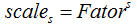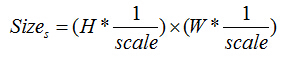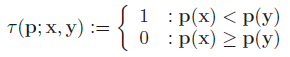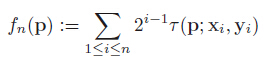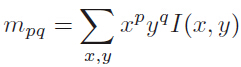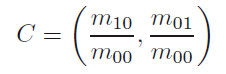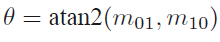主要转载自http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/48523267,本博也会陆续有部分修改
转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/48523267
CSDN-勿在浮沙筑高台
为了满足实时性的要求,前面文章中介绍过快速提取特征点算法Fast,以及特征描述子Brief。本篇文章介绍的ORB算法结合了Fast和Brief的速度优势,并做了改进,且ORB是免费。
Ethan Rublee等人2011年在《ORB:An Efficient Alternative to SIFT or SURF》文章中提出了ORB算法。结合Fast与Brief算法,并给Fast特征点增加了方向性,使得特征点具有旋转不变性,并提出了构造金字塔方法,解决尺度不变性,但文章中没有具体详述。实验证明,ORB远优于之前的SIFT与SURF算法。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
论文核心内容概述:
1.构造金字塔,在每层金字塔上采用Fast算法提取特征点,采用Harris角点响应函数,按角点响应值排序,选取前N个特征点。
2. oFast:计算每个特征点的主方向,灰度质心法,计算特征点半径为r的圆形邻域范围内的灰度质心位置。
从中心位置到质心位置的向量,定义为该特 征点的主方向。
定义矩的计算公式,x,y∈[-r,r]:
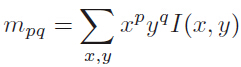
质心位置:
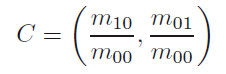
主方向:
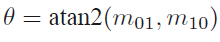
3. rBrief:为了解决旋转不变性,把特征点的Patch旋转到主方向上(steered Brief)。通过实验得到,描述子在各个维度上的均值比较离散(偏离0.5),同时维度间相关性很强,说明特征点描述子区分性不好,影响匹配的效果。论文中提出采取学习的方法,采用300K个训练样本点。每一个特征点,选取Patch大小为wp=31,Patch内每对点都采用wt=5大小的子窗口灰度均值做比较,子窗口的个数即为N=(wp-wt)*(wp-wt),从N个窗口中随机选两个做比较即构成描述子的一个bit,论文中采用M=205590种可能的情况:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.对所有样本点,做M种测试,构成M维的描述子,每个维度上非1即0;
2.按均值对M个维度排序(以0.5为中心),组成向量T;
3.贪婪搜索:把向量T中第一个元素移动到R中,然后继续取T的第二个元素,与R中的所有元素做相关性比较,如果相关性大于指定的阈值Threshold, 抛弃T的这个元素,否则加入到R中;
4.重复第3个步骤,直到R中有256个元素,若检测完毕,少于256个元素,则降低阈值,重复上述步骤;
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
rBrief:通过上面的步骤取到的256对点,构成的描述子各维度间相关性很低,区分性好;
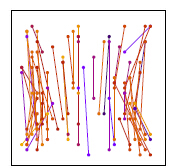
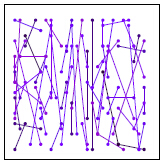
训练前 训练后
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ORB算法步骤,参考opencv源码:
1.首先构造尺度金字塔;
金字塔共n层,与SIFT不同,每层仅有一副图像;
第s层的尺度为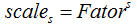 ,Fator初始尺度(默认为1.2),原图在第0层;
,Fator初始尺度(默认为1.2),原图在第0层;
第s层图像大小:
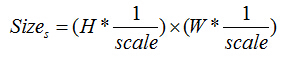 ;
;
2.在不同尺度上采用Fast检测特征点;在每一层上按公式计算需要提取的特征点数n,在本层上按Fast角点响应值排序,提取前2n个特征点,然后根据Harris 角点响应值排序, 取前n个特征点,作为本层的特征点;
3.计算每个特征点的主方向(质心法);
4.旋转每个特征点的Patch到主方向,采用上述步骤3的选取的最优的256对特征点做τ测试,构成256维描述子,占32个字节;
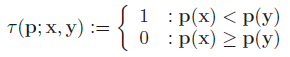 ,
,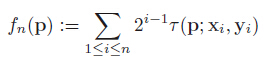 ,n=256
,n=256
5.采用汉明距离做特征点匹配;
----------OpenCV源码解析-------------------------------------------------------
ORB类定义:位置 opencv \ include \ opencv2 \ features2d.hpp
nfeatures:需要的特征点总数;
scaleFactor:尺度因子;
nlevels:金字塔层数;
edgeThreshold:边界阈值;
firstLevel:起始层;
WTA_K:描述子形成方法,WTA_K=2表示,采用两两比较;line11
scoreType:角点响应函数,可以选择Harris或者Fast的方法;
patchSize:特征点邻域大小;
-
-
-
- class CV_EXPORTS_W ORB : public Feature2D
- {
- public:
-
- enum { kBytes = 32, HARRIS_SCORE=0, FAST_SCORE=1 };
-
- CV_WRAP explicit ORB(int nfeatures = 500, float scaleFactor = 1.2f, int nlevels = 8, int edgeThreshold = 31,
- int firstLevel = 0, int WTA_K=2, int scoreType=ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, int patchSize=31 );
-
-
- int descriptorSize() const;
-
- int descriptorType() const;
-
-
- void operator()(InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints) const;
-
-
- void operator()( InputArray image, InputArray mask, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,
- OutputArray descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false ) const;
-
- AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
-
- protected:
-
- void computeImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors ) const;
- void detectImpl( const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, const Mat& mask=Mat() ) const;
-
- CV_PROP_RW int nfeatures;
- CV_PROP_RW double scaleFactor;
- CV_PROP_RW int nlevels;
- CV_PROP_RW int edgeThreshold;
- CV_PROP_RW int firstLevel;
- CV_PROP_RW int WTA_K;
- CV_PROP_RW int scoreType;
- CV_PROP_RW int patchSize;
- };
特征提取及形成描述子:通过这个函数对图像提取Fast特征点或者计算特征描述子
_image:输入图像;
_mask:掩码图像;
_keypoints:输入角点;
_descriptors:如果为空,只寻找特征点,不计算特征描述子;
_useProvidedKeypoints:如果为true,函数只计算特征描述子;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- void ORB::operator()( InputArray _image, InputArray _mask, vector<KeyPoint>& _keypoints,
- OutputArray _descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints) const //输入 图像image 掩码mask 关键点矢量 输出描述符数组 判定是否有已经提供关键点
- {
- CV_Assert(patchSize >= 2);
-
- bool do_keypoints = !useProvidedKeypoints;
- bool do_descriptors = _descriptors.needed();
-
- if( (!do_keypoints && !do_descriptors) || _image.empty() )
- return;
-
-
- const int HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE = 9;
- int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2;.
- int border = std::max(edgeThreshold, std::max(halfPatchSize, HARRIS_BLOCK_SIZE/2))+1;
-
- Mat image = _image.getMat(), mask = _mask.getMat(); // 将输入的 _image和 _mask转化成Mat 形式的image 与 mask
- if( image.type() != CV_8UC1 )
- cvtColor(_image, image, CV_BGR2GRAY);
-
- int levelsNum = this->nlevels;
-
- if( !do_keypoints )
- {
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- levelsNum = 0;
- for( size_t i = 0; i < _keypoints.size(); i++ )
- levelsNum = std::max(levelsNum, std::max(_keypoints[i].octave, 0));
- levelsNum++;
- }
-
-
- vector<Mat> imagePyramid(levelsNum), maskPyramid(levelsNum);
- for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
- {
- float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Size sz(cvRound(image.cols*scale), cvRound(image.rows*scale));
- Size wholeSize(sz.width + border*2, sz.height + border*2); // border 是之前定义的最大边界
- Mat temp(wholeSize, image.type()), masktemp;
- imagePyramid[level] = temp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height)); // Rect 函数,创建一个矩形窗口:矩形左上角横纵坐标,宽度和高度
- if( !mask.empty() )
- {
- masktemp = Mat(wholeSize, mask.type());
- maskPyramid[level] = masktemp(Rect(border, border, sz.width, sz.height));
- }
-
-
- if( level != firstLevel )
- {
- if( level < firstLevel ) //如果小于起始层 ??为什么会小于起始层
- {
- resize(image, imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR); // resize ( 原图,新图,Size dsize, double fx=0.double fy=0, int interpolation=INTER_LINER)
- if (!mask.empty()) // 图像掩码
- resize(mask, maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR);
- }
- else //如果大于起始层
- {
- resize(imagePyramid[level-1], imagePyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR); // resize ( 上一层图像,这一层图像,Size dsize, 0,0,INTER_LINER)
- if (!mask.empty()) // 图像掩码
- {
- resize(maskPyramid[level-1], maskPyramid[level], sz, 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR); // 获得该层mask
- threshold(maskPyramid[level], maskPyramid[level], 254, 0, THRESH_TOZERO); // threshold(input, output, 阈值, double maxval, type);
- // 第四个maxval 是当五的type取binary或binary_inv的最大值,第五个代表当前type为THRESH_TOZERO,当前值大于阈值不改变,否则为0
- }
- }
-
- // 所有非起始层 掩码后 扩大图像边界
- // copyMakeBorder(src输入, dst输出,int top, int bottom,int left, int right,原图四周扩充边缘的大小, int border Type)
- copyMakeBorder(imagePyramid[level], temp, border, border, border, border,
- BORDER_REFLECT_101+BORDER_ISOLATED); //扩大图像的边界
-
- if (!mask.empty()) // 扩大掩码边界
- copyMakeBorder(maskPyramid[level], masktemp, border, border, border, border,
- BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
- }
- else
- {
- copyMakeBorder(image, temp, border, border, border, border,
- BORDER_REFLECT_101);
- if( !mask.empty() ) //扩大掩码的的四个边界
- copyMakeBorder(mask, masktemp, border, border, border, border,
- BORDER_CONSTANT+BORDER_ISOLATED);
- }
- }
-
-
-
- vector < vector<KeyPoint> > allKeypoints;
- if( do_keypoints )
- {
-
- computeKeyPoints(imagePyramid, maskPyramid, allKeypoints,
- nfeatures, firstLevel, scaleFactor,
- edgeThreshold, patchSize, scoreType);
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- }
- else
- {
-
- KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(_keypoints, image.size(), edgeThreshold);
-
-
- allKeypoints.resize(levelsNum);
- for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = _keypoints.begin(),
- keypointEnd = _keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
- allKeypoints[keypoint->octave].push_back(*keypoint);
-
-
- for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
- {
- if (level == firstLevel)
- continue;
-
- vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
- float scale = 1/getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
- for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
- keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
- keypoint->pt *= scale;
- }
- }
-
- Mat descriptors;
- vector<Point> pattern;
-
- //修改处
-
- if( do_descriptors )
- {
- int nkeypoints = 0;
- for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
- nkeypoints += (int)allKeypoints[level].size();
- if( nkeypoints == 0 )
- _descriptors.release();
- else
- {
- _descriptors.create(nkeypoints, descriptorSize(), CV_8U);
- descriptors = _descriptors.getMat();
- }
-
- const int npoints = 512;
- Point patternbuf[npoints];
- const Point* pattern0 = (const Point*)bit_pattern_31_;
-
- if( patchSize != 31 )
- {
- pattern0 = patternbuf;
- makeRandomPattern(patchSize, patternbuf, npoints);
- }
-
- CV_Assert( WTA_K == 2 || WTA_K == 3 || WTA_K == 4 );
-
- if( WTA_K == 2 )
- std::copy(pattern0, pattern0 + npoints, std::back_inserter(pattern));
- else
- {
- int ntuples = descriptorSize()*4;
- initializeOrbPattern(pattern0, pattern, ntuples, WTA_K, npoints);
- }
- }
-
- _keypoints.clear();
- int offset = 0;
- for (int level = 0; level < levelsNum; ++level)
- {
-
- vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
- int nkeypoints = (int)keypoints.size();
-
-
- if (do_descriptors)
- {
- Mat desc;
- if (!descriptors.empty())
- {
- desc = descriptors.rowRange(offset, offset + nkeypoints);
- }
-
- offset += nkeypoints;
-
- Mat& workingMat = imagePyramid[level];
-
- GaussianBlur(workingMat, workingMat, Size(7, 7), 2, 2, BORDER_REFLECT_101);
- computeDescriptors(workingMat, keypoints, desc, pattern, descriptorSize(), WTA_K);
- }
-
-
- if (level != firstLevel)
- {
- float scale = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
- for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
- keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
- keypoint->pt *= scale;
- }
-
- _keypoints.insert(_keypoints.end(), keypoints.begin(), keypoints.end());
- }
- }
(1)提取角点:computeKeyPoints
imagePyramid:即构造好的金字塔
-
-
-
-
-
- static void computeKeyPoints(const vector<Mat>& imagePyramid,
- const vector<Mat>& maskPyramid,
- vector<vector<KeyPoint> >& allKeypoints,
- int nfeatures, int firstLevel, double scaleFactor,
- int edgeThreshold, int patchSize, int scoreType )
- {
- int nlevels = (int)imagePyramid.size();
- vector<int> nfeaturesPerLevel(nlevels);
-
-
- float factor = (float)(1.0 / scaleFactor);
- float ndesiredFeaturesPerScale = nfeatures*(1 - factor)/(1 - (float)pow((double)factor, (double)nlevels));
-
- int sumFeatures = 0;
- for( int level = 0; level < nlevels-1; level++ )
- {
- nfeaturesPerLevel[level] = cvRound(ndesiredFeaturesPerScale);
- sumFeatures += nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
- ndesiredFeaturesPerScale *= factor;
- }
- nfeaturesPerLevel[nlevels-1] = std::max(nfeatures - sumFeatures, 0);
-
-
-
-
-
- int halfPatchSize = patchSize / 2;
- vector<int> umax(halfPatchSize + 2);
- int v, v0, vmax = cvFloor(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2 + 1);
- int vmin = cvCeil(halfPatchSize * sqrt(2.f) / 2);
- for (v = 0; v <= vmax; ++v)
- umax[v] = cvRound(sqrt((double)halfPatchSize * halfPatchSize - v * v));
-
- for (v = halfPatchSize, v0 = 0; v >= vmin; --v)
- {
- while (umax[v0] == umax[v0 + 1])
- ++v0;
- umax[v] = v0;
- ++v0;
- }
-
- allKeypoints.resize(nlevels);
-
- for (int level = 0; level < nlevels; ++level)
- {
- int featuresNum = nfeaturesPerLevel[level];
- allKeypoints[level].reserve(featuresNum*2);
-
- vector<KeyPoint> & keypoints = allKeypoints[level];
-
-
- FastFeatureDetector fd(20, true);
- fd.detect(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, maskPyramid[level]);
-
-
- KeyPointsFilter::runByImageBorder(keypoints, imagePyramid[level].size(), edgeThreshold);
-
- if( scoreType == ORB::HARRIS_SCORE )
- {
-
- KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, 2 * featuresNum);
-
-
- HarrisResponses(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, 7, HARRIS_K);
- }
-
-
- KeyPointsFilter::retainBest(keypoints, featuresNum);
-
- float sf = getScale(level, firstLevel, scaleFactor);
-
-
- for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
- keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
- {
- keypoint->octave = level;
- keypoint->size = patchSize*sf;
- }
-
- computeOrientation(imagePyramid[level], keypoints, halfPatchSize, umax);
- }
- }
(2)为每个角点计算主方向,质心法;
- static void computeOrientation(const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints,
- int halfPatchSize, const vector<int>& umax)
- {
-
- for (vector<KeyPoint>::iterator keypoint = keypoints.begin(),
- keypointEnd = keypoints.end(); keypoint != keypointEnd; ++keypoint)
- {
- keypoint->angle = IC_Angle(image, halfPatchSize, keypoint->pt, umax);
- }
- }
- static float IC_Angle(const Mat& image, const int half_k, Point2f pt,
- const vector<int> & u_max)
- {
- int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
-
- const uchar* center = &image.at<uchar> (cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
-
-
- for (int u = -half_k; u <= half_k; ++u)
- m_10 += u * center[u];
-
-
- int step = (int)image.step1();
- for (int v = 1; v <= half_k; ++v)
- {
-
- int v_sum = 0;
- int d = u_max[v];
- for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
- {
- int val_plus = center[u + v*step], val_minus = center[u - v*step];
- v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus);
- m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
- }
- m_01 += v * v_sum;
- }
-
- return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);
- }
(3)计算特征点描述子
- static void computeDescriptors(const Mat& image, vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, Mat& descriptors,
- const vector<Point>& pattern, int dsize, int WTA_K)
- {
-
- CV_Assert(image.type() == CV_8UC1);
-
- descriptors = Mat::zeros((int)keypoints.size(), dsize, CV_8UC1);
-
- for (size_t i = 0; i < keypoints.size(); i++)
- computeOrbDescriptor(keypoints[i], image, &pattern[0], descriptors.ptr((int)i), dsize, WTA_K);
- }
- static void computeOrbDescriptor(const KeyPoint& kpt,
- const Mat& img, const Point* pattern,
- uchar* desc, int dsize, int WTA_K)
- {
- float angle = kpt.angle;
-
- angle *= (float)(CV_PI/180.f);
- float a = (float)cos(angle), b = (float)sin(angle);
-
- const uchar* center = &img.at<uchar>(cvRound(kpt.pt.y), cvRound(kpt.pt.x));
- int step = (int)img.step;
-
- #if 1
- #define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点的值
- center[cvRound(pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a)*step + \
- cvRound(pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b)]
- #else
- float x, y;
- int ix, iy;
- #define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点,插值法
- (x = pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b, \
- y = pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a, \
- ix = cvFloor(x), iy = cvFloor(y), \
- x -= ix, y -= iy, \
- cvRound(center[iy*step + ix]*(1-x)*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix]*(1-x)*y + \
- center[iy*step + ix+1]*x*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix+1]*x*y))
- #endif
-
- if( WTA_K == 2 )
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
- {
- int t0, t1, val;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
- val = t0 < t1;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(2); t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 1;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 2;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 3;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 4;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(10); t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 5;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 6;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(14); t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
- val |= (t0 < t1) << 7;
-
- desc[i] = (uchar)val;
- }
- }
- else if( WTA_K == 3 )
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 12)
- {
- int t0, t1, t2, val;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1); t2 = GET_VALUE(2);
- val = t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0);
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(3); t1 = GET_VALUE(4); t2 = GET_VALUE(5);
- val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 2;
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7); t2 = GET_VALUE(8);
- val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 4;
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(9); t1 = GET_VALUE(10); t2 = GET_VALUE(11);
- val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 6;
-
- desc[i] = (uchar)val;
- }
- }
- else if( WTA_K == 4 )
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
- {
- int t0, t1, t2, t3, u, v, k, val;
- t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
- t2 = GET_VALUE(2); t3 = GET_VALUE(3);
- u = 0, v = 2;
- if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
- if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
- k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
- val = k;
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
- t2 = GET_VALUE(6); t3 = GET_VALUE(7);
- u = 0, v = 2;
- if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
- if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
- k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
- val |= k << 2;
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
- t2 = GET_VALUE(10); t3 = GET_VALUE(11);
- u = 0, v = 2;
- if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
- if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
- k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
- val |= k << 4;
-
- t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
- t2 = GET_VALUE(14); t3 = GET_VALUE(15);
- u = 0, v = 2;
- if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
- if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
- k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
- val |= k << 6;
-
- desc[i] = (uchar)val;
- }
- }
- else
- CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "Wrong WTA_K. It can be only 2, 3 or 4." );
-
- #undef GET_VALUE
- }
关于octave
Number of OCTAVE. Increasing the scale by an OCTAVE means doubling the size of the smoothing kernel, whose effect is roughly equivalent to halving the image resolution. By default, the scale space spans as many OCTAVE as possible (i.e. roughly <code> log2(min(width,height)</code>), which has the effect of searching keypoints of all possible sizes.- <b>First OCTAVE index</b>. By convention, the OCTAVE of index 0 starts with the image full resolution. Specifying an index greater than 0 starts the scale space at a lower resolution (e.g. 1 halves the resolution). Similarly, specifying a negative index starts the scale space at an higher resolution image, and can be useful to extract very small features (since this is obtained by interpolating the input image, it does not make much sense to go past -1).
- <b>Number of levels per OCTAVE</b>. Each OCTAVE is sampled at this given number of intermediate scales (by default 3). Increasing this number might in principle return more refined keypoints, but in practice can make their selection unstable due to noise (see [1]).Keypoints are further refined by eliminating those that are likely tobe unstable, either because they are selected nearby an image edge, rather than an image blob, or are found on image structures with low contrast.
参考自 https://github.com/vlfeat/vlfeat/blob/38a03e12daf50ee98633de06120834d0d1d87e23/vl/sift.c#L1948
关于 threshold使用:
http://www.itnose.net/detail/6060285.html
参考:
Ethan Rublee et. ORB:An Efficient Alternative to SIFT or SURF
http://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/4083537.html