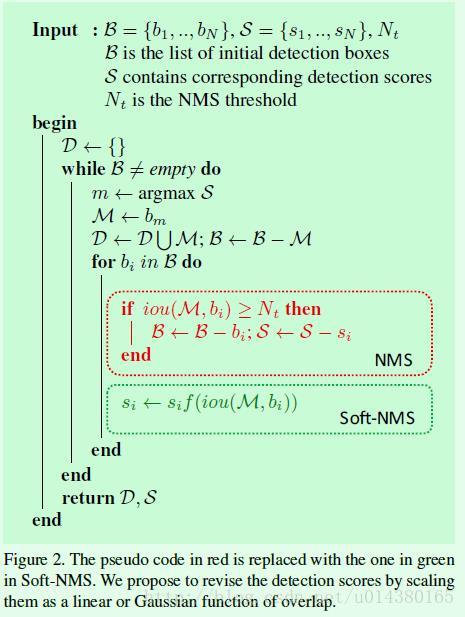
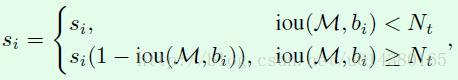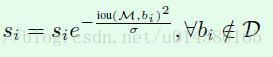nms:
步骤:
- 按打分最高到最低将BBox排序 ,例如:A B C D E F
- A的分数最高,保留。从B-E与A分别求重叠率IoU,假设B、D与A的IoU大于阈值,那么B和D可以认为是重复标记去除
- 余下C E F,重复前面两步
代码:
import numpy as np
def nms_cpu_py(dets,thre):
x1 = dets[:,0]
y1 = dets[:,1]
x2 = dets[:,2]
y2 = dets[:,3]
scores = dets[:,4]
area = (x2-x1+1) * (y2-y1+1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
keep.append(order[0])
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[order[0]], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[order[0]], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[order[0]], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[order[0]], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0., xx2-xx1)
h = np.maximum(0., yy2-yy1)
inter = w * h
union = area[order[0]] + area[order[1:]] - inter
iou = inter / union
inds = np.where(iou <= thre)[0]
order = order[inds+1]
return keep
dets = np.array([[10,20,30,50,0.6],[20,30,50,70,0.75],[20,30,50,80,0.8]])
print(nms_cpu_py(dets,0.99))soft nms
nms略显粗暴,因为它直接把和得分最高的box相交大于某个阈值的box置零了,所以就有了这样一个比较soft的算法。
SoftNMS的原理:用稍低一点的分数来代替原有的分数,而不是直接置为零,并且SoftNMS可以直接引入object detection中,不需要重新训练模型,因此这是该算法的一大优点。
下面是SoftNMS的伪代码:
简单来说就是NMS在比较IOU后,直接将把与最大置信度重合高的box给扔掉了,而SoftNMS并没有直接扔掉,而是将和最大置信度重合的box的置信度值降低,IOU与置信度变化的关系由函数f()给出。
首先NMS算法可以用下面的式子表示:
为了改变NMS这种hard threshold做法,并遵循IOU越大,得分越低的原则(IOU越大,越有可能是false positive),自然可以想到用下面这个公式来表示Soft NMS:
但是上面这个公式是不连续的,这样会导致box集合中的score出现断层,因此就有了下面这个Soft NMS式子(也是大部分实验中采用的式子):
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
14706301 查看本文章


这个式子可以满足:一个连续的惩罚函数应该对没有重叠的box不产生惩罚,而对重叠度高的产生高的惩罚。
python 代码:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import backend as K
def py_cpu_softnms(dets, scores, Nt=0.3, sigma=0.5, thresh=0.001, method=2):
"""
:param dets: boexs 坐标矩阵 format [y1, x1, y2, x2]
:param scores: 每个 boxes 对应的分数
:param Nt: iou 交叠门限
:param sigma: 使用 gaussian 函数的方差
:param thresh: 最后的分数门限
:param method: 使用的方法
:return: 留下的 boxes 的 index
"""
# indexes concatenate boxes with the last column
N = dets.shape[0]
indexes = np.array([np.arange(N)])
dets = np.concatenate((dets, indexes.T), axis=1)
# the order of boxes coordinate is [y1,x1,y2,x2]
y1 = dets[:, 0]
x1 = dets[:, 1]
y2 = dets[:, 2]
x2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = scores
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
for i in range(N):
# intermediate parameters for later parameters exchange
tBD = dets[i, :].copy()
tscore = scores[i].copy()
tarea = areas[i].copy()
pos = i + 1
#
if i != N-1:
maxscore = np.max(scores[pos:], axis=0)
maxpos = np.argmax(scores[pos:], axis=0)
else:
maxscore = scores[-1]
maxpos = 0
if tscore < maxscore:
dets[i, :] = dets[maxpos + i + 1, :]
dets[maxpos + i + 1, :] = tBD
tBD = dets[i, :]
scores[i] = scores[maxpos + i + 1]
scores[maxpos + i + 1] = tscore
tscore = scores[i]
areas[i] = areas[maxpos + i + 1]
areas[maxpos + i + 1] = tarea
tarea = areas[i]
# IoU calculate
xx1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 1], dets[pos:, 1])
yy1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 0], dets[pos:, 0])
xx2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 3], dets[pos:, 3])
yy2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 2], dets[pos:, 2])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[pos:] - inter)
# Three methods: 1.linear 2.gaussian 3.original NMS
if method == 1: # linear
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = weight[ovr > Nt] - ovr[ovr > Nt]
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(ovr * ovr) / sigma)
else: # original NMS
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = 0
scores[pos:] = weight * scores[pos:]
# select the boxes and keep the corresponding indexes
inds = dets[:, 4][scores > thresh]
keep = inds.astype(int)
print(keep)
return keep
# boxes and scores
boxes = np.array([[200, 200, 400, 400], [220, 220, 420, 420], [200, 240, 400, 440], [240, 200, 440, 400], [1, 1, 2, 2]], dtype=np.float32)
boxscores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
# tf.image.non_max_suppression 中 boxes 是 [y1,x1,y2,x2] 排序的。
with tf.Session() as sess:
# index = sess.run(tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes=boxes, scores=boxscores, iou_threshold=0.5, max_output_size=5))
# print(index)
index = py_cpu_softnms(boxes, boxscores, method=3)
selected_boxes = sess.run(K.gather(boxes, index))
print(selected_boxes)