看到一个写的比较好的帖子
出处:https://www.zhihu.com/question/317992090/answer/2561856956
oops
Oops一词本意为惊讶, 一般内核出现Oops信息, 表明当前系统遇到重大的问题, 系统当前状态的一些信息就会被内核通oops抛出, 方便定位问题. 通过了解oops信息结构格式, 可以找到异常的问题点, 或者解决的方向.普通的Oops主要包含信息有:Oops类型全局页表(pdg)地址当前CPU编号及寄存器状态正常函数执行调用栈中断异常栈系统当前加载的模块进程信息下面写一个简单的内核模块,来验证如何分析一个内核oops错误。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
static void creat_oops(void)
{
printk("******start*****\n");
*(int *)0 = 0; //人为制造一个空指针
printk("******end*****\n");
}
static int __init regulator_pmc_voltage_init(void)
{
printk("oops module init\n");
creat_oops();
return 0;
}
subsys_initcall(regulator_pmc_voltage_init);
static void __exit regulator_pmc_voltage_exit(void)
{
printk("regulator_pmc_voltage_exit goodbye\n");
}
module_exit(regulator_pmc_voltage_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
编译,打包,烧写固件后,会出现如下log:
[ 1.079767] oops module init
[ 1.079834] ******start*****
[ 1.079919] Unable to handle kernel write to read-only memory at virtual address 0000000000000000
[ 1.088829] Mem abort info:
[ 1.091521] ESR = 0x96000045
[ 1.094653] EC = 0x25: DABT (current EL), IL = 32 bits
[ 1.099899] SET = 0, FnV = 0
[ 1.102874] EA = 0, S1PTW = 0
[ 1.106050] Data abort info:
[ 1.108854] ISV = 0, ISS = 0x00000045
[ 1.112724] CM = 0, WnR = 1
[ 1.115615] [0000000000000000] user address but active_mm is swapper
[ 1.122028] Internal error: Oops: 96000045 [#1] PREEMPT SMP
[ 1.127478] Modules linked in:
[ 1.130515] CPU: 0 PID: 1 Comm: swapper/0 Not tainted 5.4.99-00006-g02e5b77f5cd8-dirty #5
[ 1.138656] Hardware name: sun50iw10 (DT)
[ 1.142646] pstate: 80400005 (Nzcv daif +PAN -UAO)
[ 1.147420] pc : regulator_pmc_voltage_init+0x2c/0x48
[ 1.152439] lr : regulator_pmc_voltage_init+0x28/0x48
[ 1.157462] sp : ffffffc01002bd90
[ 1.160756] x29: ffffffc01002bd90 x28: 0000000000000000
[ 1.166043] x27: ffffffc011293000 x26: ffffffc011267860
[ 1.171329] x25: 0000000000000000 x24: ffffffc011267888
[ 1.176616] x23: ffffffc010a2ee1c x22: ffffffc011266e50
[ 1.181903] x21: ffffffc0110e0000 x20: ffffffc010d1b000
[ 1.187189] x19: ffffffc011267000 x18: 000000000000000a
[ 1.192476] x17: 000000004aeaa4e0 x16: 00000000b1cadfb9
[ 1.197763] x15: 00000000000137da x14: ffffffc09002bab7
[ 1.203049] x13: ffffffffffffffff x12: 0000000000000030
[ 1.208336] x11: 00000000fffffffe x10: ffffffc01002bac5
[ 1.213622] x9 : 0000000005f5e0ff x8 : ffffff803f5586e4
[ 1.218909] x7 : 0000000000000038 x6 : 0000000000000004
[ 1.224196] x5 : 0000000000000000 x4 : 0000000000000001
[ 1.229483] x3 : ffffffc010d1b018 x2 : 0411eecd9ba58e00
[ 1.234769] x1 : 0000000000000000 x0 : 0000000000000000
[ 1.240056] Call trace:
[ 1.242486] regulator_pmc_voltage_init+0x2c/0x48
[ 1.247168] do_one_initcall+0x110/0x2c8
[ 1.251067] kernel_init_freeable+0x158/0x1f8
[ 1.255400] kernel_init+0x18/0x108
[ 1.258866] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x18
[ 1.262428] Code: f0fff900 9126e800 97f3ffbc d2800000 (b900001f)
[ 1.268509] ---[ end trace 06967c0c0dd91e52 ]---
[ 1.273118] Kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill init! exitcode=0x0000000b
[ 1.280712] SMP: stopping secondary CPUs
[ 1.284637] ---[ end Kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill init! exitcode=0x0000000b ]---
pc指针指向出错指向的地址,另外Call trace展示了出错时程序的调用关系。首先观察出错函数regulator_pmc_voltage_init+0x2c/0x48,其中0x2c表示指令指针在该函数第0x2c字节处,该函数本身共0x48个字节。
当有符号表时可以使用gdb进行分析
使用gdb即可以看到出错附近的代码也会给出具体出错函数的路径。
$ ./out/gcc-linaro-5.3.1-2016.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-gdb ./out/kernel/build/vmlinux
GNU gdb (Linaro_GDB-2016.05) 7.11.1.20160702-git
Copyright (C) 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying"
and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "--host=x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu --target=aarch64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from ./out/kernel/build/vmlinux...done.
(gdb) list *regulator_pmc_voltage_init+0x2c
0xffffffc010a2ee48 is in regulator_pmc_voltage_init (/home1/weidonghui/workspace/bsp/longan/kernel/linux-5.4/drivers/regulator/pmc.c:8).
3 #include <linux/kernel.h>
4
5 static void creat_oops(void)
6 {
7 printk("******start*****\n");
8 *(int *)0 = 0;
9 printk("******end*****\n");
10
11 }
12
(gdb)
当无符号表时可以使用decodecode进行分析:
对于没有编译符号表的二进制文件,内核提供了一个非常好用的脚本,可以帮助快速定位问题,该脚本位于linux内核代码目录的scripts/decodecode,首先把出错log保存到一个txt文件中。
$ ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=~/longan/out/gcc-linaro-5.3.1-2016.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu- ./scripts/decodecode < ./temp.txt
[ 1.262428] Code: f0fff900 9126e800 97f3ffbc d2800000 (b900001f)
All code
========
0: f0fff900 adrp x0, 0xfffffffffff23000
4: 9126e800 add x0, x0, #0x9ba
8: 97f3ffbc bl 0xffffffffffcffef8
c: d2800000 mov x0, #0x0 // #0
10:* b900001f str wzr, [x0] <-- trapping instruction
Code starting with the faulting instruction
===========================================
0: b900001f str wzr, [x0]
$
decodecode脚本把出错的oops日志信息转换成直观有用的汇编代码,并且告知出错具体是在哪个汇编语句中,这对于分析没有源代码的oops错误非常有用。
死锁问题
死锁(deadlock)是指两个或多个进程因争夺资源而造成的互相等待的现象。例如进程A需要资源X,进程B需要资源Y,而双方都掌握有对方所需要的资源,且都不释放,这时会导致死锁。在内核开发中,时常要考虑并发设计,即使采用正确的编程思路,也不可避免发生死锁。在Linux内核中,常见的死锁有如下两种: 递归死锁:例如在中断等延迟操作中使用了锁,和外面的锁构成了递归死锁。 AB-BA死锁:多个锁因处理不当而引发死锁,多个内核路径上的锁处理顺序不一致也会导致死锁。Linux内核在2006年引入了死锁调试模块Lockdep,经过多年发展,Lockdep为内核开发者和驱动开发者提前发现死锁提供了方便。Lockdep跟踪每个锁的自身状态和各个锁之间的依赖关系,经过一系列的验证规则来确保锁之间依赖关系是正确的。开启Lockdep要在Linux内核中使用Lockdep功能,需要打开以下选项:
CONFIG_LOCK_STAT=y
CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING=y
CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCKDEP=y
AB-BA死锁例子(基于linux-5.4)
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(hack_spinA);
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(hack_spinB);
void hack_spinAB(void)
{
printk("\nhack_lockdep:A-->B\n");
spin_lock(&hack_spinA);
spin_lock(&hack_spinB);
}
void hack_spinBA(void)
{
printk("\nhack_lockdep:B-->A\n");
spin_lock(&hack_spinB);
}
static int __init lockdep_test_init(void)
{
printk("\nfigo: my lockdep module init\n");
hack_spinAB();
hack_spinBA();
return 0;
}
static void __exit lockdep_test_exit(void)
{
printk("\ngoodbye\n");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(lockdep_test_init);
module_exit(lockdep_test_exit);
上述死锁例子初始化两个spinlock,其中hack_spinAB()函数分别申请了hack_spinA锁和hack_spinB锁,hack_spinBA()函数要去申请hack_spinB锁。因为刚才锁hack_spinB已经被成功获取了且还没有释放,它会一直等待,而且它也被锁在hack_spinA的临界区里。重新编译内核后,在proc目录下会有lockdep,lockdep_chains和lockdep_stats上个文件节点,说明lockdep模块已经生效。运行产生如下log:
[ 3.010121] sunxi_sid_init()485 - insmod ok
[ 3.010191]
[ 3.010191] figo: my lockdep module init
[ 3.014149]
[ 3.014149] hack_lockdep:A-->B
[ 3.018919]
[ 3.018919] hack_lockdep:B-->A
[ 3.023168]
[ 3.024541] ============================================
[ 3.029827] WARNING: possible recursive locking detected
[ 3.035117] 5.4.99-00006-g02e5b77f5cd8-dirty #7 Not tainted
[ 3.040661] --------------------------------------------
[ 3.045948] swapper/0/1 is trying to acquire lock:
[ 3.050715] ffffffc01120e668 (hack_spinB){
+.+.}, at: hack_spinBA+0x2c/0x34
[ 3.057561]
[ 3.057561] but task is already holding lock:
[ 3.063367] ffffffc01120e668 (hack_spinB){
+.+.}, at: hack_spinAB+0x38/0x44
[ 3.070214]
[ 3.070214] other info that might help us debug this:
[ 3.076714] Possible unsafe locking scenario:
[ 3.076714]
[ 3.082607] CPU0
[ 3.085034] ----
[ 3.087460] lock(hack_spinB);
[ 3.090580] lock(hack_spinB);
[ 3.093700]
[ 3.093700] *** DEADLOCK ***
[ 3.093700]
[ 3.099594] May be due to missing lock nesting notation
[ 3.099594]
[ 3.106356] 2 locks held by swapper/0/1:
[ 3.110254] #0: ffffffc01120e620 (hack_spinA){
+.+.}, at: hack_spinAB+0x30/0x44
[ 3.117534] #1: ffffffc01120e668 (hack_spinB){
+.+.}, at: hack_spinAB+0x38/0x44
[ 3.124814]
[ 3.124814] stack backtrace:
[ 3.129153] CPU: 0 PID: 1 Comm: swapper/0 Not tainted 5.4.99-00006-g02e5b77f5cd8-dirty #7
[ 3.137294] Hardware name: sun50iw10 (DT)
[ 3.141281] Call trace:
[ 3.143713] dump_backtrace+0x0/0x16c
[ 3.147350] show_stack+0x24/0x30
[ 3.150645] dump_stack+0xd0/0x118
[ 3.154025] __lock_acquire+0xe04/0xe9c
[ 3.157836] lock_acquire+0x14c/0x1b8
[ 3.161478] _raw_spin_lock+0x4c/0x88
[ 3.165116] hack_spinBA+0x2c/0x34
[ 3.168499] lockdep_test_init+0x24/0x30
[ 3.172398] do_one_initcall+0x110/0x2c8
[ 3.176299] kernel_init_freeable+0x158/0x1f8
[ 3.180629] kernel_init+0x18/0x108
[ 3.184097] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x18
- lockdep已经很清晰地显示了死锁发生的路径和发生时的函数的栈信息。结合gdb可以快速定位和解决问题。
$ ./out/gcc-linaro-5.3.1-2016.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-linux-gnu-gdb ./out/kernel/build/vmlinux
GNU gdb (Linaro_GDB-2016.05) 7.11.1.20160702-git
Copyright (C) 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying"
and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "--host=x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu --target=aarch64-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from ./out/kernel/build/vmlinux...done.
(gdb) list *hack_spinAB+0x30
0xffffffc010402908 is in hack_spinAB (/home1/weidonghui/workspace/bsp/longan/kernel/linux-5.4/include/linux/spinlock.h:338).
333 raw_spin_lock_init(&(_lock)->rlock); \
334 } while (0)
335
336 static __always_inline void spin_lock(spinlock_t *lock)
337 {
338 raw_spin_lock(&lock->rlock);
339 }
340
341 static __always_inline void spin_lock_bh(spinlock_t *lock)
342 {
(gdb) list *hack_spinAB+0x38
0xffffffc010402910 is in hack_spinAB (/home1/weidonghui/workspace/bsp/longan/kernel/linux-5.4/drivers/regulator/lock_test_1.c:14).
9 void hack_spinAB(void)
10 {
11 printk("\nhack_lockdep:A-->B\n");
12 spin_lock(&hack_spinA);
13 spin_lock(&hack_spinB);
14 }
15
16
17 void hack_spinBA(void)
18 {
(gdb)
- 递归死锁问题例子(基于linux-4.9)
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/freezer.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
static DEFINE_MUTEX(mutex_a);
static struct delayed_work delay_task;
static void lockdep_timefunc(unsigned long);
static DEFINE_TIMER(lockdep_timer, lockdep_timefunc, 0, 0);
static void lockdep_timefunc(unsigned long dummy)
{
schedule_delayed_work(&delay_task, 10);
mod_timer(&lockdep_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(100));
}
static void lockdep_test_worker(struct work_struct *work)
{
mutex_lock(&mutex_a);
mdelay(300); //处理一些事情,这里用mdelay代替
mutex_unlock(&mutex_a);
}
static int lockdep_thread(void *nothing)
{
set_freezable();
set_user_nice(current, 0);
while (!kthread_should_stop()) {
mdelay(500); //处理一些事情,这里用mdelay代替
//遇到某些特殊情况,需要取消delay_task
mutex_lock(&mutex_a);
cancel_delayed_work_sync(&delay_task);
mutex_unlock(&mutex_a);
}
return 0;
}
static int __init lockdep_test_init(void)
{
struct task_struct *lock_thread;
printk("figo: my lockdep module init\n");
/*创建一个线程来处理某些事情*/
lock_thread = kthread_run(lockdep_thread, NULL, "lockdep_test");
/*创建一个delay worker*/
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&delay_task, lockdep_test_worker);
/*创建一个定时器来模拟某些异步事件,比如中断等*/
lockdep_timer.expires = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(500);
add_timer(&lockdep_timer);
return 0;
}
static void __exit lockdep_test_exit(void)
{
printk("goodbye\n");
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(lockdep_test_init);
module_exit(lockdep_test_exit);
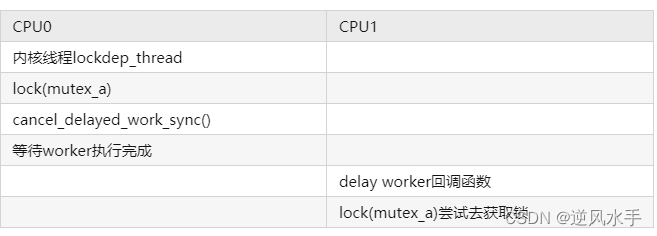
- 首先创建一个内核线程lockdep_thread,用于周期性地处理某些事情,创建一个kworker来处理一些类似中断下半部的延迟操作,最后使用一个定时器来模拟异步事件(例如中断)。在lockdep_thread内核线程中,某些特殊情况下常常需要取消kworker。代码中首先申请了一个mutex_a互斥体锁,然后调用cancel_delayed_work_sync()函数取消kworker。另一方面,定时器在定时地调用kworker,并在回调函数lockdep_test_worker()函数中申请mutex_a互斥体锁。log如下:
[ 3.229887] ======================================================
[ 3.229889] [ INFO: possible circular locking dependency detected ]
[ 3.229893] 4.9.191 #2 Not tainted
[ 3.229895] -------------------------------------------------------
[ 3.229898] kworker/0:1/32 is trying to acquire lock:
[ 3.229919] (mutex_a){
+.+...}, at: [<ffffff80083040f4>] lockdep_test_worker+0x30/0x60
[ 3.229921]
[ 3.229921] but task is already holding lock:
[ 3.229933] ((&(&delay_task)->work)){
+.+...}, at: [<ffffff80080b4858>] process_one_work+0x1a4/0x354
[ 3.229935]
[ 3.229935] which lock already depends on the new lock.
[ 3.229935]
[ 3.229937]
[ 3.229937] the existing dependency chain (in reverse order) is:
[ 3.229945]
[ 3.229945] -> #1 ((&(&delay_task)->work)){
+.+...}:
[ 3.229953] __lock_acquire+0x13a0/0x16f4
[ 3.229958] lock_acquire+0x8c/0xb4
[ 3.229962] flush_work+0x5c/0x224
[ 3.229967] __cancel_work_timer+0x128/0x1a0
[ 3.229973] cancel_delayed_work_sync+0x10/0x18
[ 3.229977] lockdep_thread+0x70/0x90
[ 3.229982] kthread+0xd4/0xdc
[ 3.229988] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x50
[ 3.229995]
[ 3.229995] -> #0 (mutex_a){
+.+...}:
[ 3.230000] print_circular_bug+0x60/0x2b8
[ 3.230004] __lock_acquire+0x1098/0x16f4
[ 3.230008] lock_acquire+0x8c/0xb4
[ 3.230016] mutex_lock_nested+0x5c/0x390
[ 3.230020] lockdep_test_worker+0x30/0x60
[ 3.230025] process_one_work+0x210/0x354
[ 3.230030] worker_thread+0x288/0x3a8
[ 3.230034] kthread+0xd4/0xdc
[ 3.230038] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x50
[ 3.230040]
[ 3.230040] other info that might help us debug this:
[ 3.230040]
[ 3.230043] Possible unsafe locking scenario:
[ 3.230043]
[ 3.230045] CPU0 CPU1
[ 3.230046] ---- ----
[ 3.230051] lock((&(&delay_task)->work));
[ 3.230056] lock(mutex_a);
[ 3.230060] lock((&(&delay_task)->work));
[ 3.230064] lock(mutex_a);
[ 3.230066]
[ 3.230066] *** DEADLOCK ***
[ 3.230066]
[ 3.230069] 2 locks held by kworker/0:1/32:
[ 3.230081] #0: ("events"){
.+.+..}, at: [<ffffff80080b4858>] process_one_work+0x1a4/0x354
[ 3.230093] #1: ((&(&delay_task)->work)){
+.+...}, at: [<ffffff80080b4858>] process_one_work+0x1a4/0x354
[ 3.230095]
[ 3.230095] stack backtrace:
[ 3.230100] CPU: 0 PID: 32 Comm: kworker/0:1 Not tainted 4.9.191 #2
[ 3.230103] Hardware name: sun50iw10 (DT)
[ 3.230112] Workqueue: events lockdep_test_worker
[ 3.230115] Call trace:
[ 3.230122] [<ffffff8008089004>] dump_backtrace+0x0/0x240
[ 3.230128] [<ffffff8008089258>] show_stack+0x14/0x1c
[ 3.230134] [<ffffff80082b257c>] dump_stack+0xb0/0xe8
[ 3.230139] [<ffffff80080e2ad0>] print_circular_bug+0x29c/0x2b8
[ 3.230144] [<ffffff80080e50dc>] __lock_acquire+0x1098/0x16f4
[ 3.230148] [<ffffff80080e5c00>] lock_acquire+0x8c/0xb4
[ 3.230154] [<ffffff80085539cc>] mutex_lock_nested+0x5c/0x390
[ 3.230159] [<ffffff80083040f4>] lockdep_test_worker+0x30/0x60
[ 3.230165] [<ffffff80080b48c4>] process_one_work+0x210/0x354
[ 3.230170] [<ffffff80080b5858>] worker_thread+0x288/0x3a8
[ 3.230175] [<ffffff80080bae78>] kthread+0xd4/0xdc
[ 3.230179] [<ffffff8008083180>] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x50
- lockdep信息首先提示可能出现递归死锁(INFO: possible circular locking dependency detected)
- 接下来提示“kworker/0:1/32”线程尝试去获取mutex_a互斥体锁,但是该锁已经被其他进程持有,持有该锁的进程是在&delay_task->work里。接下来的函数调用堆栈显示上述两个尝试去获取mutex_a锁的调用路径。(1)内核线程lockdep_thread首先成功获取了mutex_a互斥体锁,然后调用cancel_delayed_work_sync()函数取消kworker。注意cancel_delayed_work_sync()函数中会去调用flush操作和等待所有的kworker回调函数执行完成,然后才会调用mutex_unlock(&mutex_a)释放该锁。
[ 3.229945] -> #1 ((&(&delay_task)->work)){
+.+...}:
[ 3.229953] __lock_acquire+0x13a0/0x16f4
[ 3.229958] lock_acquire+0x8c/0xb4
[ 3.229962] flush_work+0x5c/0x224
[ 3.229967] __cancel_work_timer+0x128/0x1a0
[ 3.229973] cancel_delayed_work_sync+0x10/0x18
[ 3.229977] lockdep_thread+0x70/0x90
[ 3.229982] kthread+0xd4/0xdc
[ 3.229988] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x50
(2)kworker回调函数lockdep_test_worker()首先会尝试获取mutex_a互斥体锁,注意刚才内核线程lockdep_thread已经获取了mutex_a互斥体锁,并且一直在等待当前kworker回调函数执行完成,所以死锁发生了。
[ 3.229995] -> #0 (mutex_a){
+.+...}:
[ 3.230000] print_circular_bug+0x60/0x2b8
[ 3.230004] __lock_acquire+0x1098/0x16f4
[ 3.230008] lock_acquire+0x8c/0xb4
[ 3.230016] mutex_lock_nested+0x5c/0x390
[ 3.230020] lockdep_test_worker+0x30/0x60
[ 3.230025] process_one_work+0x210/0x354
[ 3.230030] worker_thread+0x288/0x3a8
[ 3.230034] kthread+0xd4/0xdc
[ 3.230038] ret_from_fork+0x10/0x50
下面画出该死锁场景的CPU调用关系图,一目了然