReducerClass(InvertedIndexReducer.class);
//设置业务逻辑 Mapper 类的输出 key 和 value 的数据类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//设置业务逻辑 Reducer 类的输出 key 和 value 的数据类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//使用本地模式指定要处理的数据所在的位置
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,"/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/InvertedIndex/input");
//使用本地模式指定处理完成后的结果所保持的位置
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/InvertedIndex/output"));
//提交程序并且监控打印程序执行情况
boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(res ? 0:1);
}
}
(6)结果展示
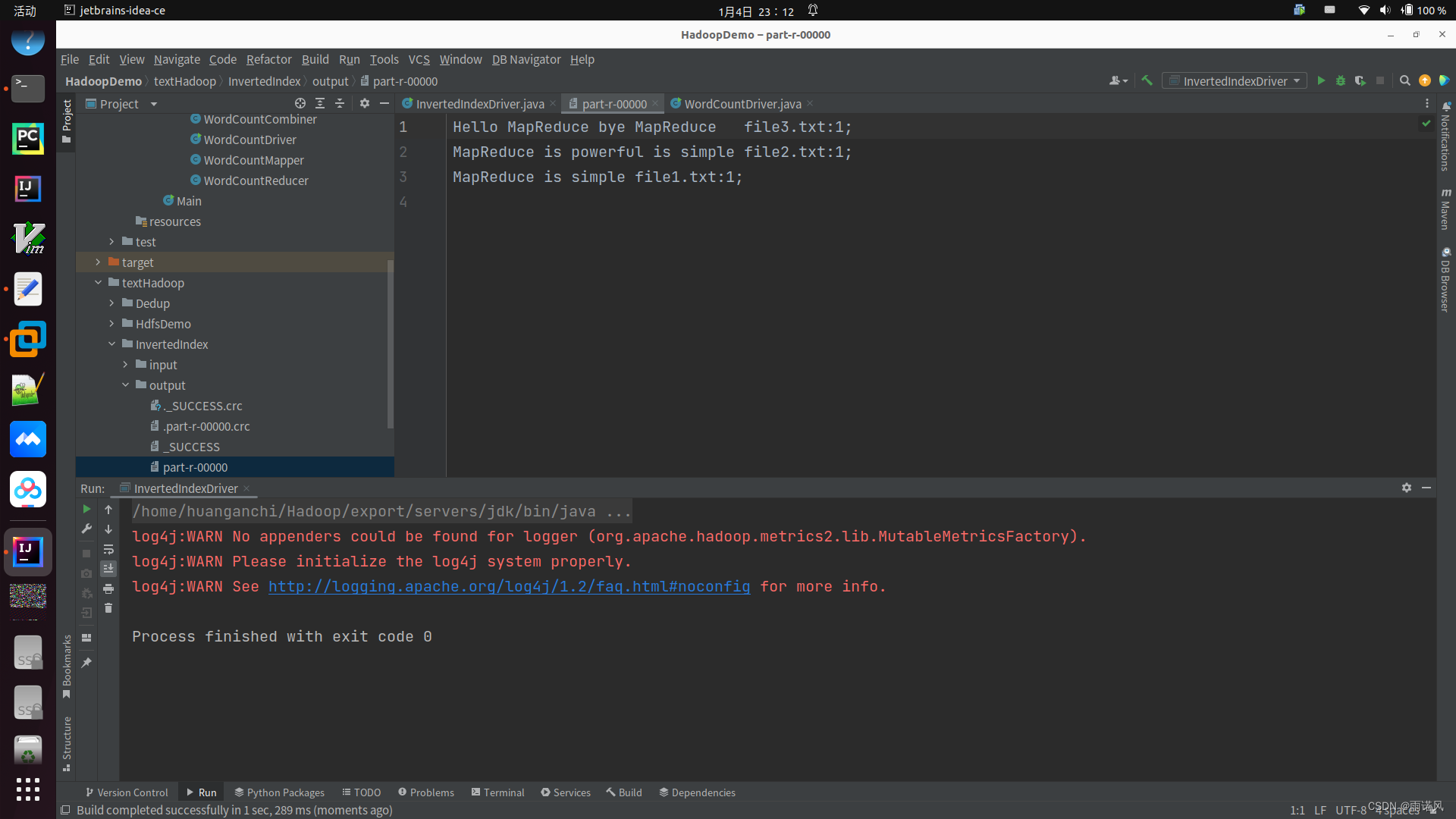
3、数据去重
(1)Map阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.dedup;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DedupMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
private static Text field = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
field = value;
context.write(field,NullWritable.get());
}
}
(2)Reduce阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.dedup;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DeupReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
(3)Driver程序主类实现
package cn.itcast.mr.dedup;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DedupDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(DedupDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(DedupMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(DeupReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/Dedup/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/Dedup/output"));
//job.waitForCompletion(true);
boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true);
if (res) {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/Dedup/output/part-r-00000");
BufferedReader reader= new BufferedReader(fr);
String str;
while ( (str = reader.readLine()) != null )
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println("运行成功");
}
System.exit(res ? 0 : 1);
}
}
(4)结果展现

4、TopN
(1)案例介绍
TopN分析法是指从研究对象中安装某一个指标进行倒序或正序排列,取其中所需的N个案例,并对这N个数据进行重点分析的方法。
(2)Map阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.topN;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TopNMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,
NullWritable, IntWritable> {
private TreeMap<Integer, String>repToRecordMap =
new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
@Override
public void map (LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) {
String line = value.toString();
String[] nums = line.split(" ");
for (String num : nums
) {
repToRecordMap.put(Integer.parseInt(num), " ");
if (repToRecordMap.size() > 5) {
repToRecordMap.remove(repToRecordMap.firstKey());
}
}
}
@Override
protected void cleanup(Context context) {
for (Integer i: repToRecordMap.keySet()
) {
try {
context.write(NullWritable.get(), new IntWritable(i));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}(3)Reduce阶段实现
package cn.itcast.mr.topN;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TopNReducer extends Reducer<NullWritable, IntWritable, NullWritable, IntWritable> {
private TreeMap<Integer, String>repToRecordMap = new
TreeMap<Integer, String>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
return b-a;
}
});
public void reduce(NullWritable key,
Iterable<IntWritable>values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (IntWritable value : values
) {
repToRecordMap.put(value.get(), " ");
if (repToRecordMap.size() > 5) {
repToRecordMap.remove(repToRecordMap.lastKey());
}
}
for (Integer i : repToRecordMap.keySet()
) {
context.write(NullWritable.get(), new IntWritable(i));
}
}
}
(4)Driver程序主类实现
package cn.itcast.mr.topN;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class TopNDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(TopNDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(TopNMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(TopNReducer.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/TopN/input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/TopN/output"));
boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true);
if (res) {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("/home/huanganchi/Hadoop/实训项目/HadoopDemo/textHadoop/TopN/output/part-r-00000");
BufferedReader reader= new BufferedReader(fr);
String str;
while ( (str = reader.readLine()) != null )
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println("运行成功");
}
System.exit(res ? 0 : 1);
}
}(5)结果展示
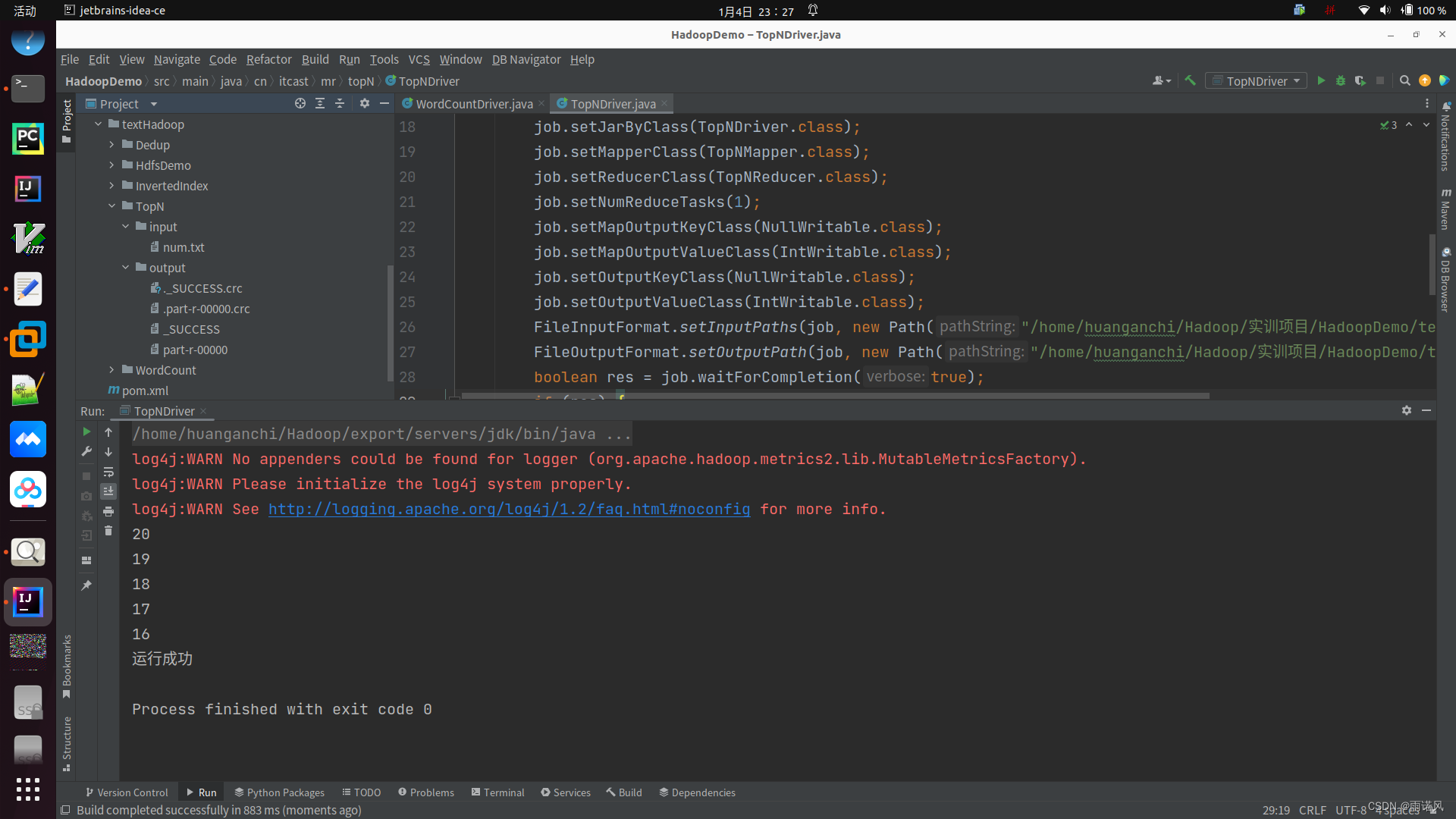
参考书籍
《Hadoop大数据技术原理与应用》