基于深度学习的多尺度通道压缩特征表面缺陷检测系统
Deep learning based multi-scale channel compression feature surface defect detection system
简述:首先应用背景分割和模板匹配技术来定义覆盖目标工件的ROI区域。提取的感兴趣区域被均匀地裁剪成若干个图像块,每个块被送到基于CNN的模型,以分类杂乱背景中不同大小的表面缺陷。最后,对空间上相邻且具有相同类别标签的图像块进行合并,以生成各种表面缺陷的识别图。
基于SqueezeNet的CNN模型,该模型结合多个不同核大小的卷积层来提取多尺度特征,并获得更大的感受野。因此,该模型能够更好地处理杂乱的背景和各种大小的缺陷。
Abstract
industrial workpieces commonly contain complex structures, including hallow regions, welding joints, or rivet holes.
工业工件通常包含复杂的结构,包括中空区域、焊接接头或铆钉孔。
we firstly proposed to incorporate multiple convolutional layers with different kernel sizes to increase the receptive field and to generate multi-scale features. As a result, the proposed model can better handle cluttered background and defects of various sizes.
我们首先提出合并具有不同核大小的多个卷积层,以增加感受野并产生多尺度特征。因此,所提出的模型可以更好地处理杂乱的背景和各种大小的缺陷。
Evaluated in a newly constructed surface defect dataset (images contain complex structures and defects of various sizes), our proposed model achieves more accurate recognition results compared with the state-of-the-art surface defect classifiers.
在新构建的表面缺陷数据集(图像包含复杂的结构和各种尺寸的缺陷)上进行评估,与最先进的表面缺陷分类器相比,我们提出的模型获得了更准确的识别结果。
I. INTRODUCTION
fully automatic machine vision-based inspection solutions for assisting or replacing the decisions made by human experts.In the past decades, many machine vision-based surface inspection methods have been proposed for non-contact, non- destructive, and fully automatic defect detection/classification of various surface textures.
基于机器视觉的全自动检测解决方案,用于协助或取代人类专家做出的决策。在过去的几十年中,已经提出了许多基于机器视觉的表面检测方法,用于各种表面纹理的非接触、非破坏性和全自动缺陷检测/分类。
how well the handcrafted features can depict the visual characteristics of surface defects.Given a number of training samples, CNNs automatically construct hierarchical features by assembling low-level features to generate high- level representations.
手工制作的特征能够多好地描绘表面缺陷的视觉特征。在给定大量训练样本的情况下,CNN通过组装低层特征来生成高层表示,从而自动构建层次特征。
A noticeable drawback of the above-mentioned deep CNN models is that they contain a large number of parameters and cannot deliver real-time speed.
上述深度CNN模型的一个明显缺点是包含大量参数,无法提供实时速度。
Yi et al. built up an end-to-end surface defects recognition system which generates saliency maps as the classification results of seven types of steel strip defects [24].Note that the surface defects are typically considered as local anomalies in homogeneous background [27], [25] which not satisfied in many practical industrial inspection tasks.
Yi等人的研究成果,建立了一个端到端的表面缺陷识别系统,该系统生成显著图作为七种带钢缺陷的分类结果[24]。请注意,表面缺陷通常被认为是均匀背景中的局部异常[27]、[25],这在许多实际的工业检测任务中是不能满足的。
Many industrial workpieces contain ob-vious structural interference such as fastener holes, bolt holes, welding joints, and grooves, incurring cluttered background to mislead the classification results.
许多工业零件含有明显的结构干扰,如紧固孔、螺栓孔、焊接接头、凹槽等,导致背景混乱,从而误导分类结果。
In this paper, we propose a surface defect detection and classification framework. It consists of three major processing steps, includ- ing Region of interest (ROI) extraction, defects classification, and defect localization.
在本文中,我们提出了一个表面缺陷检测和分类框架。它包括感兴趣区域(ROI)提取、缺陷分类和缺陷定位三个主要处理步骤。
Firstly, an ROI area is defined in a real-captured image of the target workpiece via background segmentation and template matching techniques.Then, the extracted ROI is uniformly divided into a number of image patches, and each patch is feed to a CNN-based model for surface defect classification.Finally, spatially adjacent image patches with the same class labels are merged to generate a location map to indicate the positions of various surface defects.
首先,通过背景分割和模板匹配技术,在目标工件的实时图像中定义感兴趣区域。然后,将提取的感兴趣区域均匀划分为若干个图像块,每个图像块被馈送到基于CNN的模型进行表面缺陷分类。最后,将具有相同类别标签的空间相邻的图像块合并,以生成位置图来指示各种表面缺陷的位置。
The core of our proposed framework is a compact yet effective SqueezeNet-based model to accurately classify surface defects of various sizes in cluttered background.
我们提出的框架的核心是一个紧凑而有效的基于 SqueezeNet 的模型,用于在杂乱的背景中准确地对各种尺寸的表面缺陷进行分类。
Universal Serial Bus (USB) connectors which are made of reflective stainless steel and contain complex structures (e.g., hallow areas, welding joints, and rivet holes) and defects of various sizes (e.g., Dent, Spot, Bright Line, and Scratch).
通用串行总线(USB)连接器由反光不锈钢制成,包含复杂的结构(例如,中空区、焊接接头和铆钉孔)和各种大小的缺陷(例如,凹痕、斑点、亮线和划痕)。
We propose a SqueezeNet-based CNN model that achieves more accurate recognition results compared with the state-of-the-art defect classifiers [25], [27], [15], [34], [24].It incorporates multiple convolutional layers with different kernel sizes to extract multi-scale features and achieve larger receptive fields. As a result, the proposed model can better handle cluttered background and defects of various sizes.Moreover, we experimentally demonstrate that compressing the size of the extracted multi-scale features leads to better training of defect-related features using a limited number of samples.
我们提出了一种基于SqueezeNet的CNN模型,与现有的缺陷分类器[25]、[27]、[15]、[34]、[24]相比,该模型获得了更准确的识别结果。它结合了多个不同核大小的卷积层来提取多尺度特征,并获得更大的接受场。因此,该模型能够更好地处理杂乱的背景和各种大小的缺陷。此外,我们的实验证明,压缩提取的多尺度特征的大小可以在有限的样本数量下更好地训练与缺陷相关的特征。
II. IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND USB-SD DATASET
The illumination device provides light stimulation to make the insignificant surface defects visually more obvious.As a result, a blue annular light-emitting diode (LED) lighting deceive with a 60 incident angle is used in our system.
照明装置提供光刺激,以使微不足道的表面缺陷在视觉上更加明显。因此,我们的系统使用了60度入射角的蓝色环形发光二极管(LED)照明欺骗器。
The USB-SD dataset contains 8,100 grayscale images of the normal metallic surface and six typical defects (i.e., Bright Line, Deformation, Dent, Scratch, Spot, and Stain).Since surface defects typically occur in low probability, it is impractical to capture normal and defect images of equal numbers in practical industrial inspection applications.
USB-SD数据集包含正常金属表面和六种典型缺陷(即亮线、变形、凹痕、划痕、斑点和污渍)的8,100个灰度图像。由于表面缺陷通常发生的概率很低,因此在实际工业检测应用中获取相同数量的正常和缺陷图像是不切实际的。
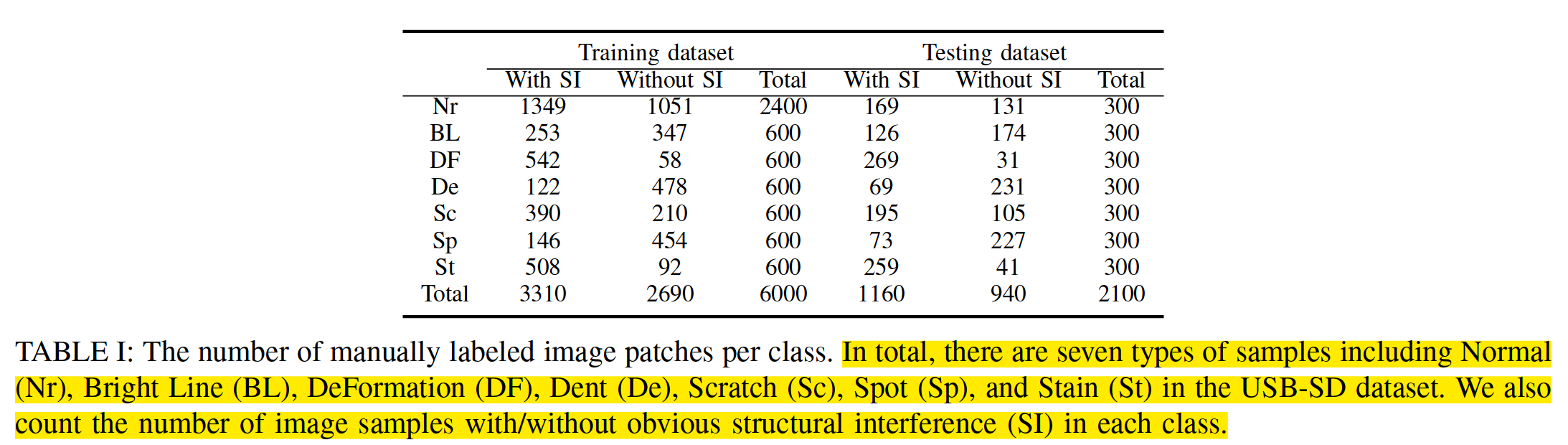
Tab. I shows the number of manually labeled image patches per class (Normal, Bright Line, Deformation, Dent, Scratch, Spot, and Stain) in the USB-SD dataset.
Tab. I 显示了USB-SD数据集中每个类别(正常、亮线、变形、凹陷、划痕、斑点和污渍)手动标记的图像补丁的数量。
We make use of images in the USB-SD dataset to evaluate the performance of different models on classifying surface defects of various sizes in cluttered background.
我们利用USB-SD数据集中的图像来评估不同模型在杂波背景下对不同尺寸的表面缺陷进行分类的性能。
III. PROPOSED METHOD
Fig. 4. Given a full-size input image, we firstly apply background segmen- tation and template matching techniques to define an ROI area which covers the target workpiece.
图4.在给定一幅全尺寸输入图像的情况下,我们首先应用背景分割和模板匹配技术来定义覆盖目标工件的ROI区域。
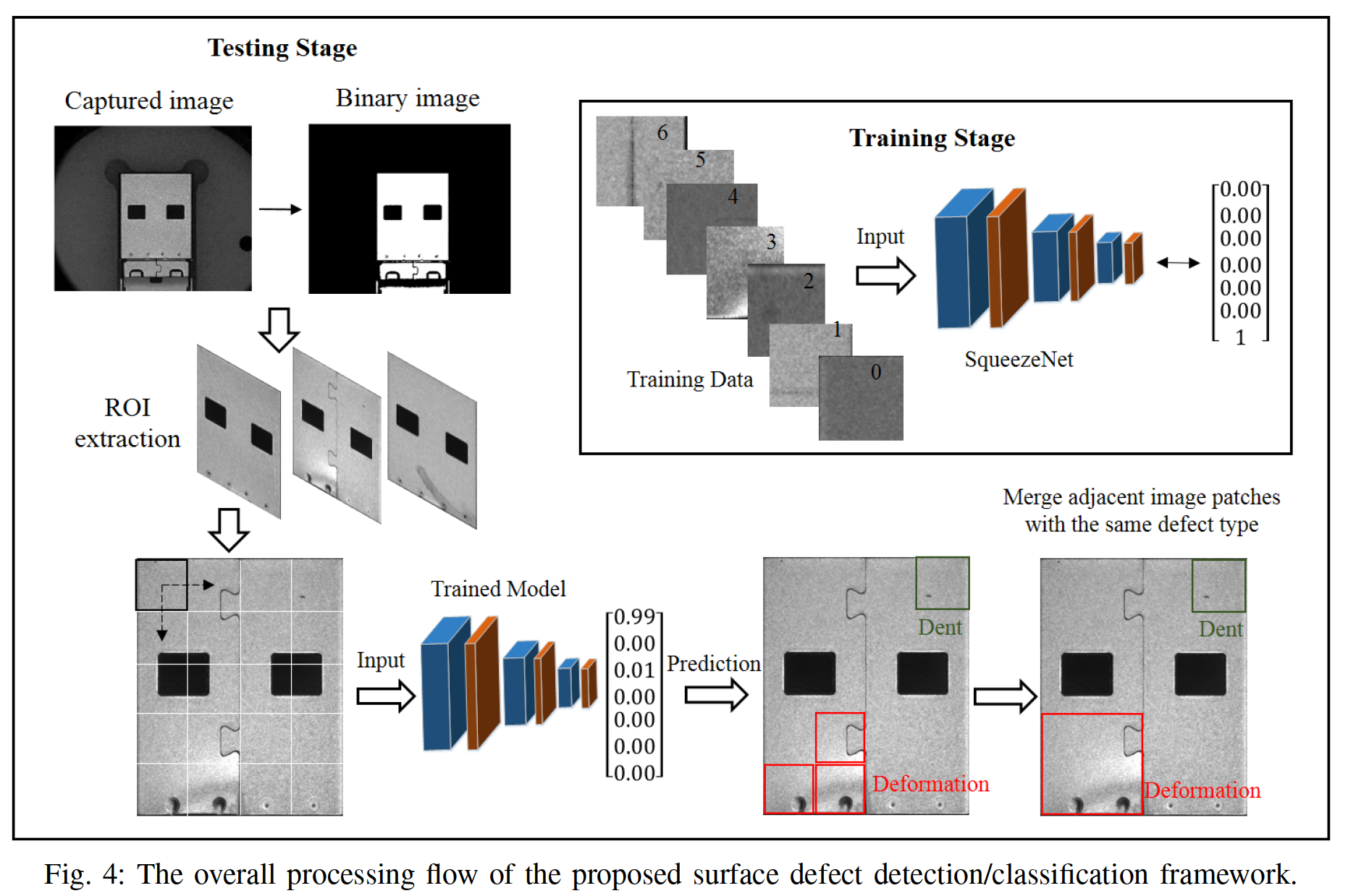
The extracted ROI is uniformly cropped into a number of image patches, and each patch is feed to a CNN-based model to classify surface defects of various sizes in cluttered background.
提取的感兴趣区域被均匀地裁剪成若干个图像块,每个块被送到基于CNN的模型,以分类杂乱背景中不同大小的表面缺陷。
CNN model is built on the pre-trained SqueezeNet and further fine-tuned using the labeled images in the USB-SD dataset in the training stage.The trained CNN model computes a number of confidence scores to predict the class label (i.e., Normal, Bright Line, Deformation, Dent, Scratch, Spot, and Stain) for each input image patch.
CNN模型建立在预先训练的SqueezeNet上,并在训练阶段使用USB-SD数据集中的标记图像进一步微调。训练好的CNN模型计算多个置信度分数来预测每个输入图像块的类别标签(即,正常、亮线、变形、凹陷、划痕、斑点和污渍)。
Finally, image patches which are spatially adjacent and have the same class label are merged to generate a location map of various surface defects.
最后,对空间上相邻且具有相同类别标签的图像块进行合并,以生成各种表面缺陷的位置图。
A. ROI extraction
We design a simple yet effective image processing method to define a ROI area in which the target workpiece is covered.
我们设计了一种简单而有效的图像处理方法来确定目标工件被覆盖的ROI区域。
Firstly, we apply the OSTU segmentation technique [35] to highlight the image regions corresponding to the target object.The non-parametric OSTU algorithm calculates a single in- tensity threshold by minimizing inter-class intensity variance to divide the input image into foreground and background pixels.Then, we compute the location and orientation of target workpiece in the captured image through template matching of a pre-defined reference frame.The extracted ROI is uniformly divided into a number of image patches, and each patch is feed to the CNN model for defect classification.
首先,我们应用OSTU分割技术[35]来突出显示与目标对象相对应的图像区域。non-parametric OSTU算法通过最小化类间强度方差来计算单个强度阈值,从而将输入图像划分为前景和背景像素。然后,通过对预先定义的参考系进行模板匹配,计算出目标工件在采集图像中的位置和方向,将提取的感兴趣区域均匀地划分为若干个图像块,每个块被送到CNN模型进行缺陷分类。
B. Surface defect classification
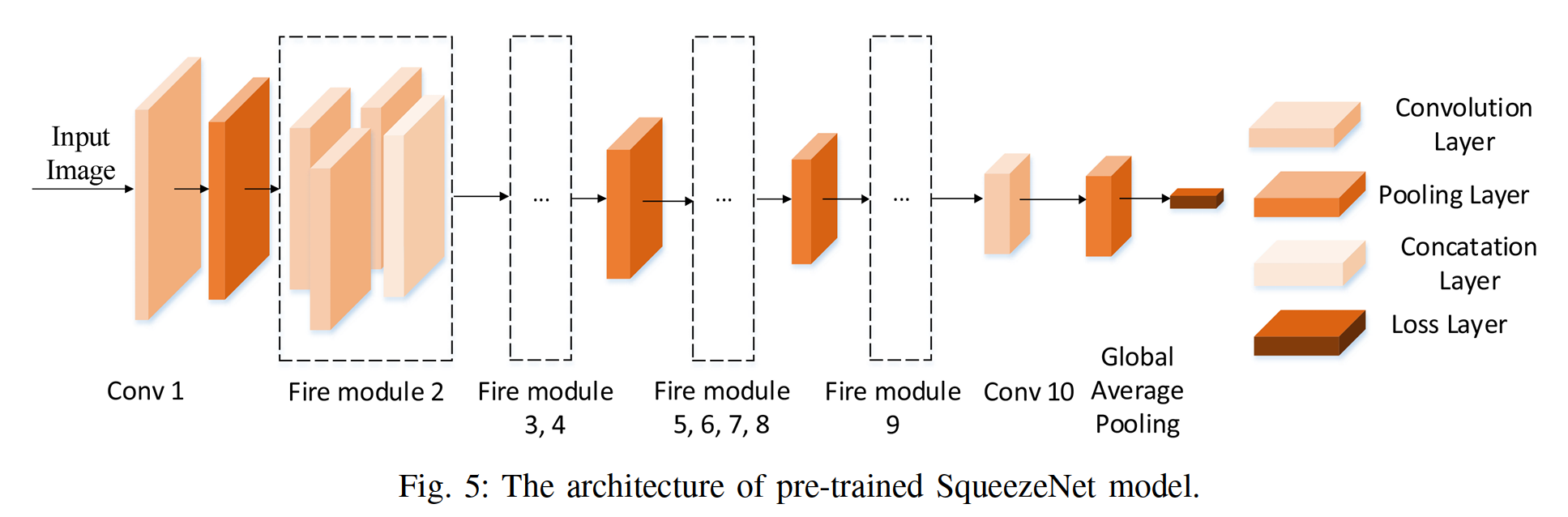
The SqueezeNet [21] is a light-weight architecture.It can achieve high-accuracy recognition results using significantly fewer parameters.the SqueezeNet model is easy to fine-tune, less prone to small dataset over- fitting, and suitable for embedded system implementation.we adopt the pre-trained SqueezeNet model as the backbone architecture for accurate surface defect classification.
SqueezeNet[21]是一种轻量级架构,它可以用更少的参数实现高精度的识别结果。SqueezeNet模型易于微调,不易出现小数据集过度拟合的情况,并且适合于嵌入式系统实现。我们采用预先训练好的SqueezeNet模型作为主干结构来实现精确的表面缺陷分类。
Fig. 5, the SqueezeNet contains nine fire modules in which a squeeze convolution layer (using 1×1 filters) and two expand layers (using 1 ×1 and 3×3 filters) are deployed.
图5,SqueezeNet包含9个火灾模块,其中部署了一个挤压卷积层(使用1×1过滤器)和两个扩展层(使用1×1和3×3过滤器)。
we modify the number of output channels in the Conv10 layer to 7 accordingly.The configurations of individual layers/modules in the baseline SqueezeNet model for surface defect classification on the USB-SD dataset are shown in Tab. II.
我们相应地将Conv-10层中的输出通道数修改为7。用于USB-SD数据集表面缺陷分类的Baseline SqueezeNet模型中各个层/模块的配置显示在Tab. II。
To better handle the cluttered background and defects of various sizes, we propose to add a multi-receptive field (MRF) module after the last feature extraction module (Fire 9) to achieve larger receptive fields.
为了更好地处理杂乱的背景和各种大小的缺陷,我们建议在最后一个特征提取模块(Fire 9)之后增加一个多感受野(MRF)模块,以获得更大的感受野。
In CNN models, receptive field defines the region in the input space that a particular neuron of the current convolutional layer is referring to. Therefore, setting a larger receptive field can improve the capability of CNN models to extract semantic features which are more robust to clutter background.
在CNN模型中,感受野定义了输入空间中当前卷积层的特定神经元所指的区域。因此,设置较大的感受野可以提高CNN模型提取语义特征的能力,从而对杂波背景具有更强的鲁棒性。
The short connection is added between multiple-stacked layers to back-propagate gradient signals directly from the higher-level layers to lower-level ones, alleviating the gradient vanish- ing/exploring problem [16].
在多层叠层之间增加了短连接,以将梯度信号直接从较高层反向传播到较低层,从而缓解了梯度消失/探索问题[16]。
incorporating multiple convolutional layers with different kernel sizes to extract multi-scale features and achieve larger receptive fields。compressing the param- eter of the newly added convolutional layers to achieve more efficient training and to alleviate small data over-fitting.
结合不同核大小的多个卷积层提取多尺度特征,获得更大的接受场,对新增加的卷积层的参数进行压缩,以实现更有效的训练,并减轻小数据的过拟合。
IV. IMPLEMENTATION DETAILS
We use 2400 normal and 3,600 defect images (600 samples for each defect cate- gory) for model training.The parameters of modified or newly added convolutional layers, including Conv10, MRF-a, MRF- b, and MRF-c, are randomly initialized with a Gaussian distribution.
我们使用2400幅正常图像和3600幅缺陷图像(每个缺陷类别对应600个样本)进行模型训练。修改或新增加的卷积层的参数,包括Conv10、MRF-a、MRF-b和MRF-c,用高斯分布随机初始化。
In this paper, we propose to reduce the number of parameters in the newly added layers so that they can be efficiently trained using a few hundreds of sample images.
在本文中,我们建议减少新增加的层中的参数数量,以便可以使用数百个样本图像来有效地训练它们。
we design a SN-MRF-CC model by integrating a MRF module (adding convolutional layers with 1×1, 3×3 and 5×5 kernels) to the pre-trained SqueezeNet model and performing feature channel compression (setting the channel number of newly added MRF-a, MRF-b and MRF-c layers to 6).
我们通过在预先训练的SqueezeNet模型中集成一个MRF模块(增加具有1×1, 3×3 and 5×5核的卷积层)并进行特征信道压缩(将新增加的MRF-a、MRF-b和MRF-c层的信道数设置为6)来设计SN-MRF-CC模型。

VII. CONCLUSION
First, we propose to incorporate multiple convolutional layers with different kernel sizes to extract multi-scale fea- tures and achieve larger receptive fields.Second, we reduce the parameter of the newly added convolutional layers to achieve more efficient training and to alleviate small data over-fitting.
首先,我们提出了结合多个不同核大小的卷积层来提取多尺度特征,以获得更大的接受场。其次,我们减少了新增加的卷积层的参数,以实现更有效的训练,并减少小数据的过拟合。
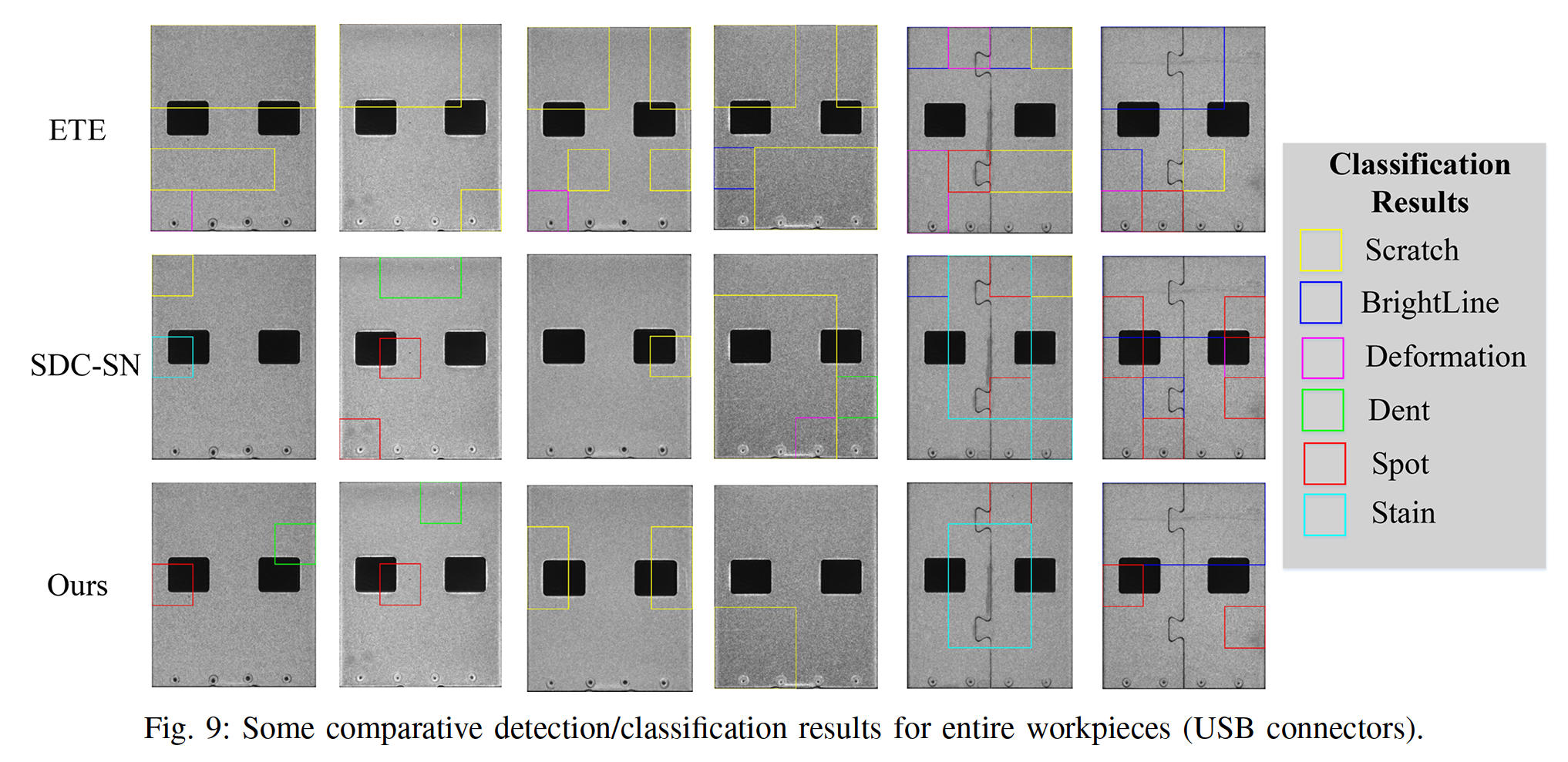
Sample images in USB-SD dataset the contain clut- tered background caused by structural interference, and the size of different surface defects changes significantly.
USB-SD数据集的样本图像中含有结构干扰引起的杂波背景,且不同表面缺陷的大小变化较大。
it is a light-weight CNN model and can process 100fp on a computer equipped with a single NVIDIA TITAN X Graphics Processing Unit (12G memory).
它是一款轻便的CNN模型,可以在配备单个NVIDIA Titan X图形处理器(12G内存)的计算机上处理100fp。