BFS
常见于求解最短路径问题,图论问题(矩阵、连通图)

关键要素在于队列queue+判重(记忆化)
- queue里可以放Integer、Strting、int[]等
- 判重可以用数组、矩阵、或者状态压缩(String、Map)
BFS模板
基于层数
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N = 110, M = 110;
static int[][] dirs = {
{
1,0},{
0,-1},{
-1,0},{
0,1}};
static int[][] mat = new int[N][M];
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[N][M];
public static void main(String[] args){
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
mat[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
int step = 0;
que.offer(new int[]{
0,0});
st[0][0] = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int sz = que.size();
while(sz-- > 0){
int[] cur = que.poll();
if(cur[0] == n - 1 && cur[1] == m - 1){
System.out.print(step);
return;
}
//遍历四个方向
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = cur[0] + dirs[i][0];
int y = cur[1] + dirs[i][1];
// 越界了或者遍历过或者是墙壁
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || st[x][y] || mat[x][y] == 1) continue;
st[x][y] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
x,y});
}
}
step++;
}
}
}
也可以将步长作为结点信息入队
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N = 110, M = 110;
static int[][] dirs = {
{
1,0},{
0,-1},{
-1,0},{
0,1}};
static int[][] g = new int[N][M];
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[N][M];
public static void main(String[] args){
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
g[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>(); // x,y,step
que.offer(new int[]{
1,1,0});
st[1][1] = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = que.poll();
int x = cur[0];
int y = cur[1];
int step = cur[2];
if(x == n && y == m){
System.out.print(step);
return;
}
//遍历四个方向
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dirs[i][0];
int ny = y + dirs[i][1];
// 越界了或者遍历过或者是墙壁
if(nx <= 0 || nx > n || ny <= 0 || ny > m || st[nx][ny] || g[nx][ny] == 1) continue;
st[nx][ny] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
nx,ny,step+1});
}
}
}
}
迷宫问题【矩阵】
link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/846/
给定一个 n×m× 的二维整数数组,用来表示一个迷宫,数组中只包含 00 或 11,其中 00 表示可以走的路,11 表示不可通过的墙壁。
最初,有一个人位于左上角 (1,1)(1,1) 处,已知该人每次可以向上、下、左、右任意一个方向移动一个位置。
请问,该人从左上角移动至右下角 (n,m)(,) 处,至少需要移动多少次。
数据保证 (1,1)(1,1) 处和 (n,m)(,) 处的数字为 00,且一定至少存在一条通路。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 m。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 m 个整数(00 或 11),表示完整的二维数组迷宫。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示从左上角移动至右下角的最少移动次数。
数据范围
1≤n,m≤1001≤,≤100
输入样例:
5 5
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
输出样例:
8
code
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N = 110, M = 110;
static int[][] dirs = {
{
1,0},{
0,-1},{
-1,0},{
0,1}};
static int[][] mat = new int[N][M];
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[N][M];
public static void main(String[] args){
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
mat[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
int step = 0;
que.offer(new int[]{
0,0});
st[0][0] = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int sz = que.size();
while(sz-- > 0){
int[] cur = que.poll();
if(cur[0] == n - 1 && cur[1] == m - 1){
System.out.print(step);
return;
}
//遍历四个方向
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = cur[0] + dirs[i][0];
int y = cur[1] + dirs[i][1];
// 越界了或者遍历过或者是墙壁
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || st[x][y] || mat[x][y] == 1) continue;
st[x][y] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
x,y});
}
}
step++;
}
}
}
八数码问题【map判重】
link: https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/847/
在一个 3×33×3 的网格中,1∼81∼8 这 88 个数字和一个 x 恰好不重不漏地分布在这 3×33×3 的网格中。
例如:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
在游戏过程中,可以把 x 与其上、下、左、右四个方向之一的数字交换(如果存在)。
我们的目的是通过交换,使得网格变为如下排列(称为正确排列):
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 x
例如,示例中图形就可以通过让 x 先后与右、下、右三个方向的数字交换成功得到正确排列。
交换过程如下:
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
x 4 6 4 x 6 4 5 6 4 5 6
7 5 8 7 5 8 7 x 8 7 8 x
现在,给你一个初始网格,请你求出得到正确排列至少需要进行多少次交换。
输入格式
输入占一行,将 3×33×3 的初始网格描绘出来。
例如,如果初始网格如下所示:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
则输入为:1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
输出格式
输出占一行,包含一个整数,表示最少交换次数。
如果不存在解决方案,则输出 −1−1。
输入样例:
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
输出样例
19
code
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// BFS,使用字符串表示状态
// 使用Map来存储<String,int> 状态,步长
static Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
static String end = "12345678x";
static int[] dx = {
1,0,-1,0}, dy = {
0,-1,0,1};
// 交换
public static String swap(String s, int a, int b){
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
char c = chs[a];
chs[a] = chs[b];
chs[b] = c;
return new String(chs);
}
// 深搜
public static int bfs(String start){
map.put(start,0);
Queue<String> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(start);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
String cur = que.poll();
int step = map.get(cur);
if(cur.equals(end)) return step;
int index = cur.indexOf('x');
int x = index / 3, y = index % 3;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= 3 || ny < 0 | ny >= 3) continue;
String ns = swap(cur,index,nx * 3 + ny);
if(map.containsKey(ns)) continue;
else{
map.put(ns,step + 1);
que.offer(ns);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] s1 = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : s1) sb.append(s);
String start = sb.toString();
System.out.print(bfs(start));
}
}
岛屿问题
link:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1235/
你有一张某海域 N×N 像素的照片,”.”表示海洋、”#”表示陆地,如下所示:
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
其中”上下左右”四个方向上连在一起的一片陆地组成一座岛屿,例如上图就有 22 座岛屿。
由于全球变暖导致了海面上升,科学家预测未来几十年,岛屿边缘一个像素的范围会被海水淹没。
具体来说如果一块陆地像素与海洋相邻(上下左右四个相邻像素中有海洋),它就会被淹没。
例如上图中的海域未来会变成如下样子:
.......
.......
.......
.......
....#..
.......
.......
请你计算:依照科学家的预测,照片中有多少岛屿会被完全淹没。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数N。
以下 N 行 N 列,包含一个由字符”#”和”.”构成的 N×N 字符矩阵,代表一张海域照片,”#”表示陆地,”.”表示海洋。
照片保证第 11 行、第 11 列、第 N 行、第 N 列的像素都是海洋。
输出格式
一个整数表示答案。
数据范围
1≤N≤10001≤1000
输入样例1:
7
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
输出样例1:
1
输入样例2:
9
.........
.##.##...
.#####...
.##.##...
.........
.##.#....
.#.###...
.#..#....
.........
输出样例2:
1
code
- 关键在于利用bfs找到岛屿(找岛屿过程中同时计数total与bound)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N = 1010;
static char[][] g = new char[N][N];
static boolean[][] st = new boolean[N][N];
static int[] dx = {
1,0,-1,0}, dy = {
0,-1,0,1};
static int n;
public static int bfs(int i, int j){
int total = 0, bound = 0;
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{
i,j});
st[i][j] = true;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = que.poll();
int x = cur[0], y = cur[1];
total++;
boolean is_bound = false;
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
if(st[nx][ny]) continue;
if(g[nx][ny] == '.') is_bound = true;
else{
st[nx][ny] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
nx,ny});
}
}
if(is_bound) bound++;
}
return total == bound ? 1 : 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
g[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(!st[i][j] && g[i][j] == '#'){
cnt += bfs(i,j);
}
}
}
System.out.print(cnt);
}
}
基于状态压缩的BFS
状态压缩
状态压缩也即用一个变量来表示当前状态,比较常用的方式是利用一个 n 位 k 进制数mask 表示当前 n 个节点的所处的 k 个不同状态。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kRffL2ta-1679202291100)(img/image-20221110163911188.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/615ce216fbf04baea45bfd57e34b810e.png)
一些状态压缩的基本操作如下:
(1)访问第 i 个点的状态:(state >> i & 1) == 0 true 或者false
注意前面部分要加括号,因为==运算优先级大于&
(2)更改第 i 个点状态为 1:mask = mask | (1 << i)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-visiting-all-nodes/solutions/918634/gtalgorithm-tu-jie-fa-ba-hardbian-cheng-v5knb/
lc 864. 获取所有钥匙的最短路径
link:https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-to-get-all-keys/description/
给定一个二维网格 grid ,其中:
- ‘.’ 代表一个空房间
- ‘#’ 代表一堵
- ‘@’ 是起点
- 小写字母代表钥匙
- 大写字母代表锁
我们从起点开始出发,一次移动是指向四个基本方向之一行走一个单位空间。我们不能在网格外面行走,也无法穿过一堵墙。如果途经一个钥匙,我们就把它捡起来。除非我们手里有对应的钥匙,否则无法通过锁。
假设 k 为 钥匙/锁 的个数,且满足 1 <= k <= 6,字母表中的前 k 个字母在网格中都有自己对应的一个小写和一个大写字母。换言之,每个锁有唯一对应的钥匙,每个钥匙也有唯一对应的锁。另外,代表钥匙和锁的字母互为大小写并按字母顺序排列。
返回获取所有钥匙所需要的移动的最少次数。如果无法获取所有钥匙,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
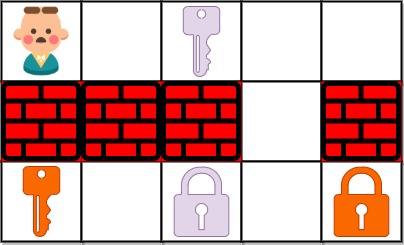
输入:grid = ["@.a.#","###.#","b.A.B"]
输出:8
解释:目标是获得所有钥匙,而不是打开所有锁。
示例 2:
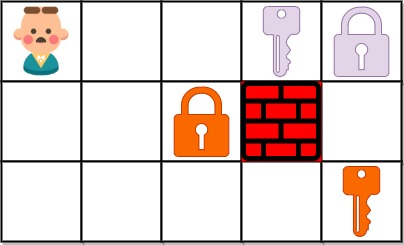
输入:grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"]
输出:6
示例 3:

输入: grid = ["@Aa"]
输出: -1
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 30grid[i][j]只含有'.','#','@','a'-``'f``'以及'A'-'F'- 钥匙的数目范围是
[1, 6] - 每个钥匙都对应一个 不同 的字母
- 每个钥匙正好打开一个对应的锁
题解
最短路径问题直接套BFS模板求解
关键api:
Queue队列
Queue<int[]> que = new ArrayDeque<>();
que.offer(new int[]{init_x,init_y,0});
que.poll();
四个方向
int dirs[][] = {
{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
状态压缩
使用位运算表示钥匙状态 需要熟悉左移右移操作
eg.101010:表示bdf钥匙找到
初始化为1 << k 当达到state == 1 << k - 1时即找到所有钥匙
每次找到字符c:n_state |= 1 << (c - 'a');
判断锁是否有对应的钥匙(Character.isUpperCase(c) && (state >> (c - 'A') & 1) == 0)
BFS需要一个visited数组做记忆化操作,记录以及遍历的结点
class Solution {
/**
最短路径:使用BFS查找
初始化:先遍历统计钥匙数量以及出发点
状态表示:使用位运算表示钥匙状态
eg.101010:表示bdf钥匙找到
初始化为1 << k 当达到state == 1 << k - 1时即找到所有钥匙
每次找到字符c:state |= 1 << (c - 'a');
**/
int dirs[][] = {
{
1,0},{
-1,0},{
0,1},{
0,-1}};
int k = 0; //钥匙数量
int init_x = 0,init_y = 0; //起始位置
public int shortestPathAllKeys(String[] grid) {
//遍历grid统计钥匙数量以及出发点
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
char c = grid[i].charAt(j);
if(Character.isLowerCase(c)){
k++;
}else if(c == '@'){
init_x = i;
init_y = j;
}
}
}
Queue<int[]> que = new ArrayDeque<>();
que.offer(new int[]{
init_x,init_y,0});
//判断当前结点是否访问过 注意必须是x,y,state
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[m][n][1<<k];
visited[init_x][init_y][0] = true;
int step = 0;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int size = que.size();
while(size > 0){
int[] cur = que.poll();
int x = cur[0];
int y = cur[1];
int state = cur[2];
//找到了所有的钥匙了
if(state == (1 << k) - 1){
return step;
}
//遍历四个位置
for(int[] dir : dirs){
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
//判断是否超出范围
if(nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
//判断是否是墙或者是没找到钥匙的锁
char c = grid[nx].charAt(ny);
if(c == '#' || (Character.isUpperCase(c) && (state >> (c - 'A') & 1) == 0)) continue;
//是钥匙 更新状态
//注意这里不能直接修改state 否则污染其他方向
int n_state = state;
if(Character.isLowerCase(c)){
n_state |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
//判断是否访问过 没有就入队列
if(!visited[nx][ny][n_state]){
visited[nx][ny][n_state] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
nx,ny,n_state});
}
}
size--;
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
}
lc 847. 访问所有节点的最短路径
存在一个由 n 个节点组成的无向连通图,图中的节点按从 0 到 n - 1 编号。
给你一个数组 graph 表示这个图。其中,graph[i] 是一个列表,由所有与节点 i 直接相连的节点组成。
返回能够访问所有节点的最短路径的长度。你可以在任一节点开始和停止,也可以多次重访节点,并且可以重用边。
示例 1:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jiS1E5es-1679202291102)(img/shortest1-graph.jpg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/48b52410b00441cea47ca21f41e9a6cf.png)
输入:graph = [[1,2,3],[0],[0],[0]]
输出:4
解释:一种可能的路径为 [1,0,2,0,3]
示例 2:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-w3gFxyCq-1679202291103)(img/shortest2-graph.jpg)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d06109cee0f743a99d2e689dfae13a3b.png)
输入:graph = [[1],[0,2,4],[1,3,4],[2],[1,2]]
输出:4
解释:一种可能的路径为 [0,1,4,2,3]
提示:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 120 <= graph[i].length < ngraph[i]不包含i- 如果
graph[a]包含b,那么graph[b]也包含a - 输入的图总是连通图
题解
本题也是状态压缩+BFS
注意由于不是矩阵每一次都遍历四个方向,因此在结点信息中加入当前步长
(curNode,state,step)因此遍历时也不需要size()来记录层数
class Solution {
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
//[n][1<<n] n表示当前结点 1<<n表示当前状态
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][1 << n];
Queue<int[]> que = new ArrayDeque<>();//数组记录三个属性(curNode,state,step)
//把所有结点入栈
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
que.offer(new int[]{
i,1 << i,0});
visited[i][1 << i] = true;
}
while(!que.isEmpty()){
//不需要size size用于记录层数
int[] cur = que.poll();
int index = cur[0];
int state = cur[1];
int step = cur[2];
//已经找到所有结点了
if(state == (1 << n) - 1) return step;
for(int i : graph[index]){
//更新状态
int n_state = state;
n_state |= 1 << i;
if(!visited[i][n_state]){
visited[i][n_state] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{
i,n_state,step+1});
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
二叉树
最小深度、最大深度
以下以LeetCode111.二叉树的最小深度https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/为例引出bfs的经典模板
最小深度就是当存在结点没有孩子结点就返回
//最小深度bfs经典模板
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return 0;
que.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
depth++;
int size = que.size();
while(size > 0){
size--;
TreeNode cur = que.poll();
if(cur.left != null) que.offer(cur.left);
if(cur.right != null) que.offer(cur.right);
if(cur.left == null && cur.right == null) return depth;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
对比:LeetCode 104. 二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
与最小深度唯一的不同就是去掉了
if(cur.left == null && cur.right == null) return depth;这一行,因为最大深度就是要遍历每一层 直接套用层次遍历模板遍历完即可
//使用bfs模板解
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return 0;
que.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!que.isEmpty()){
depth++;
int size = que.size();
while(size > 0){
size--;
TreeNode cur = que.poll();
if(cur.left != null) que.offer(cur.left);
if(cur.right != null) que.offer(cur.right);
// if(cur.left == null && cur.right == null) return depth;
}
}
return depth;
}