各位CSDN的uu们你们好呀,今天,小雅兰的内容是用栈实现队列,这和小雅兰的上一篇博客“用队列实现栈”好像有点点关系噢,事实上,也确实是这样的,下面,让我们进入Leetcode的世界吧!!!
Leetcode每日一题——“用队列实现栈”_认真学习的小雅兰.的博客-CSDN博客
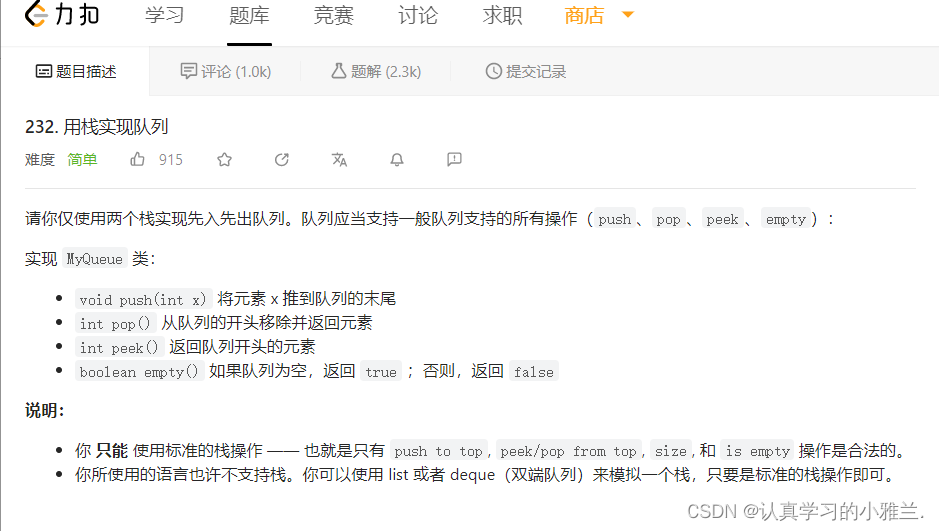


感兴趣的可以看看小雅兰写的栈和队列的内容:
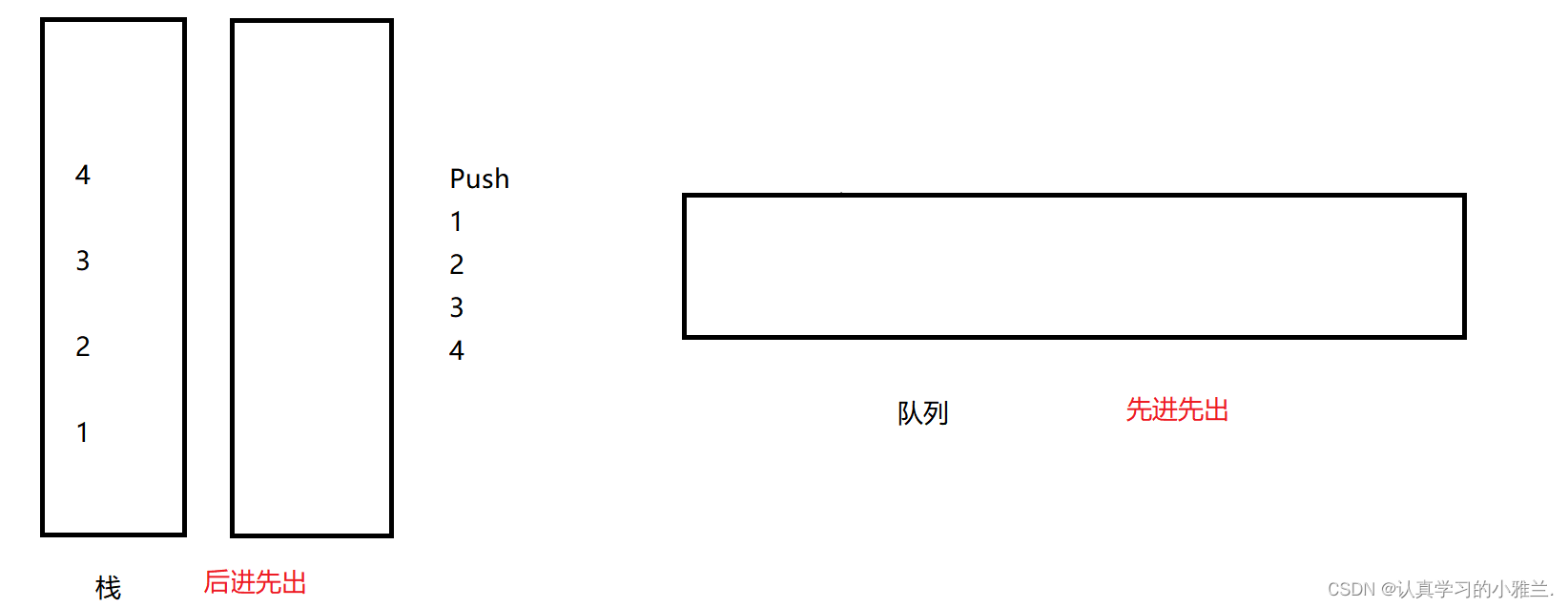
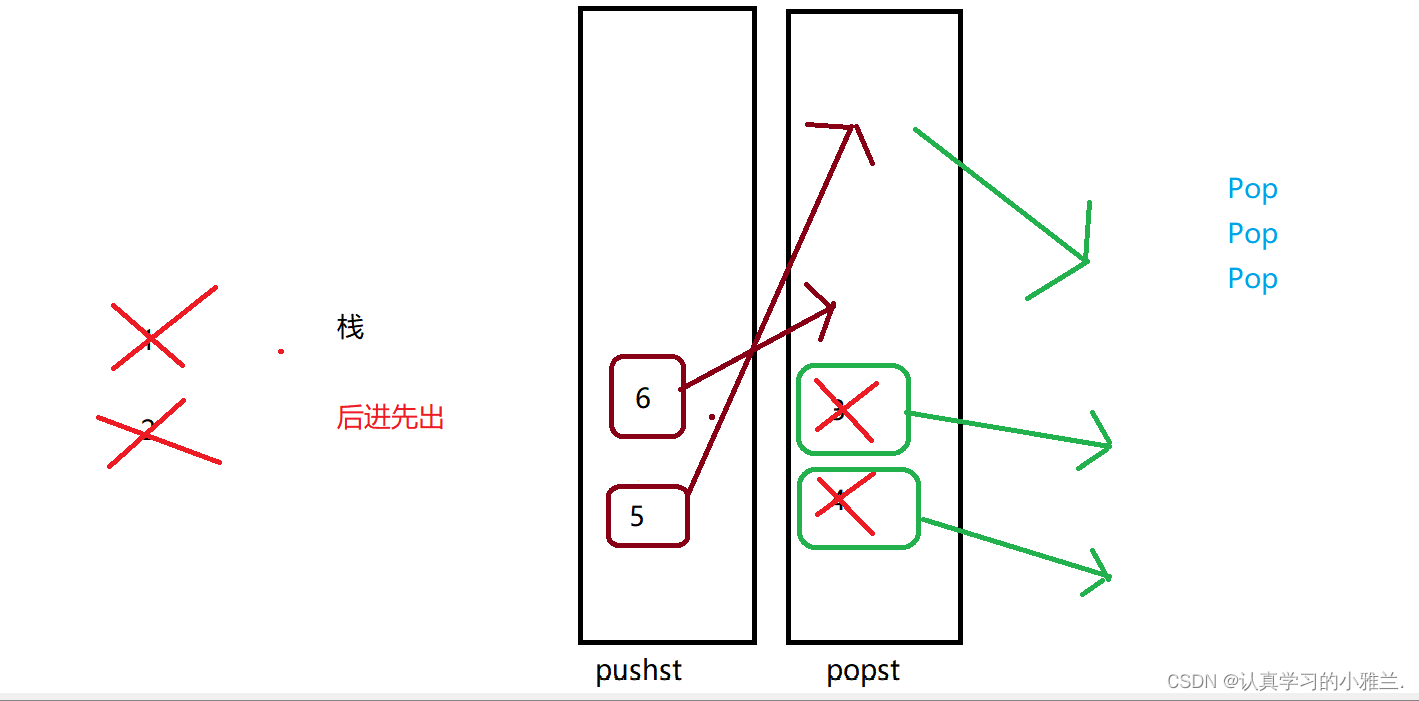
然后导数据,也就是Pop一下:

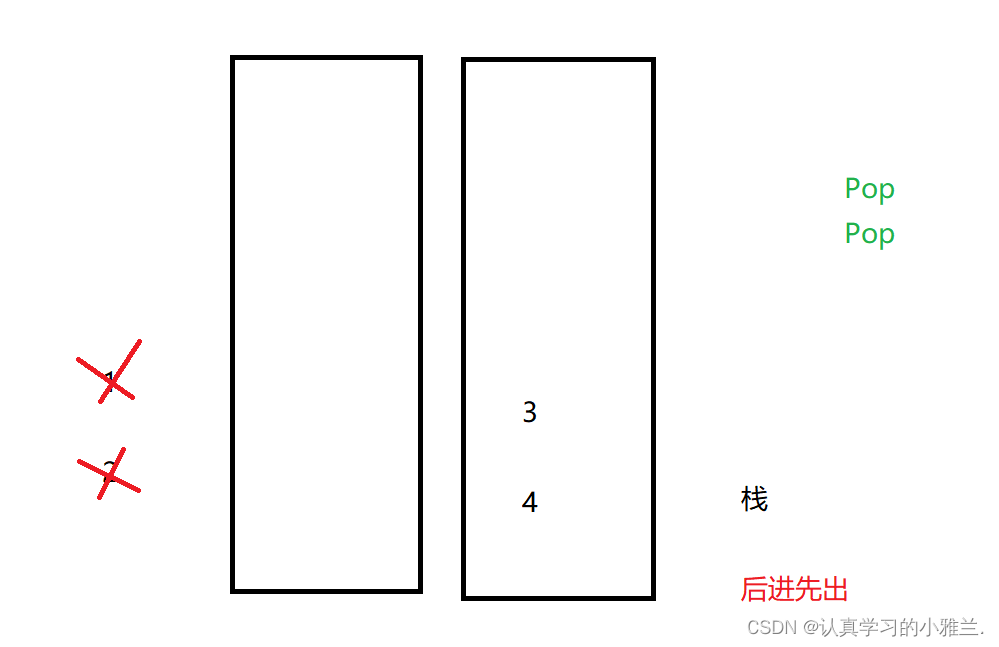
如果还要继续Pop的话,就不需要和之前那个题目“用队列实现栈”那样,再导数据啦
这次Pop就可以直接在第二个队列里面Pop
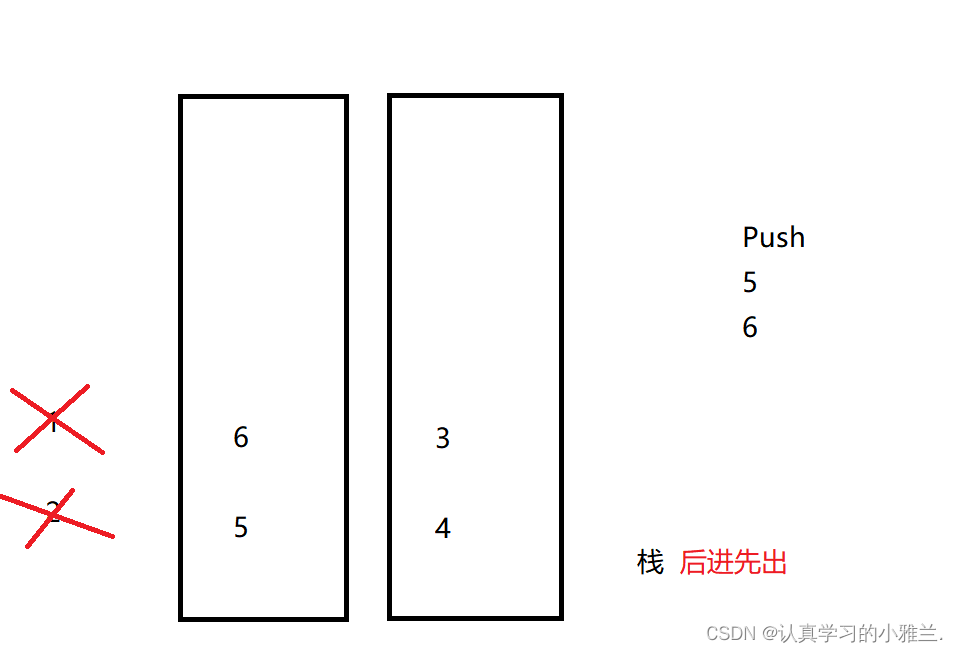
如果要Push5 6的话,那又该怎么办呢?
我们不妨这样:直接写“死”,把一个队列设为专门出数据的,另一个队列设为专门入数据的
如果是要Push5 6,那么,就这样:
如果还要再Pop三次呢?
只要知道这样一个原则:只要popst(第二个队列)不为空,就可以一直出数据,如果popst为空了,就导数据,导了之后再出!!!
那么,这个题目的思路就是这样子了,下面,我们开始写代码吧!!!
首先,我们用C语言,得手撕一个栈:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;//栈顶
int capacity;//容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
// 检测栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
// 检测栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
//return pst->top==0;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}剩余的功能跟着Leetcode上走就可以了
typedef struct { Stack pushst; Stack popst; } MyQueue;这仍然是一个匿名结构体,利用typedef重命名为MyQueue,在这个结构体中,定义了两个结构体,一个是专门出数据的popst,一个是专门入数据的pushst
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() { MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue)); if(obj==NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return NULL; } StackInit(&obj->pushst); StackInit(&obj->popst); return obj; }
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) { StackPush(&obj->pushst,x); }

peek有“窥视”的意思
//导数据了之后取顶上的数据 int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) { //popst为空才需要导数据 if(StackEmpty(&obj->popst)) { //pushst不为空 while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushst)) { //把pushst(栈顶)的数据导给popst StackPush(&obj->popst,StackTop(&obj->pushst)); //然后把pushst的数据删掉 StackPop(&obj->pushst); } } //popst本身就不为空 return StackTop(&obj->popst); }
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) { int front=myQueuePeek(obj); StackPop(&obj->popst); return front; }
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) { return StackEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&StackEmpty(&obj->popst); }
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) { StackDestroy(&obj->popst); StackDestroy(&obj->pushst); free(obj); }
这个题目的完整代码如下:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;//栈顶
int capacity;//容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
// 检测栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
// 检测栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
//return pst->top==0;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
Stack pushst;
Stack popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
StackInit(&obj->pushst);
StackInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
StackPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
StackPop(&obj->popst);
return front;
}
//导数据了之后取顶上的数据
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
//popst为空才需要导数据
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
//pushst不为空
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
//把pushst(栈顶)的数据导给popst
StackPush(&obj->popst,StackTop(&obj->pushst));
//然后把pushst的数据删掉
StackPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
//popst本身就不为空
return StackTop(&obj->popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&StackEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestroy(&obj->popst);
StackDestroy(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
好啦,小雅兰今天的用栈实现队列的内容就到这里啦,还要继续加油刷题噢!!!
