1 Algorithms for attribute computation
| 属性 | 定义 | 计算方法 | Top down | Bottom up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inherited Attributes | 依赖关系不是子节点指向父节点,包括父指向子或者兄弟指向兄弟 | preorder | function Parameter | external data structure |
| Synthesized Attributes | 该属性总是由子节点指向父节点。(先计算子节点的属性值,然后赋值给父节点) | post order | return value | value stack |
S-attributed grammar:
An attribute grammar in which all the attributes are synthesized
所有属性必须是综合属性
L-attributed Definition
- 综合属性
- 继承属性,依赖于父节点或者左边的兄弟节点
S属性一定是L属性的
继承属性转为综合属性:
继承属性一般出现在右子树得到值,然后传递给左子树,接着传递给叶子节点,导致了继承
1: 消除左递归,存在A-> A xxx|B 的,修改为两条:
A->BA’和A’->xxxxA’|e (左边改为右边)
2: 将出现A的式子中A后面的部分替代e。比如有S->A b,此时将A’->xxxxA’|e修改为A’->xxxxA’|b即可,然后将原来的修改为S->A
3: 将多余的非终结符消掉,比如将S->A b修改为S-> BA’
如果没有左递归,则消除右递归,需要修改的地方是:
1: A->xxx A | B 变为 A-> A’B A’-> A’xxx | e
一个右递归的例子:
decl -> type var-list
type -> int|float
var-list -> id,var-list|id
消除右递归:var-list -> v’ id
v’->v’ id, | e
替换e: v’->v’ id, | type
消除var-list: decl -> v’ id
v’->v’ id, | type
2 The symbol table
画Symbol table:
1: 每个节点有三个元素:类型,名称,指向下一个节点的指针
2: 执行到第i句话开始,则从i句话开始往前找,依次按照列表往下画
这是因为symbol table插入是插入到头上的,因此必须从后面开始找
如果遇到块语句(封闭的大括号),则里面声明的变量直接跳过。
3 Data types and type checking
| 各种等价 | |
|---|---|
| Structural equivalence | two types are the same if and only if they have the same structure |
| Name equivalence | type and name is same |
| Declaration equivalence | 显示声明了t1=t2 |
4 Active Record, Stack-based runtime environment
control link:指向调用该函数的函数的AR
Access link: 指向定义该函数的AR,第一个AR没有access link,
函数的定义在函数体之外,比如
program nonlocalRef;
procedure p;
var n: integer;
//函数定义,和局部变量一样
procedure q;
begin
(* a reference to n is
now non-local and
non-global *)
end; (*q*)
procedure r(n:intege r);
begin
q;
end; (*r*)
//这里是p函数的函数体定义
begin (* p*)
n :=1;
r(2);
end; (*p*)
//这里是主函数
begin (*main*)
p;
end.
fp:指向当前的AR
sp:指向堆栈顶部
在栈中的顺序:参数,之前的fp,返回地址,函数内部局部变量
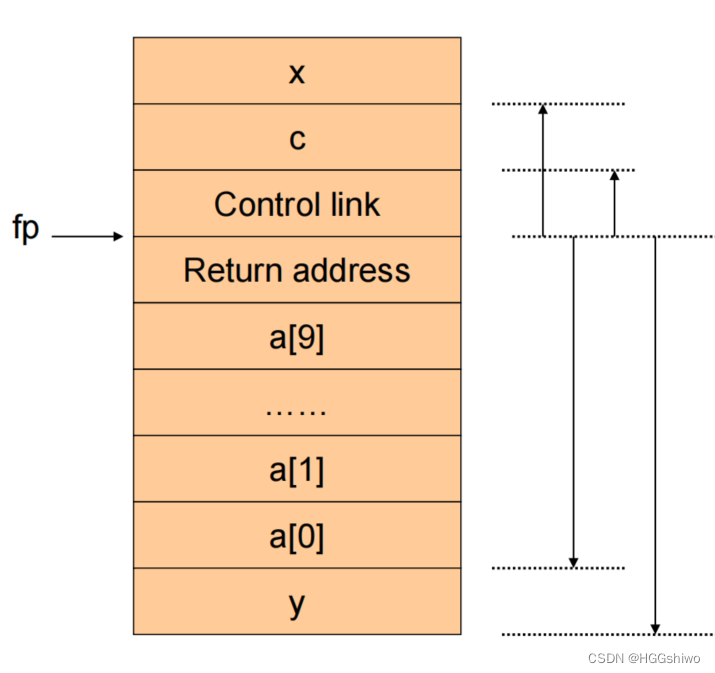
5 Parameter passing mechanisms
Pass by Value:
1: 将值拷贝到函数栈中进行计算,
2: 在函数中修改的值不影响外部的值
Pass by Reference:
1: 将值的地址进行传递,因此对变量的变化会反应到函数外部
2: 如果同一个变量传入两次,则对它们的操作是叠加的
Pass by Value-Result:
1: 对变量值的修改不是实时的,而是只在返回之前将对应的变量的值拷贝到参数中去。
int y;
calling_procedure()
{
y = 10;
copy_restore(y); //l-value of y is passed
printf y; //prints 99
}
copy_restore(int x)
{
x = 99; // y still has value 10 (unaffected)
y = 0; // y is now 0
//在这里把x的值拷贝到了y的地址中(传进来的是y的地址)
}
void p(int x, int y) {
x++; //此时x=2, a[0] = 1
y++; //此时y=2, a[0] = 1
//将x拷贝到a[0], a[0] = 2
//将y拷贝到a[0], a[0] = 2
}
int main() {
int a[2] = {
1, 1};
p(a[0], a[0]);
}
Pass by name:
1: 将函数体拷贝到main中,然后将参数文本替代
void p(int x, int y) {
x++;
i++;
y++;
}
int i = 0;
int main() {
int a[2] = {
1, 1};
p(a[i], a[i]);
printf("%d %d", a[0], a[1]);
}
执行过程为:
int i = 0;
int main() {
int a[2] = {
1, 1};
//将p函数体文本拷贝到main中
a[i]++;
i++;
a[i]++;
printf("%d %d", a[0], a[1]); //结果是2 2
}