1. YOLO格式数据集和COCO格式的区别
yolo数据集的标注文件是.txt文件,在label文件夹中每一个.txt文件对应数据集中的一张图片
其中每个.txt文件中的每一行代表图片中的一个目标。
而coco数据集的标注文件是.json文件,全部的数据标注文件由三个.json文件组成:train.json val.json test.json,其中每个.json文件中包含全部的数据集图片中的所有目标(注意是所有目标不是数据集中的所有张图片)
YOLO格式数据集和COCO数据集的文件夹组成
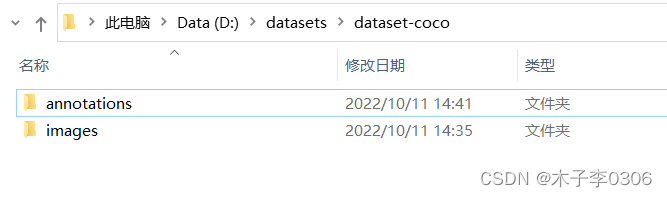
COCO数据集:
|-dataset-cooc
|-|-annotations
|-|-|-train.json
|-|-|-val.json
|-|-|-test.json
|-images
|-|-001.jpg
|-|-002.jpg
…
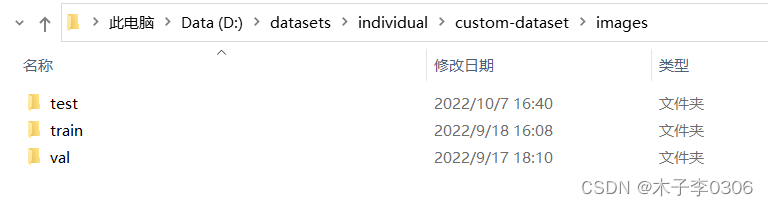
YOLO数据集:(每个.txt文件和.jpg文件是一一对应的)
|-dataset-yolo
|-|-labels
|-|-|-train
|-|-|-|-001.txt
|-|-|-val
|-|-|-|-006.txt
|-|-|-test
|-|-|-|-009.txt
|-|-images
|-|-|-train
|-|-|-|-001.jpg
|-|-|-val
|-|-|-|-006.jpg
|-|-|-test
|-|-|-|-009.jpg
…
将YOLO格式 的数据集转换为COCO格式
- 按照如上文件格式创建对应的文件夹
- 在COCO文件加下新建一个 classes.txt 文件如图:
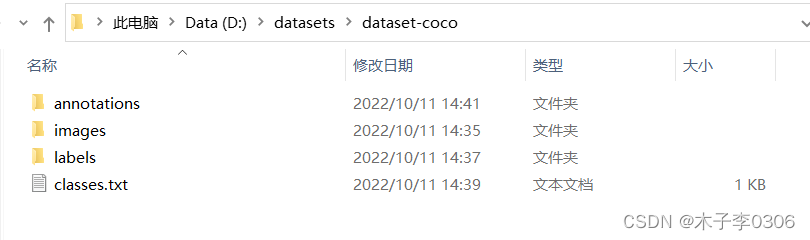
classes.txt文件中的内容:每一行是自定义数据集中的一个类别

- 运行如下代码:
"""
YOLO 格式的数据集转化为 COCO 格式的数据集
--root_dir 输入根路径
--save_path 保存文件的名字(没有random_split时使用)
--random_split 有则会随机划分数据集,然后再分别保存为3个文件。
--split_by_file 按照 ./train.txt ./val.txt ./test.txt 来对数据集进行划分。
"""
import os
import cv2
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--root_dir', default='./data',type=str, help="root path of images and labels, include ./images and ./labels and classes.txt")
parser.add_argument('--save_path', type=str,default='./train.json', help="if not split the dataset, give a path to a json file")
parser.add_argument('--random_split', action='store_true', help="random split the dataset, default ratio is 8:1:1")
parser.add_argument('--split_by_file', action='store_true', help="define how to split the dataset, include ./train.txt ./val.txt ./test.txt ")
arg = parser.parse_args()
def train_test_val_split_random(img_paths,ratio_train=0.8,ratio_test=0.1,ratio_val=0.1):
# 这里可以修改数据集划分的比例。
assert int(ratio_train+ratio_test+ratio_val) == 1
train_img, middle_img = train_test_split(img_paths,test_size=1-ratio_train, random_state=233)
ratio=ratio_val/(1-ratio_train)
val_img, test_img =train_test_split(middle_img,test_size=ratio, random_state=233)
print("NUMS of train:val:test = {}:{}:{}".format(len(train_img), len(val_img), len(test_img)))
return train_img, val_img, test_img
def train_test_val_split_by_files(img_paths, root_dir):
# 根据文件 train.txt, val.txt, test.txt(里面写的都是对应集合的图片名字) 来定义训练集、验证集和测试集
phases = ['train', 'val', 'test']
img_split = []
for p in phases:
define_path = os.path.join(root_dir, f'{
p}.txt')
print(f'Read {
p} dataset definition from {
define_path}')
assert os.path.exists(define_path)
with open(define_path, 'r') as f:
img_paths = f.readlines()
# img_paths = [os.path.split(img_path.strip())[1] for img_path in img_paths] # NOTE 取消这句备注可以读取绝对地址。
img_split.append(img_paths)
return img_split[0], img_split[1], img_split[2]
def yolo2coco(arg):
root_path = arg.root_dir
print("Loading data from ",root_path)
assert os.path.exists(root_path)
originLabelsDir = os.path.join(root_path, 'labels')
originImagesDir = os.path.join(root_path, 'images')
with open(os.path.join(root_path, 'classes.txt')) as f:
classes = f.read().strip().split()
# images dir name
indexes = os.listdir(originImagesDir)
if arg.random_split or arg.split_by_file:
# 用于保存所有数据的图片信息和标注信息
train_dataset = {
'categories': [], 'annotations': [], 'images': []}
val_dataset = {
'categories': [], 'annotations': [], 'images': []}
test_dataset = {
'categories': [], 'annotations': [], 'images': []}
# 建立类别标签和数字id的对应关系, 类别id从0开始。
for i, cls in enumerate(classes, 0):
train_dataset['categories'].append({
'id': i, 'name': cls, 'supercategory': 'mark'})
val_dataset['categories'].append({
'id': i, 'name': cls, 'supercategory': 'mark'})
test_dataset['categories'].append({
'id': i, 'name': cls, 'supercategory': 'mark'})
if arg.random_split:
print("spliting mode: random split")
train_img, val_img, test_img = train_test_val_split_random(indexes,0.8,0.1,0.1)
elif arg.split_by_file:
print("spliting mode: split by files")
train_img, val_img, test_img = train_test_val_split_by_files(indexes, root_path)
else:
dataset = {
'categories': [], 'annotations': [], 'images': []}
for i, cls in enumerate(classes, 0):
dataset['categories'].append({
'id': i, 'name': cls, 'supercategory': 'mark'})
# 标注的id
ann_id_cnt = 0
for k, index in enumerate(tqdm(indexes)):
# 支持 png jpg 格式的图片。
txtFile = index.replace('images','txt').replace('.jpg','.txt').replace('.png','.txt')
# 读取图像的宽和高
im = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root_path, 'images/') + index)
height, width, _ = im.shape
if arg.random_split or arg.split_by_file:
# 切换dataset的引用对象,从而划分数据集
if index in train_img:
dataset = train_dataset
elif index in val_img:
dataset = val_dataset
elif index in test_img:
dataset = test_dataset
# 添加图像的信息
dataset['images'].append({
'file_name': index,
'id': k,
'width': width,
'height': height})
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(originLabelsDir, txtFile)):
# 如没标签,跳过,只保留图片信息。
continue
with open(os.path.join(originLabelsDir, txtFile), 'r') as fr:
labelList = fr.readlines()
for label in labelList:
label = label.strip().split()
x = float(label[1])
y = float(label[2])
w = float(label[3])
h = float(label[4])
# convert x,y,w,h to x1,y1,x2,y2
H, W, _ = im.shape
x1 = (x - w / 2) * W
y1 = (y - h / 2) * H
x2 = (x + w / 2) * W
y2 = (y + h / 2) * H
# 标签序号从0开始计算, coco2017数据集标号混乱,不管它了。
cls_id = int(label[0])
width = max(0, x2 - x1)
height = max(0, y2 - y1)
dataset['annotations'].append({
'area': width * height,
'bbox': [x1, y1, width, height],
'category_id': cls_id,
'id': ann_id_cnt,
'image_id': k,
'iscrowd': 0,
# mask, 矩形是从左上角点按顺时针的四个顶点
'segmentation': [[x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]]
})
ann_id_cnt += 1
# 保存结果
folder = os.path.join(root_path, 'annotations')
if not os.path.exists(folder):
os.makedirs(folder)
if arg.random_split or arg.split_by_file:
for phase in ['train','val','test']:
json_name = os.path.join(root_path, 'annotations/{}.json'.format(phase))
with open(json_name, 'w') as f:
if phase == 'train':
json.dump(train_dataset, f)
elif phase == 'val':
json.dump(val_dataset, f)
elif phase == 'test':
json.dump(test_dataset, f)
print('Save annotation to {}'.format(json_name))
else:
json_name = os.path.join(root_path, 'annotations/{}'.format(arg.save_path))
with open(json_name, 'w') as f:
json.dump(dataset, f)
print('Save annotation to {}'.format(json_name))
if __name__ == "__main__":
yolo2coco(arg)
执行:python yolo2coco.py --root_dir $ROOT_PATH ,然后就能看见生成的 annotations 文件夹。
参数说明
--root_path # 输入根目录$ROOT_PATH的位置。
--save_path # 如果不进行数据集划分,可利用此参数指定输出文件的名字,默认保存为train.json
--random_split # 随机划分参数,若指定--random_split参数,则输出在annotations文件夹下包含
# train.json val.json test.json (默认随机划分成8:1:1)
--split_by_file # 自定义数据集划分,若指定--split_by_file参数,则输出在annotations文件夹
# train.json val.json test.json。需要在$ROOT_PATH文件下有 ./train.txt ./val.txt #
# ./test.txt ,可以这3个文件来定义训练集、验证集、测试集。注意, 这里里面填写的应是图片文件名字,
# 而不是图片的绝对地址。
#(在line 43也自行可以修改一下读取方式,为了方便起见,不推荐把图片放在不同位置)