实验要求
掌握词典编码的基本原理,用C/C++/Python等语言编程实现LZW解码器并分析编解码算法。
实验内容
LZW编码
编码原理
一、基本定义
LZW的编码思想是不断地从字符流中提取新的字符串,通俗地理解为新“词条”,然后用“代号”也就是码字表示这个“词条”。这样一来,对字符流的编码就变成了用码字去替换字符流,生成码字流,从而达到压缩数据的目的。LZW编码是围绕称为词典的转换表来完成的。LZW编码器通过管理这个词典完成输入与输出之间的转换。LZW编码器的输入是字符流,字符流可以是用8位ASCII字符组成的字符串,而输出是用n位(例如12位)表示的码字流。
二、算法步骤
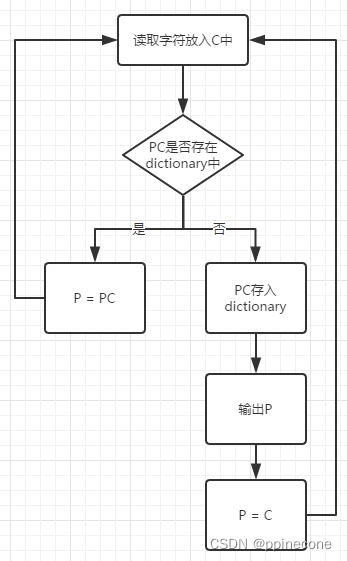
1:将词典初始化为包含所有可能的单字符,当前前缀P初始化为空
2:当前字符C=字符流中的下一个字符
3:判断P+C是否在词典中
如果“是”,则用C扩展P,即让P=P+C,返回第2步
如果“否”,则输出与当前前缀P相对应的码字W,将P+C添加到词典中,令P=C,返回第2步
解码原理
一、基本定义
LZW解码算法开始时,译码词典和编码词典相同,包含所有可能的前缀根。
二、算法步骤
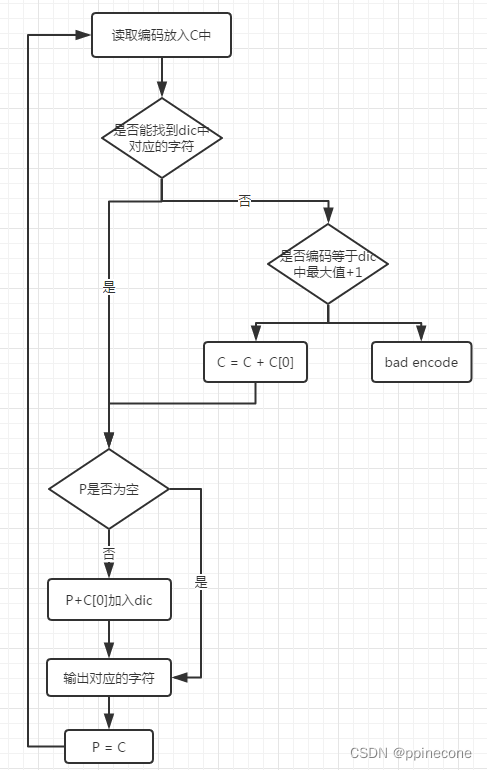
1:在开始译码时词典包含所有可能的前缀根
2:令CW:=码字流中的第一个码字。
3:输出当前缀-字符串string.CW到码字流。
4:先前码字PW:=当前码字CW。
5:当前码字CW:=码字流的下一个码字。
6:判断当前缀-字符串string.CW 是否在词典中。
如果”是”,则把当前缀-字符串string.CW输出到字符流。当前前缀P:=先前缀-字符串string.PW,当前字符C:=当前前缀-字符串string.CW的第一个字符。把缀-符串P+C添加到词典。
如果”否”,则当前前缀P:=先前缀-字符串string.PW。 当前字符C:=当前缀-字符串string.CW的第一个字符。 输出缀-符串P+C到字符流,然后把它添加到词典中。
7:判断码字流中是否还有码字要译。
如果”是”,就返回第4步。
如果”否”,结束。
实验代码
定义词典树
#define MAX_CODE 65535
struct {
int suffix;
int parent, firstchild, nextsibling;
} dictionary[MAX_CODE+1];
int next_code;
int d_stack[MAX_CODE];
初始化词典树
void InitDictionary( void){
int i;
for( i=0; i<256; i++){
dictionary[i].suffix = i;
dictionary[i].parent = -1;
dictionary[i].firstchild = -1;
dictionary[i].nextsibling = i+1;
}
dictionary[255].nextsibling = -1;
next_code = 256;
}
判断当前字符是否在词典中
int InDictionary( int character, int string_code){
int sibling;
if( 0>string_code) return character;
sibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
while( -1<sibling){
if( character == dictionary[sibling].suffix) return sibling;
sibling = dictionary[sibling].nextsibling;
}
return -1;
}
添加新字符
void AddToDictionary( int character, int string_code){
int firstsibling, nextsibling;
if( 0>string_code) return;
dictionary[next_code].suffix = character;
dictionary[next_code].parent = string_code;
dictionary[next_code].nextsibling = -1;
dictionary[next_code].firstchild = -1;
firstsibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
if( -1<firstsibling){
nextsibling = firstsibling;
while( -1<dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling )
nextsibling = dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling;
dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling = next_code;
}else{
dictionary[string_code].firstchild = next_code;
}
next_code ++;
}
编码
void LZWEncode( FILE *fp, BITFILE *bf){
int character;
int string_code;
int index;
unsigned long file_length;
fseek( fp, 0, SEEK_END);
file_length = ftell( fp);
fseek( fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
BitsOutput( bf, file_length, 4*8);
InitDictionary();
string_code = -1;
while( EOF!=(character=fgetc( fp))){
index = InDictionary( character, string_code);
if( 0<=index){
string_code = index;
}else{
output( bf, string_code);
if( MAX_CODE > next_code){
AddToDictionary( character, string_code);
string_code = character;
}
}
output( bf, string_code);
}
解码
void LZWDecode( BITFILE *bf, FILE *fp){
int character;
int new_code, last_code;
int phrase_length;
unsigned long file_length;
file_length = BitsInput(bf, 4 * 8);
if (-1 == file_length) file_length = 0;
InitDictionary();
last_code = -1;
while (0 < file_length) {
new_code = input(bf);
if (new_code >= next_code) {
d_stack[0] = character;
phrase_length = DecodeString(1, last_code);
}
else {
phrase_length = DecodeString(0, new_code);
}
character = d_stack[phrase_length - 1];
while (0 < phrase_length) {
phrase_length--;
fputc(d_stack[phrase_length], fp);
file_length--;
}
if (MAX_CODE > next_code) {
AddToDictionary(character, last_code);
}
last_code = new_code;
}
}
实验结果
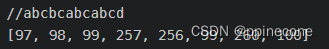
解码](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/602fa10a7b6849fc8d99992a159a7a70.png)

2.对不同文件编码
| 文件格式 | 编码前(KB) | 编码后(KB) | 压缩比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| jpg | 923 | 1034 | 1.12 |
| png | 267 | 378 | 1.42 |
| bmp | 4700 | 5674 | 1.21 |
| txt | 0.67 | 0.83 | 1.24 |
| docx | 2586 | 3005 | 1.16 |
| 80 | 104 | 1.30 | |
| mp3 | 8094 | 1231 | 0.15 |
| wav | 3785 | 3084 | 0.81 |
| mp4 | 983 | 1129 | 1.15 |
| avi | 5564 | 6123 | 1.10 |
LZW编码在不同文件格式的压缩上有不同的效果:
文件冗余度更高,重复内容更多,压缩比就更小;
压缩文件格式冗余度比低,采用词典编码相比无压缩的格式压缩比应该高
LZW编码的特点为:
1.LZW只需要一遍扫描,具有自适应的特点;
2.算法简单,便于快速实现(利用数字查找树/建树);
3.字符串重复概率低时,影响压缩效率;
4.词典中的字符串不再出现的时候,会影响压缩效率。