1.简述
基于图像识别技术实现自动印刷电路板(PCB)缺陷检测,具有高效、准确、可靠、自动化程度高和可扩展性强等优点,大大提高了检测效率,节省了人力成本。传统的检测方法通常需要大量的人力和时间,并且容易受到环境、工人技能和疲劳等因素的影响,而基于图像识别的缺陷检测方法可以实现自动化的缺陷检测,无需人工干预,提高了生产效率。
此外,图像识别技术可以通过不断的学习和训练,不断完善自身的识别能力,适应更多的缺陷类型,具有很强的可扩展性。
2.数据集介绍
使用北京大学公开的PCB数据集,包含1386张图像,具有6种缺陷类型分别为:漏孔、鼠咬、开路、短路、杂散、杂铜。 下载地址:北京大学智能机器人开放实验室
3.数据集构建
先把数据集划分为train, val ,处理代码 split_train_val.py如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.8
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()
然后再把VOC的标签格式转换为yolov5的格式,代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val']
classes = ["missing_hole","mouse_bite","open_circuit","short","spur","spurious_copper"] # 改成自己的类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def conver_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
#difficult = obj.find('Difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('labels/'):
os.makedirs('labels/')
image_ids = open('ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
conver_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
4.模型训练
(1)创建数据集配置文件
在 yolov5/data/ 目录下创建自己的数据集配置文件 pcb.yaml,内容如下,nc表示类别为6个分类
# PCB data
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
train: ./data/PCB_DATASET/train.txt
val: ./data/PCB_DATASET/val.txt
nc: 6 # number of classes
names: ['missing_hole', 'mouse_bite', 'open_circuit', 'short', 'spur', 'spurious_copper']
(2)创建模型文件
在 yolov5/models/ 目录下,拷贝一个版本模型作为自己的模型,这里我使用yolov5s,然后把文件中的类别数改为6即可:
cp yolov5s.yaml yolov5s_pcb.yaml# Parameters
nc: 6 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32(3)模型训练
执行以下命令进行训练:
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 100 --data ./data/pcb.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt经过100 epochs的训练,效果如下:

[email protected] 达到了0.953,效果还是不错的。
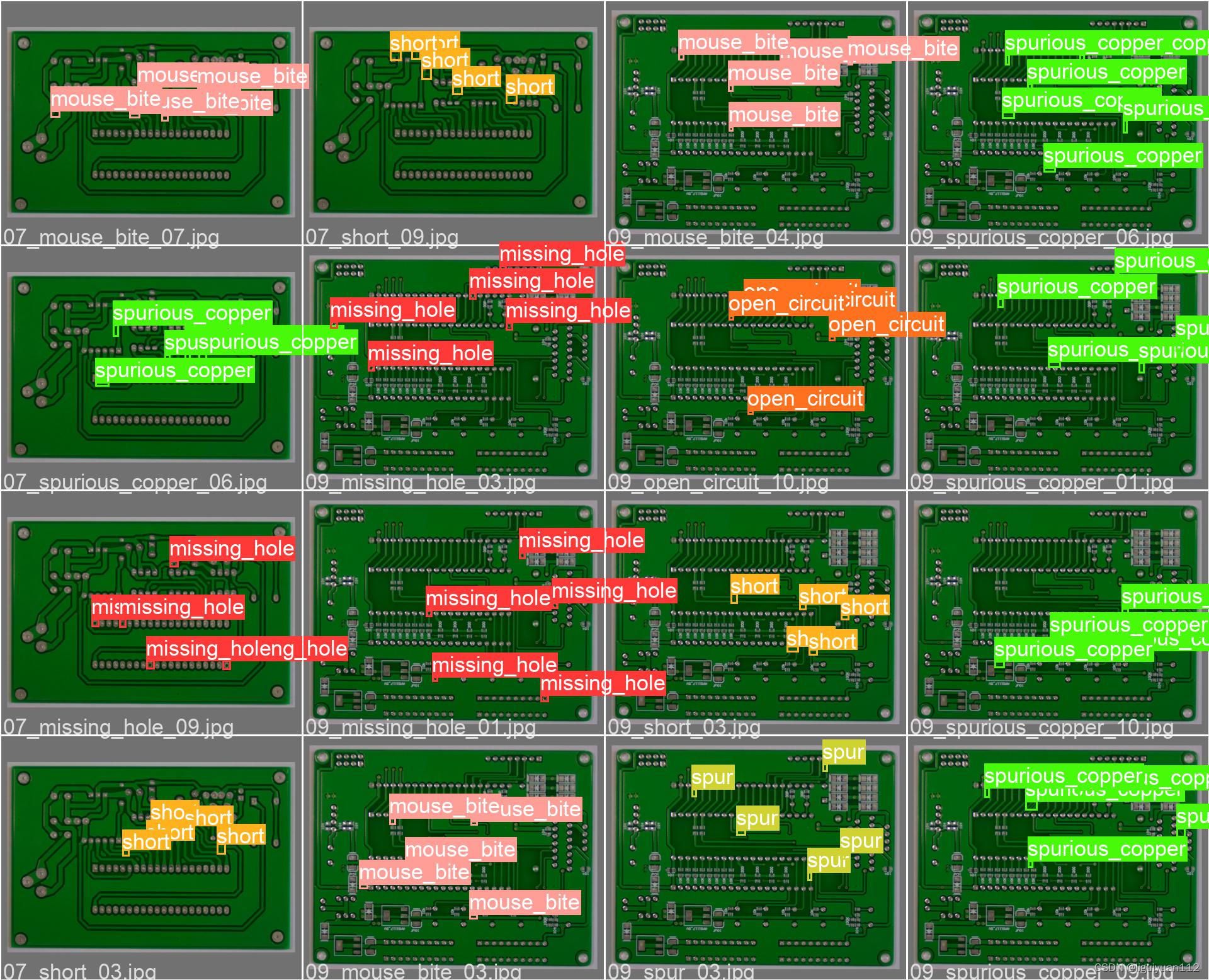
(4)实测验证效果



参考: