一、什么是JDBC
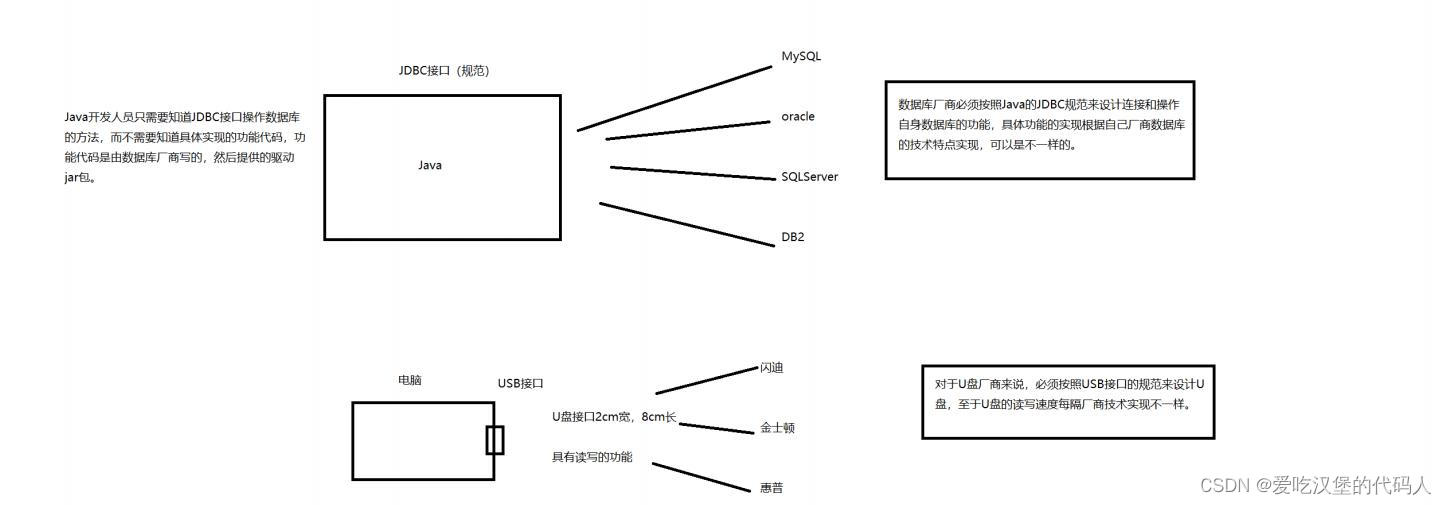
概念: Java 数据库连接,( Java Database Connectivity ,简称 JDBC )是 Java 语言 中用来规范客户端程序如何来访问数据库的 应用程序接口 ,提供了诸如查询和更新数据库中数据的方法。 JDBC 也是 SunMicrosystems 的商标。我们通常说的 JDBC 是面向关系型数据库的。各数据库厂商根据 JDBC 的规范,实现自身数据库操作的功能代码,然后以 jar 包(数据库厂商提供的驱动包)的形式提供给开发人员使用,开发人员使用反射的机制创建这些具体实现类,按照 JDBC 的规范来完成数据库的操作。
1.1 接口和JDBC规范的理解:
1.2 JDBC常用的接口与类:
DriverManager:这个类管理数据库驱动程序的列表,查看加载的驱动是否符合JAVA Driver API的规范
Connection:与数据库中的连接对象,通过该对象与数据库进行通信
Statement:把创建的SQL对象,转而存储到数据库当中
ResultSet:它是一个迭代器,用于检索查询数据
1.3 JDBC优缺点:
优点:
1.JDBC使得编程人员从复杂的驱动器调用命令和函数中解脱出来,可以致力于应用程序中的关键地方。
2.JDBC支持不同的关系数据库,这使得程序的可移植性大大加强。
3.JDBC API是面向对象的,可以让用户把常用的方法封装为—个类,以备后用。
缺点:
1.使用JDBC,访问数据记录的速度会受到一定程度的影响。
2.JDBC结构中包含不同厂家的产品,这就给更改数据源带来了很大的麻烦。
1.4 主要任务:
JDBC技术主要是完成以下几个任务:
1.与数据库建立一个链接
2.向数据库发送SQL语句
3.处理从数据库返回的结果
1.5 JDBC 步骤六步(重点)
第一步:加载驱动程序(项目中要引入jar包【驱动程序包】)
第二步:使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接(表示JVM的进程与数据库进程之间的通道打开了,属于进程之间的通信)
第三步:获取数据库操作对象(专门执行sql语句的对象)
第四步:执行sql语句(DQL,DML…)
第五步:处理查询结果集(当执行的是DQL查询语句时,才需要处理查询结果集)
第六步:关闭资源(使用完一定记得要关闭资源)
二、JDBC连接数据库以及增删改查操作
junit可以使方法脱离main方法直接执行,方便进行程序测试。
junit用法:1.方法要定义为无参无返回值的。且测试类的名字不能是Test
2.在方法上使用@Test 这个注解
3.光标放在后面,然后使用 alt + 回车,进行自动导包,选择---Add 'JUnit4' to classpath
4.这个方法就不需要依赖main方法就可以执行
2.1 创建一个数据库
2.1.1 创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE demo;
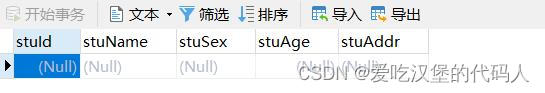
2.1.2 创建表 起名student
CREATE TABLE student(
stuId INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
stuName VARCHAR(16),
stuSex VARCHAR(4),
stuAge INT,
stuAddr VARCHAR(32)
);代码运行结果如下:
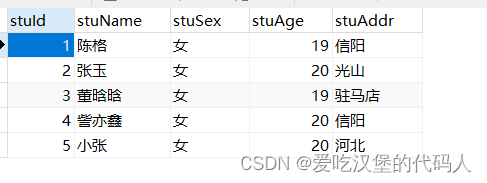
2.1.3 向表中插入数据
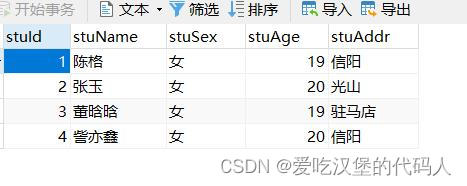
INSERT INTO student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr)VALUES('陈格','女',19,'信阳');
INSERT INTO student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr)VALUES('张玉','女',20,'光山');
INSERT INTO student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr)VALUES('董晗晗','女',19,'驻马店');
INSERT INTO student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr)VALUES('訾亦鑫','女',20,'信阳');代码运行结果如下:
2.2 使用JDBC进行对数据库的操作
2.2.1 先在IDEA中创建实体类:类名对应数据库中表的名、类的属性对应表的字段
//自动构造代码快捷键: alt + insert
public class Student {
//类的属性
private int stuId;
private String stuName;
private String stuSex;
private int stuAge;
private String stuAddr;
//自动构造代码快捷键: alt + insert
//无参构造函数
public Student() {
}
//有参构造函数
public int getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public void setStuId(int stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public String getStuSex() {
return stuSex;
}
public void setStuSex(String stuSex) {
this.stuSex = stuSex;
}
public int getStuAge() {
return stuAge;
}
public void setStuAge(int stuAge) {
this.stuAge = stuAge;
}
public String getStuAddr() {
return stuAddr;
}
public void setStuAddr(String stuAddr) {
this.stuAddr = stuAddr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", stuSex='" + stuSex + '\'' +
", stuAge=" + stuAge +
", stuAddr='" + stuAddr + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
连接数据库需要配置的四大参数,同时需要驱动jar包 在项目根目录创建lib文件夹,放入jdbc驱动程序,然后Add As Library 驱动包在官网搜mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar的下载链接:下载链接
服务器一年后过期,过期的话先用百度网盘下载吧
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/187wdM_EU_Nc8adLdMnwUoQ?pwd=1111
提取码:1111
//通信协议 数据库服务端地址:本机地址 MySQL端口号 数据库名 账号 密码
jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1: 3306/ demo", "root", "root"
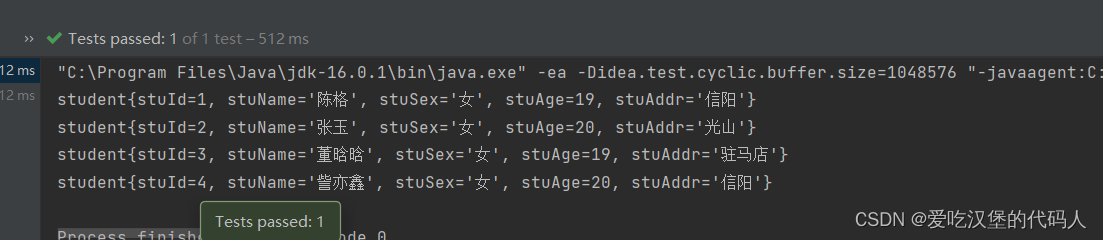
2.2.2 全查操作
public void testSelctAll() throws Exception {
//JDBC操作数据库的步骤
//1.首先在项目根目录创建lib文件夹,放入jdbc驱动程序,然后Add As Library
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象--PreparedStatement对象可以对sql语句预处理
String sql = "select * from student";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.使用PreparedStatement对象执行sql语句,查询返回的是结果集,增删改返回的是影响的行数(int)
ResultSet rs = pstm.executeQuery();
//ResultSet 结果集的游标默认指向的是表的标题,需要让游标向下移动指向数据行
//6.操作判断--增删改返回的是影响的行数(返回值是int),只有查询获得结果集(返回值ResultSet)
//定义一个集合,用来存储每一行的数据(封装在了Student对象中)
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
//根据字段名获取字段值
int stuId = rs.getInt("stuId");
String stuName = rs.getString("stuName");
String stuSex = rs.getString("stuSex");
int stuAge = rs.getInt("stuAge");
String stuAddr = rs.getString("stuAddr");
//把以上数据装载到Student对象中
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuId(stuId);
student.setStuName(stuName);
student.setStuSex(stuSex);
student.setStuAge(stuAge);
student.setStuAddr(stuAddr);
//把Student对象存储到List集合中
studentList.add(student);
}
for (Student c :studentList){
System.out.println(c.toString());
}
//7.回收资源
if (rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (pstm!=null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
}
2.2.3 增--添加数据
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values(?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 构造数据,数据封装在Student对象中
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuName("小张");
student.setStuSex("女");
student.setStuAge(20);
student.setStuAddr("河北");
//5.1传参
pstm.setObject(1,student.getStuName());
pstm.setObject(2,student.getStuSex());
pstm.setObject(3,student.getStuAge());
pstm.setObject(4,student.getStuAddr());
//5.2执行更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("添加成功");
}else{
System.out.println("添加失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
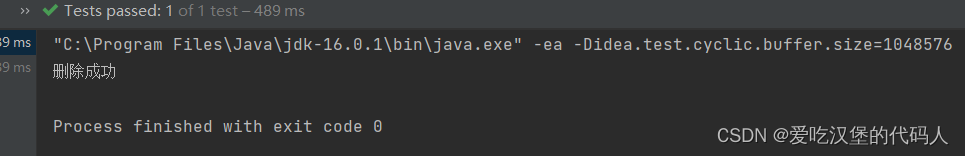
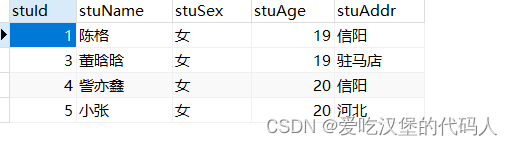
2.2.4 删--删除数据
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "delete from student where stuId = ?";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.1执行?的传参
int stuId = 2;
pstm.setObject(1,stuId);
//5.2执行数据的更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else{
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
2.2.5 改--修改数据
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "update student set stuName = ?,stuSex = ? where stuId = ?";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.1执行?的传参
pstm.setInt(3,4);
pstm.setString(1,"张玉");
pstm.setString(2,"女");
//5.2执行数据的更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
}


整体代码:
package com.hp.test02;
import com.hp.bean.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentTest {
/**
* 数据库的查询操作
*/
@Test
public void testSelctAll() throws Exception {
//JDBC操作数据库的步骤
//1.首先在项目根目录创建lib文件夹,放入jdbc驱动程序,然后Add As Library
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象--PreparedStatement对象可以对sql语句预处理
String sql = "select * from student";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.使用PreparedStatement对象执行sql语句,查询返回的是结果集,增删改返回的是影响的行数(int)
ResultSet rs = pstm.executeQuery();
//ResultSet 结果集的游标默认指向的是表的标题,需要让游标向下移动指向数据行
//6.操作判断--增删改返回的是影响的行数(返回值是int),只有查询获得结果集(返回值ResultSet)
//定义一个集合,用来存储每一行的数据(封装在了Student对象中)
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
//根据字段名获取字段值
int stuId = rs.getInt("stuId");
String stuName = rs.getString("stuName");
String stuSex = rs.getString("stuSex");
int stuAge = rs.getInt("stuAge");
String stuAddr = rs.getString("stuAddr");
//把以上数据装载到Student对象中
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuId(stuId);
student.setStuName(stuName);
student.setStuSex(stuSex);
student.setStuAge(stuAge);
student.setStuAddr(stuAddr);
//把Student对象存储到List集合中
studentList.add(student);
}
for (Student c :studentList){
System.out.println(c.toString());
}
//7.回收资源
if (rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
if (pstm!=null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
}
/**
* 数据库的增加操作
*/
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values(?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 构造数据,数据封装在Student对象中
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuName("小张");
student.setStuSex("女");
student.setStuAge(20);
student.setStuAddr("河北");
//5.1传参
pstm.setObject(1,student.getStuName());
pstm.setObject(2,student.getStuSex());
pstm.setObject(3,student.getStuAge());
pstm.setObject(4,student.getStuAddr());
//5.2执行更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("添加成功");
}else{
System.out.println("添加失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
/**
* 数据库的删除操作
*/
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "delete from student where stuId = ?";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.1执行?的传参
int stuId = 2;
pstm.setObject(1,stuId);
//5.2执行数据的更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else{
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
/**
* 数据库的修改操作
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.使用DriverManager建立程序与数据库的连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo","root","root");
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象
String sql = "update student set stuName = ?,stuSex = ? where stuId = ?";
PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.1执行?的传参
pstm.setInt(3,4);
pstm.setString(1,"张玉");
pstm.setString(2,"女");
//5.2执行数据的更新 (更新操作)
int c = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6.判断受影响的行数,如果n>0 表示添加成功,否则添加失败
if (c>0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
//7.资源回收
if (pstm != null){
pstm.close();
}
if (conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}
}