一、介绍
在Android开发过程中,经常会有弹窗业务,在正常的弹窗业务中,常用到的是Dialog,Dialog的原理也是通过将view,添加到Dialog中。Dialog自身是一个独立的窗口,和Activity一样,有自己的window管理。如果简单的使用Dialog不方便管理,在后面Google提供了DialogFragment弹窗。
二、DialogFragment的介绍
看到DialogFragment,从单词可以看到是Dialog与Fragment组合而成,但是在DialogFragment中,DialogFragment其实是一个fragment,内部持有一个Dialog,这样方便了开发者的管理。fragment在碎片管理中其实就是一个View,最终view的显示是通过dialog来完成。
class NamelessClass_1 implements Observer<LifecycleOwner> {
NamelessClass_1() {
}
@SuppressLint({"SyntheticAccessor"})
public void onChanged(LifecycleOwner lifecycleOwner) {
if (lifecycleOwner != null && DialogFragment.this.mShowsDialog) {
View view = DialogFragment.this.requireView();
if (view.getParent() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("DialogFragment can not be attached to a container view");
}
if (DialogFragment.this.mDialog != null) {
if (FragmentManager.isLoggingEnabled(3)) {
Log.d("FragmentManager", "DialogFragment " + this + " setting the content view on " + DialogFragment.this.mDialog);
}
DialogFragment.this.mDialog.setContentView(view);
}
}
}
}同样,在类中也提供了丰富的方法
1、显示
public void show(@NonNull FragmentManager manager, @Nullable String tag) {
this.mDismissed = false;
this.mShownByMe = true;
FragmentTransaction ft = manager.beginTransaction();
ft.add(this, tag);
ft.commit();
}2、消失
public void dismiss() {
this.dismissInternal(false, false);
}3、获取dialog
@Nullable
public Dialog getDialog() {
return this.mDialog;
}
4、初始化内部资源
@Nullable
View onFindViewById(int id) {
return this.mDialog != null ? this.mDialog.findViewById(id) : null;
}5.dialog创建
@MainThread
@NonNull
public Dialog onCreateDialog(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (FragmentManager.isLoggingEnabled(3)) {
Log.d("FragmentManager", "onCreateDialog called for DialogFragment " + this);
}
return new Dialog(this.requireContext(), this.getTheme());
}三、实战
通过以上介绍,我们大概熟悉了DialogFragment的大概工作方式,如果想仔细研究,可以查看源码。
在实战使用中
1、继承重写
基类:
abstract class BaseBindDialogFragment<V : ViewDataBinding> : DialogFragment() {
val TAG=javaClass::class.java.name
lateinit var bind: V
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
bind = DataBindingUtil.inflate(inflater, getLayoutId(), container, false)
initView(bind.root)
return bind.root
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
initConfig(dialog)
}
@LayoutRes
abstract fun getLayoutId(): Int
abstract fun initView(view: View)
abstract fun initConfig(dialog:Dialog?)
}class MyDialogFrgament : BaseBindDialogFragment<DialogFragmentbind>() {
override fun getLayoutId(): Int {
return R.layout.layout_dialog_view
}
override fun initView(view: View) {
bind.textInfo.text="我在测试"
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
MyLog.log(TAG,"onResume")
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
MyLog.log(TAG,"onPause")
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
MyLog.log(TAG,"onStop")
}
override fun initConfig(dialog: Dialog?) {
dialog?.let {
}
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data class="DialogFragmentbind"></data>
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</FrameLayout>
</layout>执行:
private fun dialogExport() {
dialog = MyDialogFrgament()
dialog.show(supportFragmentManager, "dialogExport")
}注意:
在开发过程中,好多新手会报错:
DialogFragment can not be attached to a container view
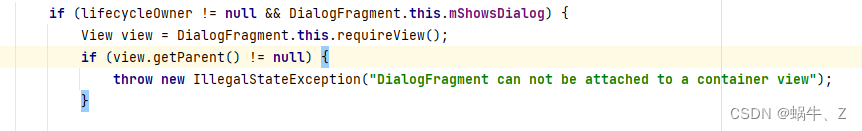
报错这个问题的原因是view的parent不为null,在消失后,又重新显示,这个时候会校验parent是否为null。
发生这个问题的核心是语法使用
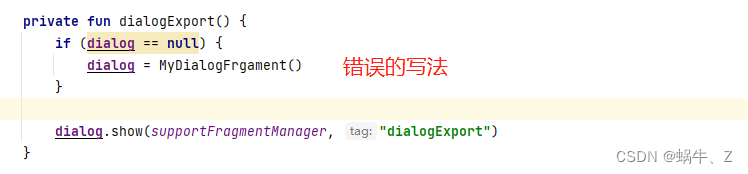
解决:
1.获取view的parent,通过remove自己
2.每次展示的时候重新new一个对象