目录:Seaborn库
一、前言
Seaborn是一个建立在matplot之上,可用于制作丰富和非常具有吸引力统计图形的Python库。
Seaborn库旨在将可视化作为探索和理解数据的核心部分,有助于帮人们更近距离了解所研究的数据集。无论是在kaggle官网各项算法比赛中,还是互联网公司的实际业务数据挖掘场景中,都有它的身影。
二、实践
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
tips = pd.read_csv('tips.csv')
tips.head()

2.1 各属性相关性
# 相关性
tips.corr()
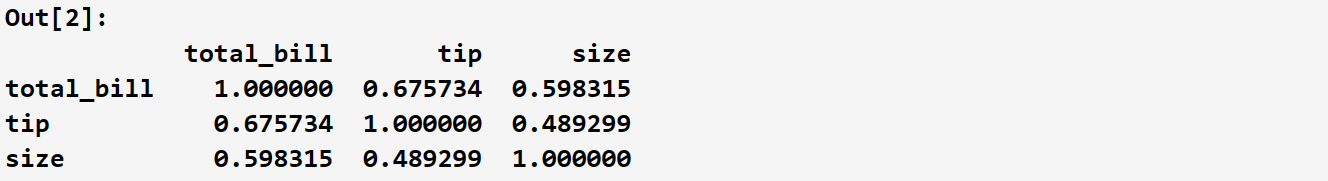
2.1.1 pair plot图
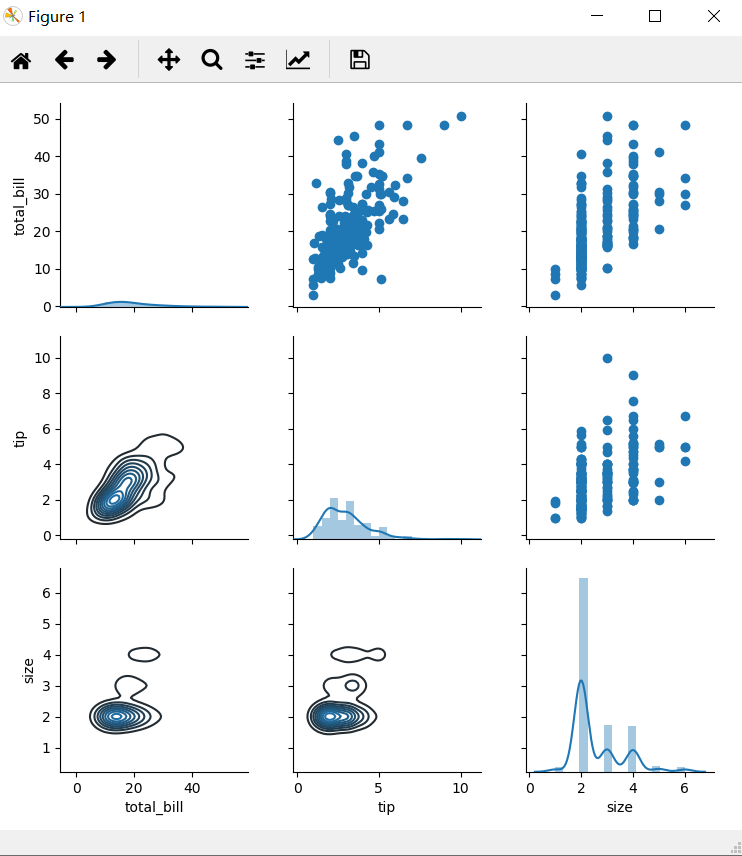
#相关性图 很壮观
sns.pairplot(tips)
看图说话:这些图展现了数据集中消费总额、小费金额以及顾客数量三个特征(变量)之间的联系。
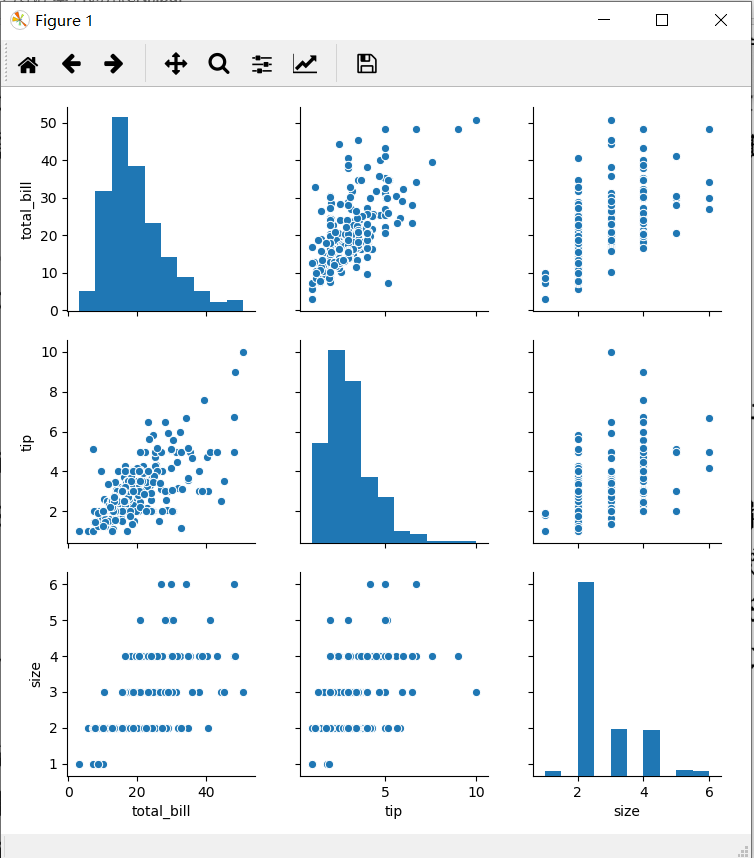
#相关性图,和某一列的关系
sns.pairplot(tips ,hue ='sex', markers=["o", "s"])
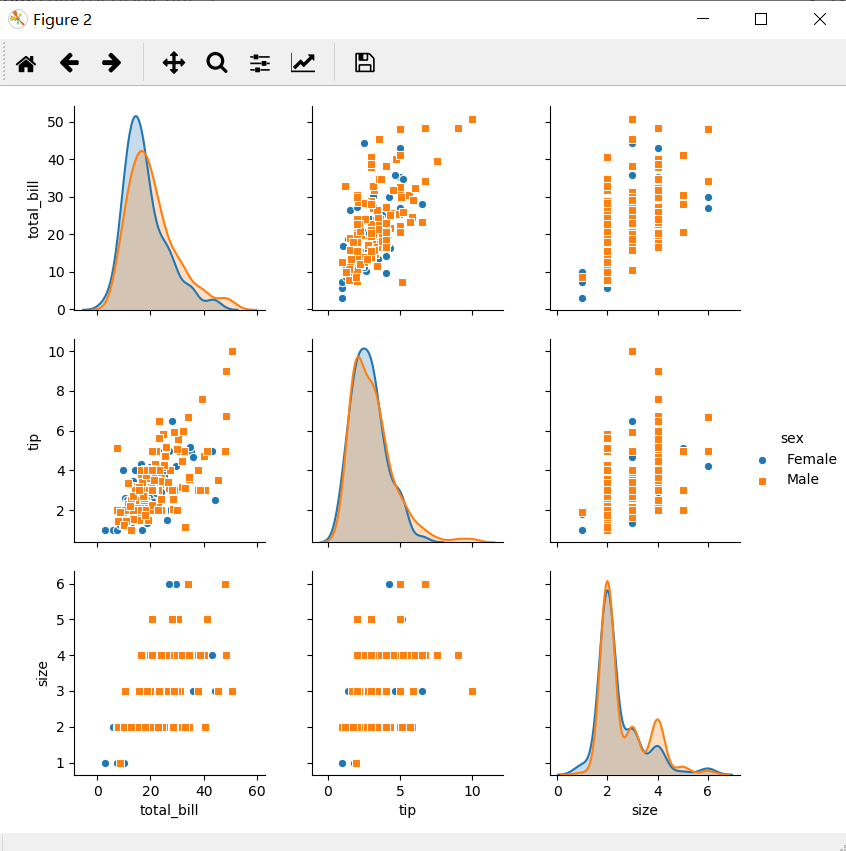
2.1.2 热力图
# 相关性热力图
sns.heatmap(tips.corr())
看图说话:热力图可用来显示两变量之间的相关性,在这里两变量间对应的矩形框的颜色越浅,代表两者之间越具有相关性。
# 分层相关性热力图
sns.clustermap(tips.corr())
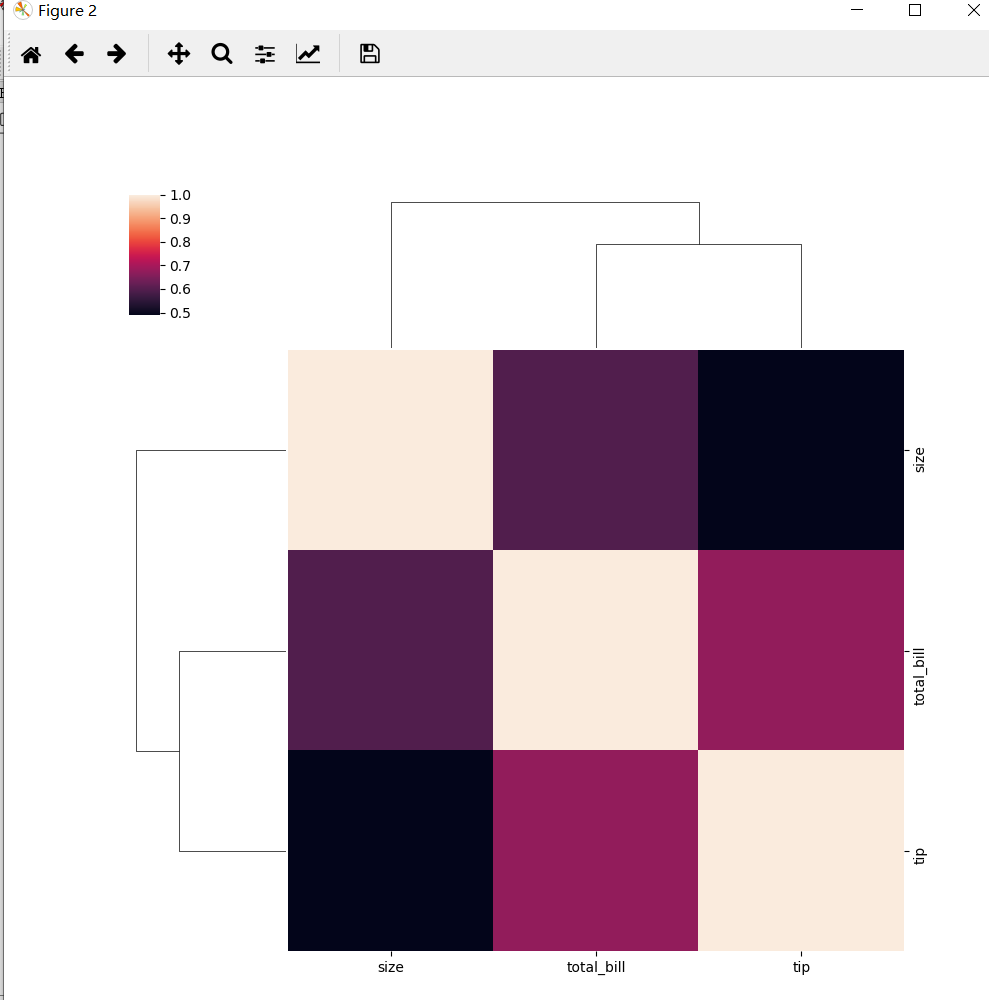
2.1.3 pair grid图
g = sns.PairGrid(tips)
g.map_diag(sns.distplot)
g.map_upper(plt.scatter)
g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot)
在pair grid图中,你可以根据自己需求,在这里呈现上述介绍的各种类型的图形。
2.2 单个属性的分布
2.2.1 dist plot图
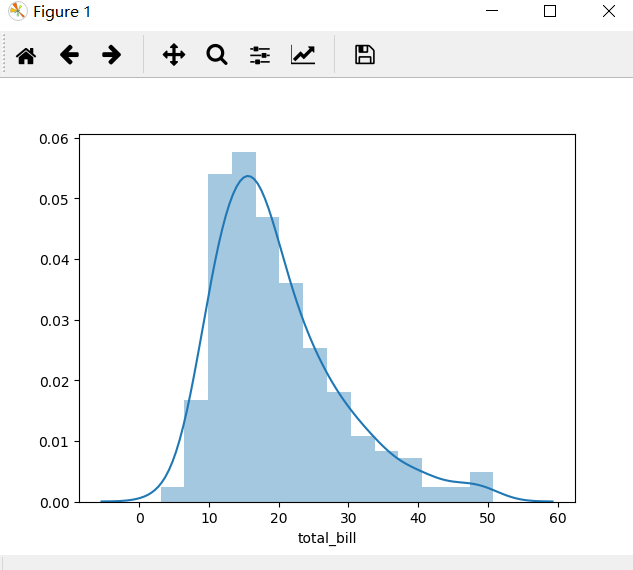
sns.distplot(tips['total_bill'])
sns.distplot(tips['total_bill'],kde = False)
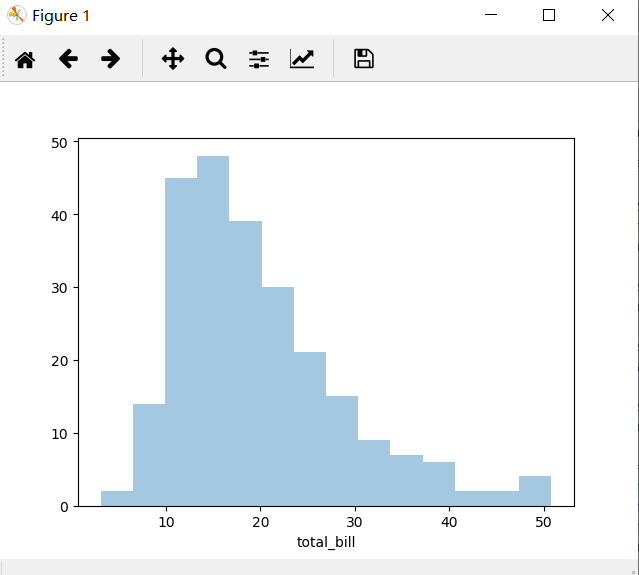
看图说话:上图显示,顾客在餐厅的消费总金额主要是在5-35的范围内分布的。
2.2.2 count plot图
sns.countplot(x = 'smoker', data = tips)
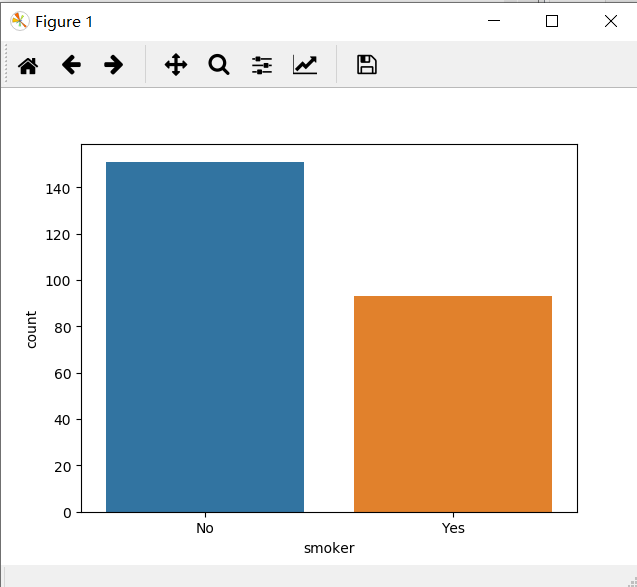
看图说话:上图显示,来餐厅就餐的顾客,不抽烟者比会抽烟者多
sns.countplot(x = 'size', data = tips)
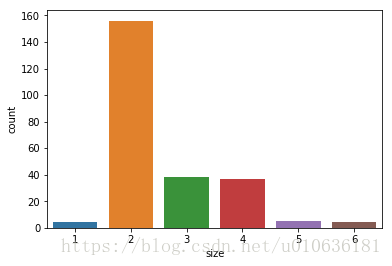
看图说话:上图显示,2个人来餐厅就餐的总次数多一些。
2.2.3 rug plot图
sns.rugplot(tips['total_bill'])

看图说话:上图呈现的是,顾客就餐消费总额在各个值上的边缘分布。
2.2.4 kde plot图
sns.kdeplot(tips['total_bill'], shade=True)
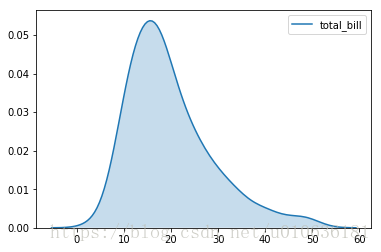
看图说话:KDE代表内核密度估计,它也显示了各个消费总金额数值的统计分布。
2.3 两两属性的相关性图
2.3.1 joint plot图
sns.jointplot(x = 'total_bill', y = 'tip', data = tips)
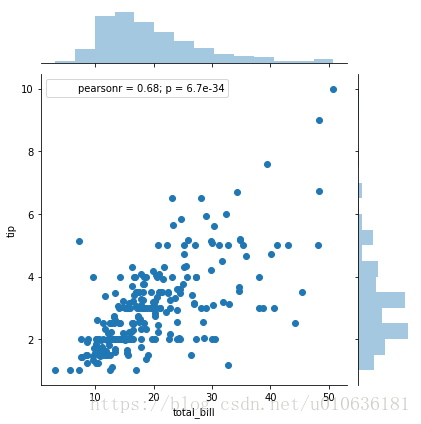
看图说话:上图显示,顾客主要消费水平在10-30远之间,而此时,对应给侍者小费的钱在1-5元之间。
sns.jointplot(x = 'total_bill', y = 'tip', data = tips ,kind = 'hex')
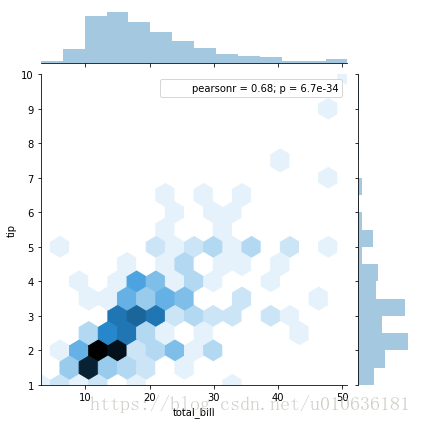
另一种清晰地可视化视图,颜色的深度代表频次。
sns.jointplot(x = 'total_bill', y = 'tip', data = tips ,kind = 'reg')
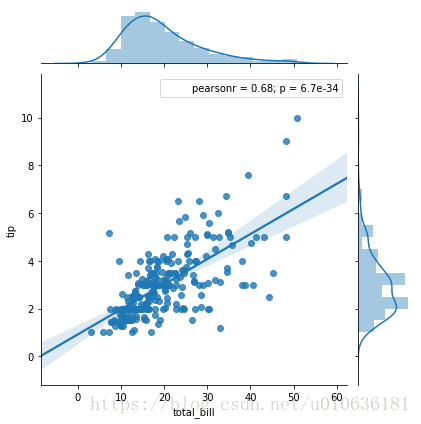
看图说话:通过做一条简单的回归线,它表明了小费的金额是随着总账单金额的增加而增加的。
sns.jointplot(x = 'total_bill', y = 'tip', data = tips ,kind = 'kde')
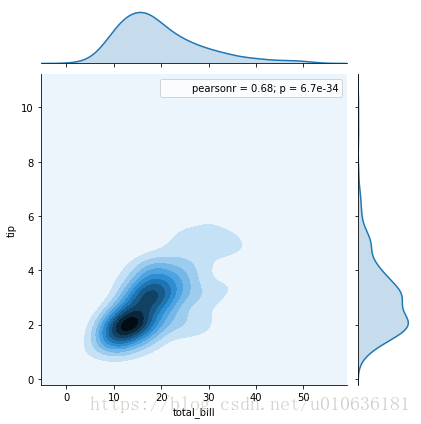
另一种可视化统计图:某个区域越暗,表明这个区域对应的频次越多。
2.3.2 box plot图
sns.boxplot(x = 'day', y= 'total_bill', data = tips)
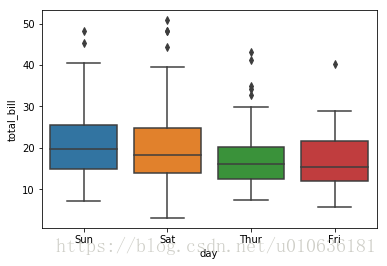
看图说话:上图显示大部分账单是在周六和周日支付的。
sns.boxplot(x = 'day', y= 'total_bill', data = tips, hue = 'sex')
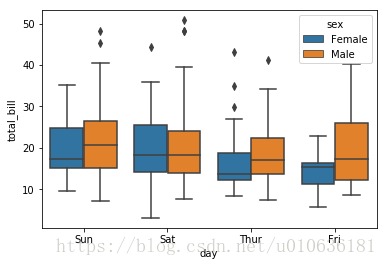
看图说话:在上面的图表中你可以看到,在周六时,女性买单的次数会比男性多。
2.3.3 violin plot
sns.violinplot(x = 'day', y= 'total_bill', data = tips)

看图说话:voilin plot和box plot很相似,但它结合了box plot图和密度痕迹。
sns.violinplot(x = 'day', y= 'total_bill', data = tips, hue = 'sex', split = True)
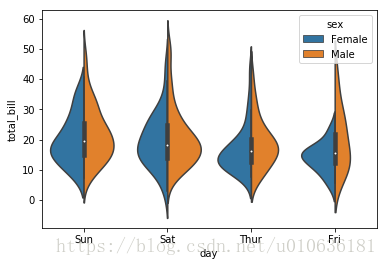
看图说话:增加了性别的区分
2.3.4 strip plot图
sns.stripplot(x = 'day', y = 'total_bill', data = tips)
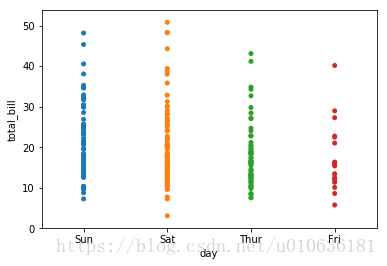
看图说话:这幅图呈现的是周四、周五、周六和周日这四天,顾客消费总额的散点图。
sns.stripplot(x = 'day', y = 'total_bill', data = tips, jitter= True,hue = 'sex', dodge = True)
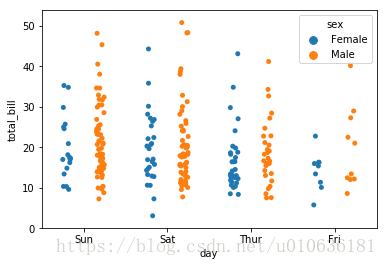
看图说话:和上图一样,只不过对性别进行了区别。
2.3.5 swarm plot图
sns.swarmplot(x = 'day', y = 'total_bill', data = tips)
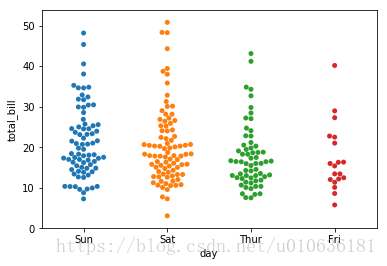
看图说话:Swarn plot和stripplot比较类似,但Swarn plot的不同之处在于它不会重叠数据点。
2.3.6 factor plot图
sns.factorplot(x = 'day', y = 'total_bill', kind = 'box', data = tips)
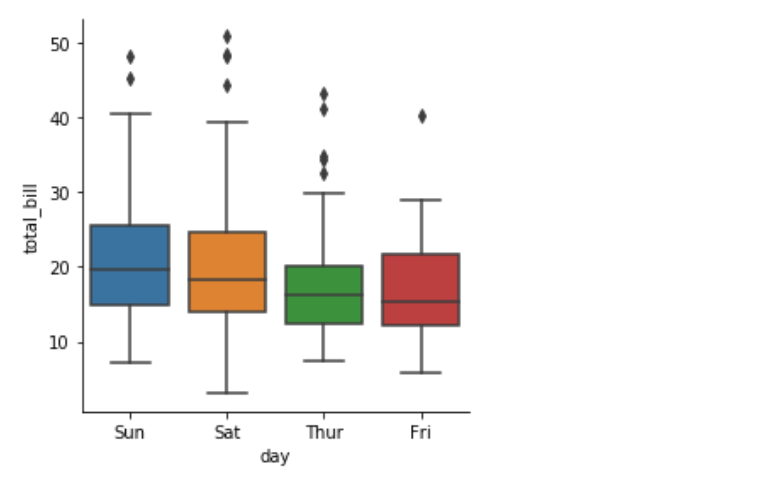
看图说话:在factorplot图中,你可以给出任何你需要显示的图形。